This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by MSc Tran Quynh Trang - Doctor of Biochemistry, Laboratory Department - Vinmec Times City International General Hospital.Worldwide, hepatocellular carcinoma is the third leading cause of cancer death. The incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in the United States has doubled in the past 25 years, mainly due to the increasing incidence of hepatitis C virus infection. When diagnosed at an early stage, hepatocellular carcinoma with liver transplantation or surgical resection can be curative.
Despite effective therapies for early-stage HCC and efforts to diagnose HCC early through screening patients at risk for cancer In this regard, most patients with hepatocellular carcinoma are diagnosed at an advanced stage.
Early diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma is difficult, in part because hepatocellular carcinoma patients are asymptomatic until the tumor is large or infiltrated, and serum AFP testing can be Poor sensitivity to detect small tumors. AFP (Alpha-fetoprotein) is a tumor marker used to evaluate in cases of suspected hepatocellular carcinoma. However, elevated serum AFP levels can be seen in chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis as well as in other tumor types (eg, germ cell carcinoma...) reducing the specificity of the test. AFP assay for hepatocellular carcinoma.
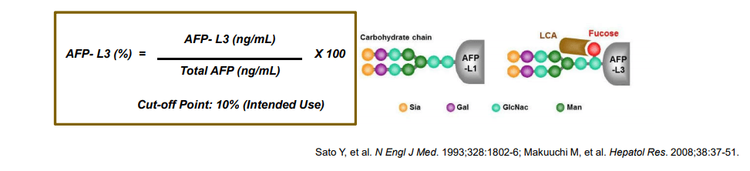
AFP (Alpha-fetoprotein) in hepatocellular carcinoma has a difference in affinity for the Lens culinaris agglutinin (LCA) lectin compared with that in chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis. Based on their ability to bind to LCA, total AFP is separated into three different glycoforms: AFP-L1, AFP-L2, AFP-L3. AFP-L1 is the LCA-unbound fraction, forming the major glycoform of AFP in the serum of chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis. AFP-L2 has a moderate affinity for LCA found in yolk sacs. AFP-L3 is the LCA association part of AFP.
Many studies have shown that malignant hepatocytes produce AFP-L3 even when HCC is in its early stages, and especially when the tumor is supplied by the hepatic artery. AFP-L3 is a highly specific marker for HCC. AFP-L3 can be detected in the serum of approximately 35% of patients with small (<2 cm) hepatocellular carcinoma. AFP-L3-positive HCC is likely to grow rapidly and metastasize early. Compared with imaging techniques, it has been shown to have a lead time of 9-12 months for early recognition of HCC. The combined sensitivity of AFP-L3 for hepatocellular carcinoma was 56%, with specificity >95%.
AFP-L3 % [(AFP-L3/total AFP) × 100], an isoform of AFP has been used as a marker for early diagnosis, assessment of treatment efficacy, and to predict prognosis. incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma.
According to study Apinya Leerapun et al (2008): In patients with total AFP of 10-200 ng/ml, AFP-L3% threshold > 10% had a sensitivity of 71% and specificity of 63% for the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. AFP-L3% cutoff > 35% had a 33% decrease in sensitivity, but increased specificity of 100% for the diagnosis of HCC. The high specificity of AFP-L3% cut off 35% allows an additional confident diagnosis of 10% of undiagnosed HCC using a limited total AFP of 200 ng/ml. AFP-L3% > 35% had 100% specificity for HCC in these patients. AFP-L3%, used in combination with AFP, may be a clinically useful adjunctive marker for the diagnosis of HCC.
Relationship between AFP-L3% and tumor size. According to the study of Hau-Tsai Cheng et al (2007): For tumors <2 cm, 60% of the studied patients had AFPL3 ≥ 15%; 81.3% for tumor size 2–5 cm and 90% for tumor > 5 cm. A significant correlation of AFP-L3 with tumor size was found (p=0.037).
Distinguishing between hepatocellular carcinoma and chronic liver disease. Monitor people with cirrhosis from any cause for the development of hepatocellular carcinoma. Monitoring the development of hepatocellular carcinoma in individuals with a family history of liver cancer. Monitoring response to treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References:1. THE UTILITY OF AFP-L3% IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA: EVALUATION IN A U.S. REFERRAL POPULATION
Apinya Leerapun, Sri V. Suravarapu, John P. Bida et al.
2. THE UTILITY OF AFP-L3% IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA: EVALUATION IN A U.S. REFERRAL POPULATION
Apinya Leerapun, Sri V. Suravarapu, John P. Bida et al