This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Ta Quang Hung - Department of General Surgery - Vinmec International General Hospital Da Nang. The doctor has more than 10 years of experience in teaching and practicing in the field of Anesthesia.Myasthenia gravis can be an indicator to help examine and detect thymoma, so in patients with these symptoms, it is often diagnosed earlier, so that appropriate treatment can be instituted.
1. Learn about thymoma in patients with myasthenia gravis
Myasthenia gravis is a rare autoimmune neuromuscular disease with symptoms such as muscle weakness, drooping eyelids, fatigue during exertion, high activity... If not detected early and treated promptly, the patient can respiratory failure and mortality. One of the causes is a thymic tumor.Myasthenia gravis is a tumor in the mediastinum. All cases of thymoma are potentially invasive and should be considered malignant. The causes and risk factors for thymoma are currently unknown. About half of patients have thymoma but have no clinical manifestations, 1/3 have symptoms of cough, chest pain, difficulty swallowing... and the rest are detected when examining patients with symptoms. myasthenia.
Treatment methods for thymoma include radiation therapy, chemotherapy alone, in combination depending on the stage of the disease or surgery to remove thymoma. This disease has a good prognosis if detected at an early stage.

2. Diagnosis of thymic tumors in patients with myasthenia gravis
Functional diagnosis: Clinically, it is possible to meet debilitating thymic tumors in children and the elderly. Some patients present with chest pain, shortness of breath, dry cough, and muscle weakness. Manifestations of myasthenia gravis are seen in over 70% of cases, the rest of patients only have symptoms of myasthenia gravis. Therefore, myasthenia gravis may be a marker for earlier tumor detection. Physical diagnosis: In the late stages, the symptoms caused by tumor invasion and compression on mediastinal organizations will cause shortness of breath leading to reduced movement of the diaphragm on the same side. Symptoms of myasthenia gravis range from mild, such as drooping eyelids, then whole muscle weakness, respiratory failure. Some patients have manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus, polymyositis-musculoskeletal disease... Chest X-ray: When chest X-ray is taken, if there is a sign of raised diaphragm on one side, it may be a possibility. tumor invasion into the phrenic nerve. Thoracic tomography: This method is valuable in diagnosing the extent of tumor invasion into adjacent structures, and at the same time, diagnosing whether or not the lesions have metastasized to the pleura. Magnetic resonance imaging will have a high diagnostic value, especially when the thymus tumor invades large blood vessels. Needle biopsy combined with immunohistochemical staining will increase the accuracy of the diagnostic method of thymoma. Needle biopsy is only used in cases where the tumor is too extensive or in differential diagnosis with lymphoma or seminoma. Mediastinoscopy under general anaesthesia: Mediastinoscopy helps to obtain a specimen that can accurately diagnose histopathology. Some biochemical and hematological tests to determine if there are other disorders such as: decreased erythropoiesis, hypogammaglobulinemia...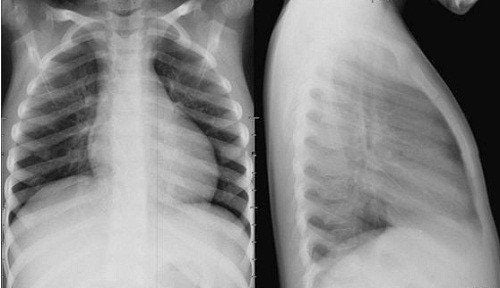
3. Anesthesia for thymectomy in patients with myasthenia gravis
Thymic resection in patients with myasthenia gravis often presents many problems with the safe use of anesthetics, so the anesthesiologist must be familiar with the medical condition and the interactions between anesthetics and medications. other. Steps of anesthesia for thymectomy in patients with myasthenia gravis are as follows:Step 1: Evaluation, chest X-ray, CT scan, MRI, echocardiography, and venography to investigate areas of invasion to prevent cardiovascular and respiratory problems. Attention should be paid to voluntary muscle strength and respiration, the ability to protect and maintain the airway after surgery. Step 2: Control the patient's airway and heart rate. Conscious intubation through a flexible bronchoscope is recommended, allowing the patient to breathe spontaneously and ventilating noninvasively. Step 3: Prepare the rigid bronchoscope and the extracorporeal circulation to be ready for adverse reactions. Step 4: Preoperative assessment of patients with myasthenia gravis includes assessment of disease severity and treatment regimen. Particular attention should be paid to voluntary muscle strength and respiration. The patient's ability to protect and maintain a clear airway after surgery may be impaired by preoperative medullary involvement. Step 5: Local and regional anesthesia with low dose amide anesthetic to avoid high blood concentration. For safe anesthesia, clinicians need to be mindful of monitoring the patient and analyzing the different responses of myasthenia gravis to multiple drugs. Avoid muscle relaxants. If necessary, use only moderate-acting muscle relaxants such as vecuronium or atracurium adjusted in small doses if intubation fails, and intraoperative muscle relaxants if necessary. For sternotomy, the combination of general anesthesia and thoracic epidural has the advantage of better postoperative pain control and leads to a higher likelihood of early extubation.
4. Monitoring of complications after thymectomy surgery in patients with myasthenia gravis
Post-anesthesia complications of thymectomy in patients with myasthenia gravis should be noted for prompt treatment. Specifically:Respiratory complications: When starting anesthesia, it can lead to complete airway obstruction, causing high mortality for patients. Patients at high risk for complications can be identified by respiratory signs and symptoms, assessed by CT scan if tracheal compression is >50%, and mixed on pulmonary function testing. Cardiovascular complications: Including cardiovascular compression due to superior vena cava obstruction, cardiac tamponade and mechanical compression of the pulmonary artery. The diagnostic technique for these complications is mainly echocardiography, however, the patient should be allowed to breathe on his own and should be closely monitored during the recovery period. Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in medical examination and treatment, patients can rest assured to visit. and treatment of thymic tumors at the Hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.