This is an automatically translated article.
Calories are a factor that many people care about when building diets. Consuming the same amount of calories from different foods will have different effects on the body. So calories are not calories.
1. Explain the concept: Calories are not calories
What are calories? Calories (calories) are units to calculate the energy content of foods put into the body. All foods contain a certain amount of calories.
There is an opinion that: Calories are the most important part of the diet, and the source of calories is not important. They assume that 1 calorie is 1 calorie, no matter whether you eat 100 calories of candy or 100 calories of broccoli, they will have the same impact on your weight.
In fact, it is true that all calories have the same amount of energy. 1 calorie contains 4,184 joules of energy. In that respect, 1 calorie is 1 calorie. However, when it comes to the body, the calculation is not so simple. The human body is a complex biochemical system with processes that regulate energy balance. Different foods go through different biochemical pathways. Some of them are ineffective and lose calories as heat. In addition, different foods and macronutrients affect the hormones and brain centers that control hunger and eating behavior. The type of food you eat can have a huge impact on the biological processes that control when, what, how much you eat, etc. Thus, calories are not calories.
2. 6 examples that prove calories are not calories
2.1 Fructose and Glucose
2 main simple sugars in your diet are glucose and fructose. Both provide the same number of calories per gram. However, the way the body metabolizes them is completely different. Specifically, glucose is metabolized by all tissues of the body. However, the majority of fructose is only metabolized by the liver.
Here is an example of why the calories of glucose are not the same as the calories of fructose:
Ghrelin is the hormone that makes you feel hungry. It goes up when you're hungry and goes down after you eat. One study showed that fructose led to higher levels of ghrelin (which increases hunger) than glucose; Fructose does not stimulate satiety centers in the brain in the same way that glucose does. So, fructose makes the body feel less or less full; High fructose consumption can cause insulin resistance, increased belly fat, increased triglycerides, increased blood sugar, and more concentrated LDL cholesterol than the same amount of calories from glucose. Thus, with the same amount of calories per glucose and fructose, they have different effects on hunger, hormones, and metabolism. Therefore, a nutrient rating based on the number of calories a food provides or an assessment based on how many calories are consumed are not optimal options.
Fructose only has a negative effect when eaten in excess. Sugar and candy are great sources of fructose. Besides, you can eat a lot of fruit, although they contain fructose, they are also rich in fiber and water, so they can reduce the negative effects of fructose.
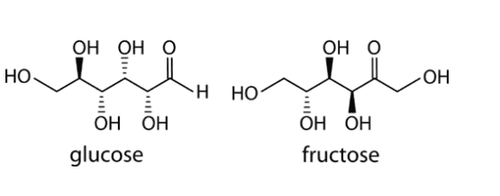
Fructose và Glucose không phải là calo
2.2 Thermic effect of food
Different foods have different metabolic pathways. There will be one way more efficient than others. The more efficient the metabolic pathway, the better the food's energy will be used and the less it will be dissipated as heat.
The metabolic pathways for protein are less efficient than the metabolic pathways for carbs and fats. 1g of protein contains 4 calories, but most of the protein calories are lost as heat when it is metabolized by the body.
Thermic effect of food is a measure of the energy consumption of different foods. The thermic effect of macronutrients is as follows:
Fat: 2 – 3%; Carbs: 6-8%; Protein: 25 - 30%. As such, protein requires more energy to metabolize than carbs and fats. Calculating on the thermic effect of 25% for protein and 2% for fat, this means that 100 calories of protein is 75 calories, 100 calories of fat is 98 calories.
Studies have shown that a high-protein diet has metabolic advantages. In short, calories from protein are less fattening than calories from carbs and fat, because protein requires more energy to metabolize. Whole foods (unprocessed and refined) will also require more energy to digest than processed foods.
2.3 Protein reduces cravings, helping you eat fewer calories
Protein also reduces cravings, causing you to automatically eat fewer calories. If you increase your protein consumption, you can lose weight without counting calories or controlling portion sizes. If you do not want to diet but just want to balance your metabolic rate, adding protein to your diet is the simplest way to lose weight naturally.Thus, when it comes to metabolism and appetite regulation, a calorie from protein is not the same as a calorie from carbs or fat. Here's the argument to be made: Calories are not calories.
2.4 No
Different foods have different effects on satiety. This means that certain foods can keep you feeling full for longer.
You can easily eat 500 calories of ice cream but it is very difficult to eat 500 calories of eggs or broccoli. This is an example of how food choices have a huge effect on the total number of calories you consume.
There are many factors that determine the satiety value of different foods - calculated on a scale called the satiety index. The satiety index is a measure of increasing satiety and decreasing hunger. If you eat foods with a low satiety index, you will feel hungry more quickly and will eventually eat more. If you choose foods with a high satiety index, you will eat less and achieve better weight loss results.
Foods with a high satiety index are: Boiled potatoes, beef, eggs, beans, fruit. High-calorie foods with a low satiety index include cakes and donuts. Thus, the choice of foods that create a feeling of fullness or not will have a great influence on the energy balance.

Mỗi thực phẩm có giá trị về cảm giác no khác nhau
2.5 Low-carb diets restrict calories
Since 2002 to date, more than 20 trials have compared low-carb (low-carb) and low-fat (low-fat) diets. The results showed that the low-carb diet lost more weight, often 2-3 times more than the low-fat diet. One of the main reasons for this is that low-carb diets reduce cravings. People will tend to eat fewer calories.
Even when calorie intake was similar between the low-carb and low-fat groups, people on the low-carb diet often lost more weight. This is because a low-carb diet causes significant dehydration and reduces bloating. Furthermore, low-carb diets tend to consume more protein than low-fat diets. The body will need more energy to convert protein into glucose. And this is also an argument that explains the point of the article: Calories are not calories.
2.6 Glycemic Index
Refined carbs are not good for health. It includes added sugars such as sucrose, corn syrup, and high-fructose refined grain products. Refined carbs tend to be low in fiber, quickly digested and absorbed by the body, causing blood sugar spikes. They have a high glycemic index (GI), which is a measure of how quickly a food raises blood sugar.
When you eat a high-calorie food that raises blood sugar quickly, it tends to drop blood sugar a few hours later. When you do, you will experience cravings, especially cravings for other high-carb foods. Therefore, the rate at which carb calories enter the body can cause overeating and rapid weight gain. So if you are following a high-carb diet then you should choose unprocessed and high-fiber sources of carbs. Fiber can reduce the rate at which glucose enters the body.
Through the above 6 examples, it can be confirmed that different sources of calories will have different effects on hunger, hormones, energy expenditure, and brain regions that control food consumption. Therefore, in addition to paying attention to the amount of calories your body consumes, you also need to pay attention to the choice of food to be able to lose weight more effectively.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: healthline.com