This is an automatically translated article.
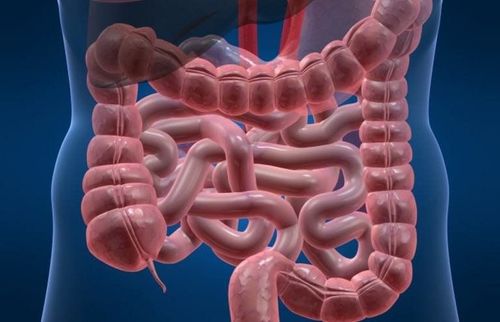
Colon cancer is a common and dangerous disease, causing the leading death rate among cancer types. Currently, not only the elderly but also more and more young people die from colon cancer.1. What is colon cancer?
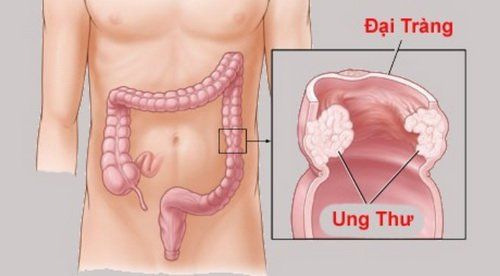
Colon cancer, also known as colorectal cancer, is a condition in which abnormal cells appear and grow in the lining of the large intestine, colon, or rectum. Both men and women are at risk for this disease. According to survey data in the US, colon cancer is the second leading cause of cancer death in this country. However, if detected early, doctors can cure colorectal cancer.
2. Definition of Colorectal Polyps
Colorectal polyps are benign, tumor-like lesions that grow inside the large intestine. Most polyps are harmless, but they can also become colorectal cancer if not removed early. There are two common types of colon polyps: adenomas and hyperplastic polyps. Abnormal growths in the lining of the colon are the cause of polyps.
3. Natural disease risk
Contributing causes of colon cancer that the patient cannot control include:
Age: Most people with colon cancer are over 50 years old. Medical history: The patient has had colorectal polyps or pre-existing inflammatory bowel disease. Family history: Having a close relative with colorectal cancer or precancerous colon polyps.

Sử dụng nhiều thực phẩm được chế biến sẵn là nguyên nhân mắc bệnh ung thư ruột già
4. Risk of disease due to lifestyle
The incidence is higher for people who:
Eat a lot of red meat cooked at high temperatures or processed (canned) Obesity, have too much belly fat Do not exercise regularly Smoking Leaves Heavy Alcoholism
5. Symptoms of colon cancer
It should be noted that the early stages of colon cancer are often quite subtle. Therefore, if you want to detect it early to make it easier to treat, it is important for patients to go to the hospital for examination. When the disease has progressed to a more advanced stage, this time may appear signs such as: blood in the stool, abdominal pain, constipation or diarrhea, unexplained weight loss and fatigue. The above symptoms mean that the colorectal tumor is already quite large and much more difficult to treat.
6. Colorectal Cancer Screening Test
As mentioned above, screening tests are key to getting an early diagnosis. Doctors recommend that middle-aged people over 45 years old should have a colonoscopy every 10 years. This procedure is done using a tube with a small camera attached to it to look at the entire colon and rectum, helping to detect tumors early if any. Your doctor will remove polyps to prevent colon cancer.
7. CT colonoscopy (virtual colonoscopy)
This is a method of computerized tomography, called CT scan for short, which produces 3D images of the large intestine to detect polyps or other abnormalities. The advantage of this procedure is that there is no need to place the camera inside the patient's body. In contrast, the main disadvantage of CT colonography is that it can miss small polyps. Furthermore, if some abnormalities are seen on the colonoscopy, the patient will still need actual colonoscopy. For this virtual colonoscopy, it is recommended that you do it every 5 years.
8. Flexible sigmoidoscopy
This is another type of test that can be an alternative to conventional endoscopy. Similarly, the doctor will use a thin tube with a light and camera to look inside the rectum and the bottom part of the colon. This test helps find polyps as well as cancer cells. Depending on the case, the doctor may ask the patient to have a flexible sigmoidoscopy every 5 years.
9. Stool blood test
Fecal occult blood test and fecal immunochemical test (FIT) are used to determine the presence of blood in the stool, as this is one of the signs of colon cancer. You will be asked to provide up to three small stool samples depending on the type of test. If blood is detected in the stool sample, further endoscopy should be performed. The recommended cycle for a stool blood test is one year.10. Cologuard - Stool DNA test
Cologuard is the name of a new type of test that looks for abnormal blood or DNA in a patient's stool sample. This is a very accurate test to help detect colon cancer. However, Cologuard cannot completely replace the role of endoscopy and endoscopic follow-up is still needed if there is any abnormality. The American Cancer Society recommends considering fecal DNA testing every 3 years.
11. Biopsy of the large intestine
If a tumor is discovered after performing the above tests, the next step to do is a biopsy. During a colonoscopy, your doctor will remove suspicious-looking polyps and tissue samples from any part of the colon. These tissues are then studied under a microscope to determine if they are cancerous.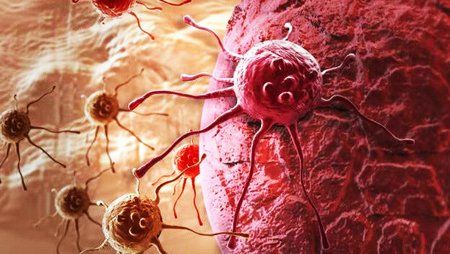
Hình ảnh minh họa tế bào ung thư ruột kết.
12. Stages of colon cancer
The definition of "stage" is used by experts to describe how far a cancer has spread. The higher the stage, the more serious the cancer. Meanwhile, tumor size does not always reflect the disease state. It is also easy for the doctor to make the decision to choose the appropriate treatment for the patient depending on the different stages.
There are 5 stages of development of colon cancer:
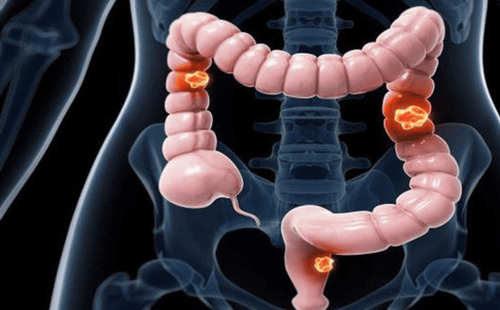
Stage 0: The cancer has just appeared and is in the innermost lining of the colon or rectum. Stage I: Cells have grown in the lining of the colon or rectum. Stage II: The cancer has invaded the outermost wall of the colon or rectum. Stage III: Involved in lymph and spread to one or more lymph nodes in the area. Stage IV: Cancer cells have spread to other parts of the body, such as the liver, lungs, or bones.
13. Survival rate
A patient's outlook for recovery depends on the stage at which the cancer was discovered. Approximately 87% to 92% of patients live at least 5 years from the time they are diagnosed with stage I colorectal cancer. However, the above statistics are for reference only and do not reflect accuracy for all cases. The rate of cure and survival time of cancer patients depends on many other factors, so it is necessary to closely coordinate and follow the doctor's treatment regimen. maintain optimism.14. Effects of surgery
Surgery has a very high chance of cure if done in the early stages of colorectal cancer. Doctors will remove tumors and tissue around the cancerous bowel, but if they are too large, the diseased colon or rectum may need to be removed. In the late stages, when the tumor has spread to the liver, lungs or other organs, surgery will no longer work or be effective.
15. When is radiotherapy and chemotherapy needed?
A small number of cases can still be cured of colon cancer, even if the tumor has spread to the lymph nodes in stage III. Treatment options include surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation therapy. However, if the disease recurs and metastasizes to other organs, it is very difficult to cure. After all, radiation and chemotherapy can still alleviate painful symptoms and help patients live longer with cancer.
16. Does chemotherapy make the patient's body uncomfortable?
You can rest easy with today's new generation of chemotherapy because they are less likely to make the patient tired. In addition, some medications can help patients control nausea.

Thuốc hóa trị thế hệ mới có nhiều cải tiến trong hạn chế tác dụng phụ.
17. Radiofrequency ablation RFA
The feature of this treatment is the use of high heat to burn the tumors. Through the CT scan, the doctor inserts a needle-like device into the tumor and surrounding area to burn. Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) can destroy tumors that cannot be removed with surgery, such as tumors located in the liver. This method can be combined with chemotherapy.
18. Lifestyles that help prevent colorectal cancer
Building healthy living habits will help you significantly reduce the incidence of colon cancer. The American Cancer Society recommends that you:
Stick to a sensible diet: Eat more fruits and vegetables, cut down on processed and red meat, and use whole grains instead of refined grains. . Exercise regularly. Control weight and body fat.
19. The importance of exercise
Exercise - regular sports is a powerful weapon to help fight colorectal cancer in particular and diseases in general. A study has shown that people who are active in physical activity, whether at work or at sports, have a 24% lower risk of disease than those who are less active.
The American Cancer Society recommends moderate exercise, such as brisk walking, 150 minutes a week, or 75 minutes a week of more vigorous exercise such as jogging. Don't forget to evenly distribute your training time and try to maintain it weekly.
Because it is not possible to find signs of colon cancer at the initial stage of onset, the patient must conduct the necessary and periodic tests as directed by the doctor if he wants to detect it early and increase the likelihood of cure. cured. The stage of diagnosis, a healthy lifestyle and an optimistic spirit are important considerations in the prevention and treatment of colon cancer.
Vinmec International General Hospital is implementing a Package of Screening and Early Detection of Colorectal Cancer, implemented by a team of experienced doctors and nurses in the field of colorectal cancer diagnosis and treatment. colon, with the support of a system of modern technological equipment and facilities, full of specialized means to diagnose the disease and stage it before treatment such as: Endoscopy, CT scan, PET-CT scan, MRI, mammogram, histopathological diagnosis, gene-cell testing, ... help detect colon cancer early even when there are no symptoms.
Besides, at Vinmec, we also take the lead in implementing the treatment of colorectal cancer by robotic laparoscopic surgery. Coming to Vinmec, patients will be completely satisfied when experiencing international standards of examination, treatment, and care.
Customers wishing to examine, treat and screen for colorectal cancer can go to Vinmec International General Hospital for service.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: Webmd.com