Considerations for Small Hard Lumps Developing Beneath the Skin
Small, hard lumps under the skin can be caused by various tumors, with epithelial cysts being the most common. Although they do not significantly affect overall health, this type of tumor can cause many inconveniences in daily life if you do not know how to address it.
1. What are Small Hard Lumps Under the Skin Caused by Epithelial Cysts?
Epithelial cysts, also known as sebaceous cysts or epidermoid cysts/keratinous cyst, are characterized by small, hard lumps developing under the skin. These nodules typically grow slowly but can recur multiple times in the same location and are especially unlikely to become malignant.
These epithelial cyst lumps usually appear on the head, face, neck, back, or genital areas in both males and females, with sizes ranging from about 6mm to 50mm. Epithelial cysts do not cause specific symptoms and appear similar to a small skin swelling, containing a thick substance inside and typically having an odor. This type of cyst is usually painless, with a yellow or dark color.
2. Specific Characteristics of a Cyst
Besides being a small, hard lump developing under the skin, epithelial cysts have the following characteristics:
- Usually round or oval in shape, soft but firm.
- The center of the cyst typically has a black opening, similar to a blackhead developing on the nose.
- Epithelial cysts commonly appear on the face, neck, or male/female genitals.
- The cyst wall is thin, surrounding an internal fluid containing multiple lipid and keratin fragments, creating a white or yellow mucus with an unpleasant odor.
- When ruptured, without appropriate antibacterial measures, they can cause inflammation/infection, swelling, and pain.

3. What Causes Small Hard Lumps Under the Skin?
Epithelial cysts with small, hard lumps forming beneath the skin are primarily caused by long-term accumulation of keratin (a natural protein produced within skin cells). When this protein becomes trapped under the skin, it creates a swollen mass without causing pain.
Keratin cell accumulation is typically a response to health conditions such as skin trauma, acne, HPV virus infection, or frequent sun exposure.
Specifically, the following factors can increase the risk of developing small hard lumps under the skin:
- Being in puberty (for both males and females)
- Having certain skin surface damage
- Rare genetic factors
- People who have experienced recurring acne...
4. How Do Epithelial Cysts Typically Progress?
When initially forming, epithelial cysts usually do not cause painful symptoms, so when they grow in well-concealed areas, patients typically do not pay much attention. However, if the cyst progresses to other stages, they can have negative impacts on health, including:
- Cyst inflammation: When swollen, the cyst can become inflamed when exposed to external impacts, making surgical removal difficult.
- Ruptured epithelial cyst: When ruptured, the yellow mucus inside the cyst will flow out and potentially lead to skin infection.
- Epithelial cyst abscess: In cases of severe infection with signs of swelling, redness, and severe pain, the fluid in the cyst may mix with blood during drainage.
- In the most dangerous cases, epithelial cysts can cause skin cancer. However, this progression is extremely rare.

5. How to Diagnose Epithelial Cysts?
Besides the presence of small hard lumps under the skin, doctors will further examine the swelling level of the lump and surrounding skin. You will also need to honestly answer some questions about the cyst's formation time and changes over time.
To diagnose an epithelial cyst, doctors typically only need a clinical examination. In some cases, patients might need additional tests for more accurate results:
- Blood and secretion tests: Usually unnecessary for initial diagnosis, but in cases of recurring infected cysts or poor antibiotic response, bacterial samples from the cyst fluid will be cultured and tested for antibiotics.
- Image-based cyst diagnosis: If the cyst is in an unusual location like bone or breast, doctors may perform imaging techniques like X-rays, ultrasound, MRI... to ensure it's not a malignant tumor.
- Additional diagnostic tests: When small hard lumps appear in unusual locations, doctors might aspirate the cyst to observe keratin under a microscope.
6. How to Treat Small Hard Lumps Under the Skin?
Typically, epithelial cysts may not require treatment, but they can shrink and recur quickly without completely disappearing naturally. In cases where the cyst causes aesthetic inconvenience, the following solutions are recommended for Small Hard Lumps Developing Beneath the Skin:
6.1. Incision and Fluid Drainage
In this approach, doctors will make a small cut in the cyst and then push out all the mucus inside. Although a simple treatment method, the cyst may recur.
6.2. Complete Surgical Removal of Epithelial Cysts
For this surgery, your cyst will be completely removed to prevent its recurrence. You don't need to worry too much about this procedure, as it is a minor surgery with high effectiveness and relatively safe for epithelial cysts.
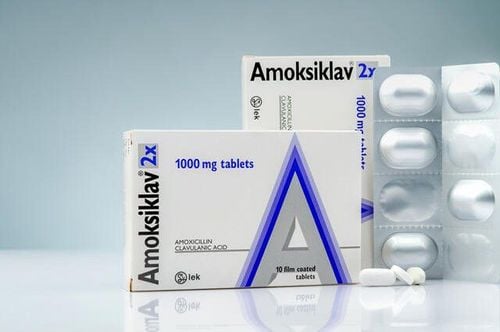
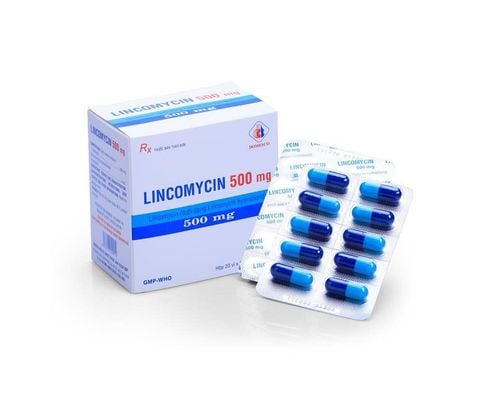
6.3. Medication Treatment for Hard Lumps Under the Skin
In cases where the cyst is painful, swelling, rapidly changing size, or infected... you will need to use medication for treatment, including antibiotics, injections, and drainage to support swelling reduction and pain relief.
It can be said that small hard lumps under the skin are often associated with the formation of epithelial cysts. This type of cyst does not significantly affect health but can cause many inconveniences in your life if formed in prominent external locations.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.