This is an automatically translated article.
“Is it dangerous to have anal polyps” is an issue that receives a lot of attention. The fact is that only certain types of polyps (called adenomas) are more likely to become cancerous, while others (hyperplastic or inflammatory polyps) have virtually no chance of becoming malignancies. future.
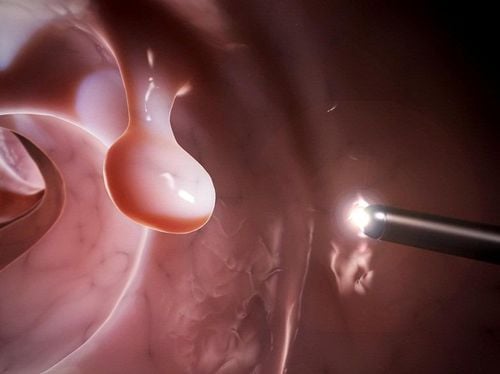
1. What are anorectal polyps?
Anorectal polyps, which occur at each respective site in the colon or rectum, are estimated to occur in at least 30%. However, anorectal polyps can also occur in an estimated 12% of children with intestinal bleeding.
Most anorectal polyps are found to be harmless, but some can develop into cancer later in life. However, the process of malignancy can still take many years.
2. Types of anorectal polyps
Although the same tumors develop in the large intestine, anorectal polyp types can carry different risk factors. Furthermore, the size of the polyps is also related to their potential severity, specifically:
Hyperplastic polyps: Hyperplastic or inflammatory polyps are usually harmless and not a cause for concern with the potential low malignancy. Adenomas: Adenomas, also known as adenomatous polyps, are not cancerous, but they can become malignant in the future. Larger adenomas are more likely to become cancerous. Doctors often recommend that patients remove the adenoma as soon as possible. Malignant Polyps: Malignant polyps contain cancerous cells. The best treatment for these polyps will depend on the severity of the cancer and the person's overall health.
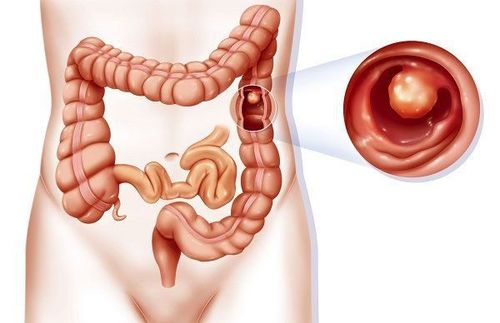
Hình ảnh bị polyp hậu môn trực tràng
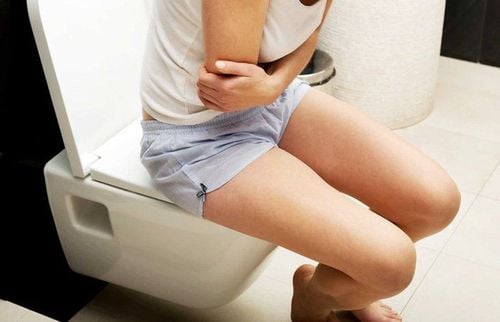
3. Symptoms of anorectal polyps
People with colon polyps in general or anorectal polyps in particular most often have no signs or symptoms of this condition.
Doctors usually only find these polyps during routine exams or tests for another disorder of the digestive tract. Your doctor may also recommend that older adults and people with risk factors for colon polyps get tested more often. When your doctor finds tumors early, you have a better chance of completely removing the growing tumor without complications.
When polyps have caused symptoms, you may notice the following:
Bleeding from the rectum: This is the most common symptom of polyps. Abdominal pain: Large polyps that partially block the intestines can cause abdominal cramps. Change in stool color: Bleeding from polyps can cause red or black streaks in the stool. However, other factors can also change the color of stool, such as foods, medications, and iron supplements. Iron deficiency anemia. If polyps cause oozing bleeding over time, you may have iron-deficiency anemia. Acquired symptoms are weakness, pale skin, shortness of breath, dizziness or fainting. Change in bowel habits lasting more than 1 week, including constipation or diarrhea.
4. Causes of anorectal polyps
Eating a lot of red meat can increase the risk of colon polyps. On the other hand, a person may have been born with colon polyps or will develop them throughout life.
Doctors still don't know the exact cause of colon polyps but the appearance of these structures may be related to the following lifestyle factors:
A high-fat diet; Not eating enough fiber; Smoke ; Fat. In some people, genetic factors cause the cells of the colon to multiply more than normal. When this happens in the colon, the person will develop colon polyps. When it occurs in the rectum, the patient will have an anorectal polyp. Thus, a person is more likely to develop colon polyps if he or she has the following genetic conditions:
Familial adenomatous polyposis; Gardner's syndrome; Peutz-Jeghers syndrome. Also, people with these conditions are at increased risk of developing cancer in several organs, including the small intestine and colon. For this reason, your doctor may recommend that older adults and people with risk factors for colon polyps get screened regularly, especially after age 50.

Chế độ ăn nhiều chất béo không tốt là nguyên nhân hình thành polyp hậu môn trực tràng
5. How is anorectal polyp diagnosed?
The doctor may start by taking a medical history, assessing risk factors, and performing a physical exam. If colon polyps are suspected, your doctor may recommend further tests. Early detection of colon polyps can reduce the risk of long-term complications.
Screening tools may include:
Colonoscopy: During a colonoscopy, your doctor inserts a camera tube called a colonoscope into your anus for examination. The doctor can then remove any polyps or take a biopsy and send it to a lab for examination under a microscope. Sigmoidoscopy: A shorter version of the colonoscope called a sigmoid is used to examine the limited portion of the colon. If polyps are found, the doctor will have to perform an endoscopy to remove them. Virtual colonoscopy: This is a non-invasive procedure in which a doctor uses imaging methods to examine it, which may include X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans. Stool test: Doctors may also look for the presence of blood from bloody stools or test the DNA of the stool. Depending on the results, your doctor may perform an endoscopy to confirm the diagnosis
6. How to treat anorectal polyps
Doctors will usually recommend surgery to remove anorectal polyps. At the same time, patients also need to be counseled to adhere to certain lifestyle changes to prevent colon polyps from recurring.
Doctors can remove colon polyps by the following methods:
Colonoscopy: Doctors can use a cutting instrument or a loop of wire at the end of the colonoscope to perform polypectomy. . For smaller polyps, your doctor may inject a fluid underneath to elevate and isolate the surrounding area. Laparoscopy: During a laparoscopy, the doctor makes a small incision into the abdomen or pelvis and inserts the laparoscope into the intestines. This technique is used to remove polyps that are too large or cannot be safely removed endoscopically. Resection of the colon and rectum: This is a total surgical removal, needed only when a person has severe disease or cancer. After the polyp is removed, the doctor will send the sample to a laboratory for testing, where specialists will check for cancer. A pathologist is an expert in analyzing tissue samples who will examine polyp tissue under a microscope to see if the structure is benign or precancerous. These results will form the basis of the recommended interval for the next colonoscopy.
In people who already have polyps or colon cancer, the doctor may prescribe aspirin and coxibs (COX-2 inhibitors) to stop new polyps from forming. For people with a family history of colon polyps, genetic counseling is recommended to prevent the development of lesions.
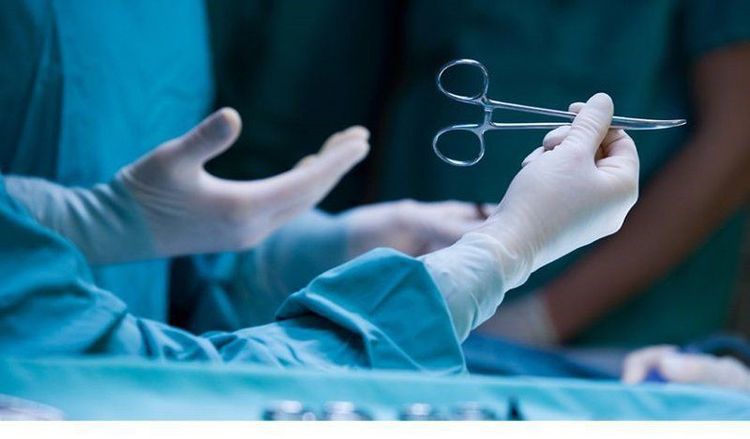
Trường hợp bị polyp hậu môn trực tràng bệnh nhân cần phải phẫu thuật
7. How to prevent anorectal polyps?
Everyone can reduce their risk of developing anorectal polyps or all colon polyps by adopting healthy lifestyle habits, such as:
Eating a low-fat diet; plenty of fruits, vegetables and fiber; Maintain a normal body weight; Quit or avoid smoking; Avoid excessive alcohol use. People who have had colon polyps should have regular colon health checkups because they are more likely to develop the disease themselves.
In summary, the majority of people with anorectal polyps usually have no symptoms. Although most cases are harmless, some types can become cancerous. Therefore, polypectomy is the best way to treat anorectal polyps and prevent cancer from developing in the future. In addition, people with risk factors should have regular colon polyp screening, especially if they are over 50 years old.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.