This is an automatically translated article.
The spleen is located in the left quadrant of the human body, has an important function to help the body fight infections and filter old blood cells. Splenic rupture or splenic trauma is the most common occurrence of blunt abdominal trauma that can be life-threatening.
1. Causes of closed abdominal trauma
Closed abdominal trauma is an injury to the abdomen, these lesions can be outside the abdominal wall or inside hollow organs such as the stomach, intestines, bladder or in solid organs such as the liver, spleen, and pancreas.
These injuries will cause acute blood loss for solid organs and peritonitis for hollow organs. Visceral lesions can be one or more organs at the same time.
Closed abdominal trauma to the abdominal wall will form ecchymosis, subcutaneous edema or hematomas due to epigastric artery rupture, skin peeling. Spleen injury is one of the blunt abdominal trauma with the highest rate; Up to 60% of people have spleen damage with a mortality rate of 1%.
The most common cause of abdominal trauma is traffic accidents, accounting for 75% of all injuries. In addition, due to accidents in daily life and work, falling from a height, accidents in sports practice, fights, and fights leading to abdominal injuries.
2. Spleen rupture symptoms in blunt abdominal trauma

đau ở bên trái phía dưới bụng là một trong các triệu chứng vỡ lách trong chấn thương bụng kín
Spleen rupture at any level should be diagnosed and treated promptly to avoid life-threatening complications. The doctor can rely on some of the following clinical signs:
The patient feels pain in the lower left side of the abdomen, the degree of pain depends on the extent of the damage Left shoulder pain caused by the location of the ruptured spleen causing irritation Nerves Spleen rupture causes internal bleeding, leading to a drop in blood pressure, causing patients to have symptoms of restlessness, anxiety, paleness, dizziness, blurred vision, fainting...
3. Diagnosis of splenic rupture in blunt abdominal trauma
To diagnose splenic rupture in blunt abdominal trauma, doctors will do more tests to make a final diagnosis:
3.1 Abdominal CT (computed tomography) The doctor will inject into a vein in the abdomen. Contrast in the patient's arm to determine the amount of bleeding from the spleen. However, this method is only used if the patient is not in a dangerous state because the procedure is quite long. Also do not use this method in patients with contrast allergy.
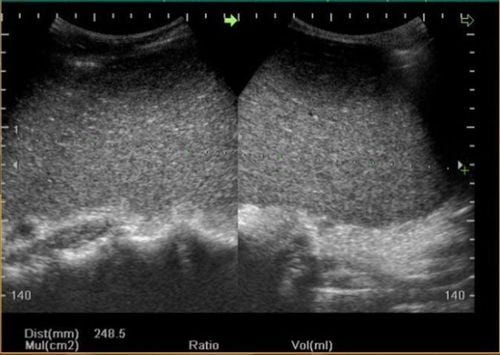
3.2 Focused Abdominal Ultrasound Focused Abdominal Ultrasound : Helps check for fluid accumulation in the abdomen.
3.3 Diagnostic peritoneal lavage This is the fastest and least expensive method to quickly determine if blood is concentrated in the abdomen.
3.4 MRI Abdominal MRI: Used for patients with kidney failure or allergy to contrast, unable to do CT scan.
4. Spleen rupture degrees in blunt abdominal trauma
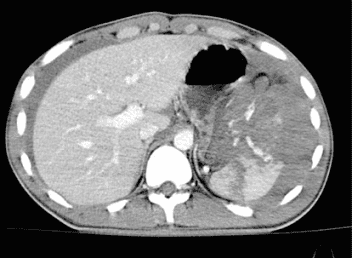
vỡ lách trong chấn thương bụng kín
According to the American Society of Surgery, splenic rupture in blunt abdominal trauma is divided into 5 different grades:
4.1 Grade 1 Splenic tear less than 1cm deep, subcortical hematoma usually less than 10% Spleen surface area and no bleeding
4.2 Grade 2 laceration 1-3cm deep, vascular rafts uninjured, hematoma in splenic tissue less than 5cm, subcortical hematoma 10-50 % surface, minimal bleeding
4.3 Grade 3 Tear more than 3cm deep, vascular rafts damaged, hematoma in splenic tissue larger than 5cm and diffuse signs, more than 50% of surface area present congestion.
4.4 Grade 4 Bleeding in the tissue, rupture of the splenic stalk causing 25% of the spleen volume to be deprived of blood supply
4.5 Grade 5 Spleen completely ruptured, splenic stalk
5. How to treat ruptured spleen in blunt abdominal trauma
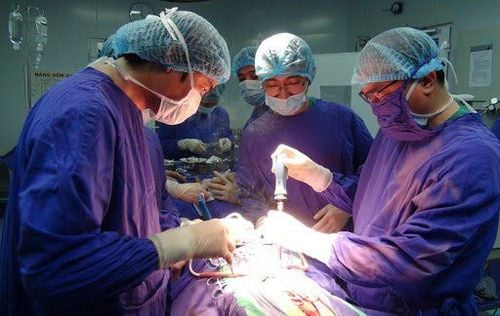
Phẫu thuật cắt toàn bộ lách
Depending on the degree of spleen rupture, the doctor will offer the most appropriate treatment for the patient:
5.1 Medical treatment Patients under 55 years of age and injuries in the first three levels, signs of birth Stable survival, not accompanied by other organ injuries in the body will be monitored vitals, urine output, fluid administration, antibiotics, analgesics, hemostatics...
5.2 Surgical treatment Surgery Total splenectomy: Usually for grade 5 splenic rupture or cases of splenic rupture causing significant internal bleeding, the patient has unstable vital signs. Splenectomy carries a high risk of infection, especially in young children. Surgery to remove part of the spleen: Depending on the rupture of the spleen at grades 3, 4, 5, the doctor will remove part of the spleen, the risk of infection will be reduced. Spleen-conserving surgery: Levels 1 ,2,3 spleen will be preserved by suturing the tear. To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, please book an appointment on the website for the best service.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
MORE:
Notes after laparoscopic splenectomy
Indications of laparoscopic splenectomy
Diagnostic image of splenomegaly on ultrasound