This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by MSc CCII Phan Thi Minh Huong - Gastroenterologist, Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.Gastrointestinal polyps are often an incidental finding when patients have gastrointestinal disorders and are indicated for endoscopy. There are many types of polyps, but they all have one thing in common: they do not manifest clearly, making patients confused, worried, and do not know what disease they have. The information presented below will provide a basic understanding of this pathology.
1. What are gastrointestinal polyps?
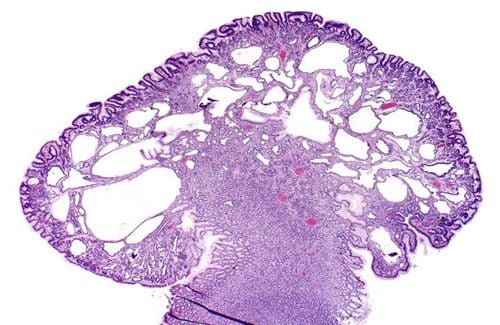
Polyp is defined as an organization that proliferates from the mucosa and pushes protrusion into the lumen of the gastrointestinal tract. Polyps are epithelial or subepithelial in nature; Therefore, polyps are also called submucosal tumors.
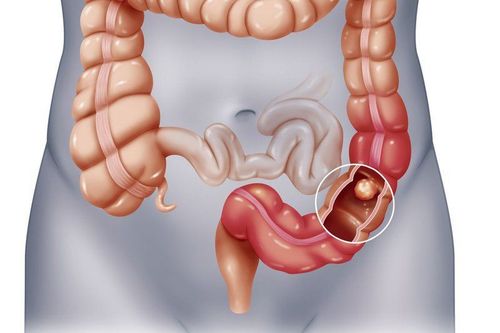
Gastrointestinal polyps are mucosal papillomas that appear anywhere on the digestive tract, from the mouth to the anus. The most common locations for polyps are in the stomach and colon, and rarely in the small intestine and esophagus.
2. Classification of gastrointestinal polyps
There are ways to classify polyps such as: dividing by size (small polyps < 5mm in diameter, medium polyps from 6 to 10 mm and large polyps > 10 mm), dividing by shape (pedunculated polyps and pedunculated polyps). sessile), classified according to histopathology.
Classification of gastrointestinal polyps according to histopathology includes:
2.1 Polyps originating from the epithelial layer Including:
Esophageal papillomas (esophageal polyps): Size from 0.2-2 cm, no stalk, Same color as normal esophageal mucosa, smooth or rough surface. Gastric polyps: Including types of polyps of the fundus of the stomach, hyperplastic polyps, and polyps of the stomach. Small bowel polyps: Uncommon, mainly in the duodenum. Colon polyps: Includes hyperplastic polyps and adenomatous polyps. Excess histiocytosis: The essence is proliferation of epithelial cells with smooth muscle bundles, usually benign when <1cm in size, found in any position of the gastrointestinal tract. 2.2 Polyps originating under the epithelium Including the following types:
GIST: The surface resembles the surrounding mucosa, variable size, 70% of cases are found in the stomach, 20% of the cases are found in the small intestine, 10% of cases occur in the esophagus. Neuroma: Also belongs to the GIST group. Lipoma: Found at any location, the tumor is submucosal, pale yellow, soft, often with a solitary tumor. Carcinoid tumors: Common in the appendix, ileum, and rectum. Endoscopic image is a submucosal tumor, yellow. Hemangiomas: Rarely in the gastrointestinal tract, submucosal tumors are red or blue. Lymphoma: Rare in the gastrointestinal tract, may occur in the duodenum or colon. Ectopic pancreas: Common in the stomach, duodenum or first part of the jejunum. 2.3 Polyps Syndromes Some common gastrointestinal polyposis syndromes are familial polyposis, Peutz-Jegher syndrome, and juvenile polyposis.
Familial polyposis syndrome: There is an inherited dominant gene, due to mutations in the APC gene. One out of every 10,000 to 15,000 babies is born with this syndrome. Symptoms include: bloody diarrhea, diarrhea, dandruff when there is cancer, can progress to colon cancer. Peutz-Jegher syndrome: An inherited genetic disease caused by mutations in the STK11/LKB1 gene. One in every 25,000 to 300,000 babies is born with the disease. Symptoms include: black pigment spots in the lips, oral mucosa, palms, soles of the feet, bloody diarrhea, intestinal obstruction. People with this syndrome have an increased risk of cancers of the gastrointestinal tract, pancreas, lungs, testicles in men and cancers of the uterus, ovaries, and breasts in women. Juvenile polyposis syndrome: Inherited dominant gene, caused by mutations in the BMPR1A and SMAD4 genes. The disease usually occurs between the ages of 4 and 14 years.

Hội chứng Peutz- Jeghers là do đột biến gen STK11/LKB1
3. Symptoms of gastrointestinal polyps
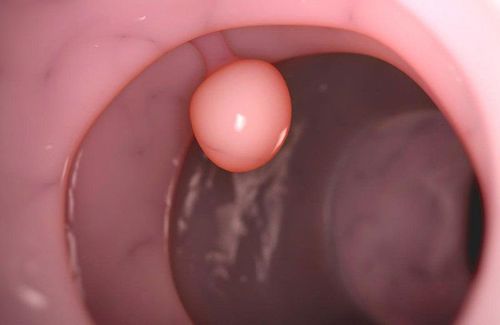
Most cases of patients with gastrointestinal polyps are discovered incidentally through endoscopy, clinical symptoms are quite poor. Symptoms of polyps are caused by complications of polyps such as bleeding during defecation or black stools, intestinal obstruction, constipation and malignancy.
If polyps appear in pediatric patients, especially when there are hereditary polyp syndromes, children often have intussusception with symptoms of severe abdominal pain that causes children to cry, stretch, twist to relieve pain. Each pain lasts from 5-15 minutes, always starts and disappears suddenly. After the pain, the baby may be completely normal, feeding, sleeping and playing, but then the pain will return.
In addition, the child may have a lot of vomiting, bloody stools or constipation - defecation, abdominal distension. If the abdominal wall is thin, and especially when the pain is out, the intussusception can be palpated, which is a long, unstable mass of solid density and will cause a sharp pain when the baby is pressed.
4. Are gastrointestinal polyps dangerous or not?

Sự nguy hiểm đáng sợ khi bị polyp ống tiêu hóa là nằm ở biến chứng của nó
The scary danger of having a gastrointestinal polyp lies in its complications.
Intestinal polyps can cause many dangers such as gastrointestinal bleeding, leading to 14% of patients with anemia, iron; 43% of patients had recurrent bowel obstruction due to the size of the polyp; 5% to 16% of cases of intussusception in adults, and account for only 1% of all causes of intestinal obstruction. The most common types of intussusception in this syndrome are the jejunum, jejunum, ileum, and ileum.
In particular, Peutz-Jegher syndrome (PJS) is associated with gastrointestinal cancer, because it can promote the development of hamartomatous tumors in the gastrointestinal tract, breast and other cancers, increasing the risk. develop colorectal cancer.
Gastrointestinal polyp is a disease with few clinical symptoms and is usually discovered only by incidental endoscopy or when the disease has appeared complications. Therefore, you should not be subjective with abnormal signs of the body, take the initiative to visit the hospital regularly to detect the disease at the earliest, helping to improve the effectiveness of treatment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.