This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Master, Doctor Mai Vien Phuong - Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General HospitalGastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) are uncommon tumors of the gastrointestinal tract with distinctive clinical, genetic, and imaging features. Preoperative knowledge of risk stratification and mutation status is important to guide appropriate patient management. Predicting the clinical behavior and biological malignancy of GISTs based on conventional computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) assessments is challenging, unless the lesion has metastasized at the time of diagnosis. diagnostic point.
1. Overview
Data visualization is emerging as a promising tool for quantifying lesion heterogeneity on diagnostic imaging, extracting additional data that cannot be assessed by visual analysis.Data visualization applications have been explored for differential diagnosis of GISTs from other gastrointestinal tumours, risk stratification and prognosis prediction after surgical resection, and assessment of mutation status. in GISTs. Published studies on data visualization for GISTs have obtained excellent performance of derived data visualization models on CT and MRI. However, the lack of standardization and differences in research methods challenge the application of scintigraphy in clinical practice.
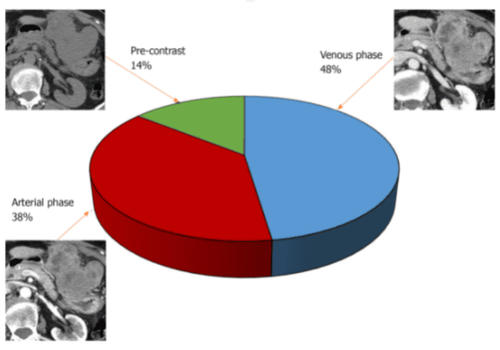
2. Application of data modeling techniques in GISTS
Differential Diagnosis Between GIST and Other Tumors The stomach is the most common organ affected by GISTs. The differential diagnosis should be made with other benign mesenchymal gastric tumors (eg, schwannomas and hemangiomas) or malignant neoplasms (eg, gastric adenocarcinomas and adenocarcinomas). lymphoma), and can be difficult due to overlapping images. Using texture analysis, Ba-Ssalamah et al. differentiated GISTs from gastric adenocarcinomas and lymphomas with high success rates on arterial and venous phase CT images.Another challenging site for differential diagnosis of GISTs from other gastrointestinal neoplasms is the duodenum. GISTs rarely occur in the duodenum (less than 5% of cases) and differentiate them from the more common types of duodenal adenocarcinoma (DAC), pancreatic ductal carcinoma (PDAC), or tumor Pancreatic neuroendocrinology is significantly associated with preoperative management and patient prognosis. To improve the preoperative characteristics of these lesions, a study by Lu et al investigated the entire lesion histogram analysis on contrast-enhanced CT, reporting excellent discrimination between GISTs and DACs. and PDAC in the perimedullary region.
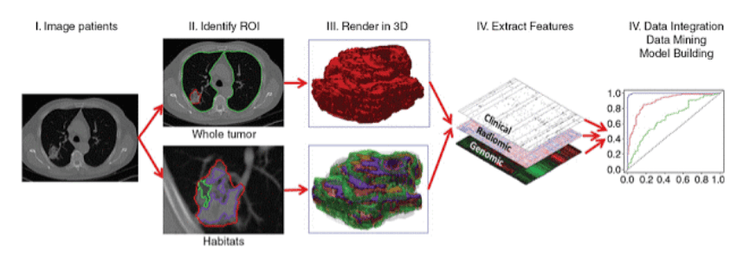
Assessment of mutation status
Genetic changes and mutation status are critical for optimal target therapy of GISTs. Approximately 80%-85% of GISTs have mutations in the KIT gene, 10% of GISTs have mutations in PDGFRα, while the remaining 10%-15% of GISTs are wild-type due to lack of mutations in either of these genes. In particular, wild-type PDGFRα and GISTs have lower rates of response to or resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitor-targeted therapies, depending on the specific mutation status Very little data exist on an association. relationship between CT imaging features and mutations in GISTs. The performance of data visualization and image analysis features of Data Modelers to distinguish GISTs with and without the KIT exon 11 mutation was explored by Xu et al in a research group. Research and validation of 69 and 17 GIST, respectively. In that investigation, the standard deviation was strongly correlated with the absence of the KIT exon 11 mutation and an AUROC gain of 0.904-0.962. In contrast, there was no statistically significant difference in the imaging ratings of heterogeneous lesions between GISTs with and without the KIT exon 11 mutation. Further studies are needed to correlate markers. scintigraphy with genetic patterns of mutational status (known as genomic data visualization) to provide reliable information to guide the most appropriate treatment, especially in non-advanced GISTs suitable for surgical resection.
3. Prospects for data modeling
Dataimaging is emerging as a promising tool for quantifying lesion heterogeneity, extracting additional quantitative data from datagramming images that cannot be assessed by the human eye. Okay. In recent years, many studies have explored the performance of data visualization models in abdominal cancer applications, with significant results in lesion characterization, response assessment and evaluation. treatment and predict patient survival after surgical or systemic treatment. The application of scintigraphy in GISTs can be used to further improve patient management and provide new advances in quantitative lesion assessment due to the unique clinical, genetic and imaging features of these tumors.Conclusion
Datagrammetry is emerging as a promising tool for the quantitative assessment of GIST, with excellent diagnostic performance for differential diagnosis with other gastrointestinal tumors, predicting stool risk stratification and assessment of mutation status. Future implementation of data visualization models in clinical practice may provide additional information from data visualizations that will be useful to guide patient management and treatment modalities. more suitable treatment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References Cannella R, La Grutta L, Midiri M, Bartolotta TV. New advances in scintigraphy of gastrointestinal stromal tumors. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26 (32): 4729-4738 [PMID: 32921953 DOI: 10.3748 / wjg.v26.i32.4729 ]