This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by MSc Pham Thi Mai Thanh - Gastroenterologist, Department of General Internal Medicine - Vinmec Times City International HospitalGastric polyps are protrusions that protrude from the surface of the gastric mucosa. Gastric polyps are often discovered incidentally, occur in 2-3% of patients with upper gastrointestinal endoscopy, rarely cause symptoms such as bleeding or delayed digestion. However, proper diagnosis and management are important because some polyps carry a risk of cancer.
1. Epidemiology
Hyperplastic polyps are the predominant type in areas with high prevalence of HP infection. In contrast, in Western countries, where the prevalence of HP infection is lower and proton pump inhibitors are widely used, gastric polyps are predominant.2. Treatment of stomach polyps
In patients with small, solitary gastric polyps, biopsy or removal of polyps is recommended for histopathological diagnosis. Hyperplastic polyps or polyps > 1 cm in size should be removed because biopsies do not remove all high-grade dysplasia or early gastric cancer. In patients with multiple polyps, the largest polyp requires resection and a representative biopsy of the remaining polyps.Normal-looking mucosa in the antrum and body should also be biopsied to rule out dysplasia occurring against a background of atrophic gastritis and HP infection. Treatment of HP eradication is required if HP infection is detected.
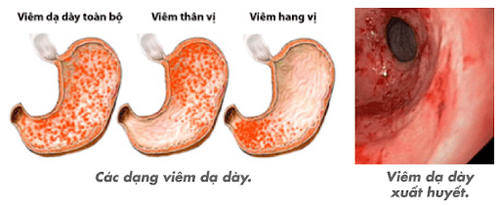
3. Some types of stomach polyps
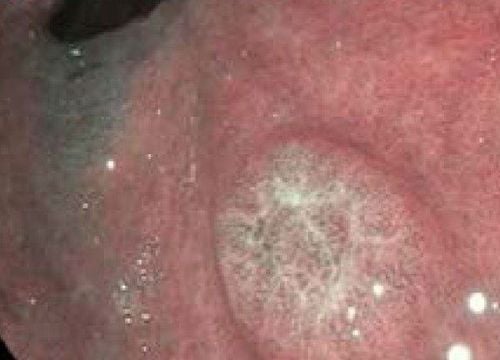
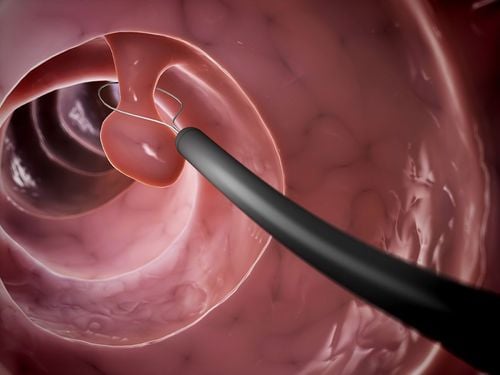
Gastric adenomatous polyps: account for 47% of all gastric polyps. Gastric gland polyps can be solitary or multiple polyps, without stalks, appearing only in the gastric aneurysm and upper body. Taking proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) increases the risk of developing gastric polyps, which are less likely to be malignant. Gastric adenomatous polyps associated with the polypolyposis syndrome may be dysplastic but rarely progress to malignancy. Gastric adenomatous polyps >1cm in size, ulcerative polyps on the surface or in the antrum need to be removed. Patients with multiple polyps (>20) or a solitary polyp in gastric aneurysm >1cm should consider discontinuing PPI therapy. Hyperplastic polyps are benign, accounting for 28-75% of all gastric polyps. The mechanism of formation is believed to be due to excessive mucosal remodeling following Helicobacter Pylori (HP) gastritis injury, pernicious anemia, near ulceration and erosion or near the gastrojejunal junction. These polyps are usually benign but have the potential to become malignant. Hyperplastic polyps > 5mm must be thoroughly removed. Gastroscopy every 1-2 years for follow-up because of the risk of cancer due to concomitant chronic atrophic gastritis and other risks. Gastric adenomas typically form on the background of atrophic gastric mucosa and may be associated with multiple polyp syndromes. Most gastric adenomas have no symptoms. Symptomatic adenomatous polyps are usually bleeding or rarely obstructing. Because gastric adenomas are precancerous, resection of all gastric adenomas is recommended either endoscopically or surgically. Follow-up by gastrointestinal endoscopy over 1 year after polypectomy. Depending on the specific case, there is a high risk of cancer that needs to continue to be followed up by endoscopy. Gastric neuroendocrine tumors may be associated with hypergastrinemia (types 1 and 2) or present alone (type 3). Type 1 and 2 neuroendocrine tumors that are less than 1-2 cm in size are selected for endoscopic resection, while type 3 can metastasize at the time of resection, so they are often treated with surgery. Partial or total gastrectomy with regional lymphadenectomy. Inflammatory fibroids are very rare, accounting for 0.1% of all polyps. After excision of inflammatory fibrous polyps typically do not recur and do not require follow-up. During a gastroscopy, a gastroenterologist or technician inserts a flexible tube with a camera into the mouth and down the throat allowing the doctor to see inside the stomach.
This is a common method for high accuracy today to examine and diagnose gastric pathologies and gastric polyps such as:
Early diagnosis of gastric lesions, even if small, are visible. whole stomach, inner regions of stomach spasmodic, torsion dyskinesia Inflammation of atrophic or hypertrophic gastric mucosa Gastric ulceration Gastroduodenal tumors (benign, malignant, neoplasms) blood vessels, cancer...) Stomach polyps Gastric polyps are removed during endoscopy Combined with biopsies and tests to help diagnose more accurately Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the best The hospital not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, a system of modern equipment and technology. The hospital provides comprehensive and professional medical examination, consultation and treatment services, with a civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space. Customers when choosing to perform tests here can be completely assured of the accuracy of test results.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.