This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Dong Xuan Ha - Digestive Endoscopy - Department of Medical Examination and Internal Medicine - Vinmec Ha Long International Hospital1. What are colon polyps?
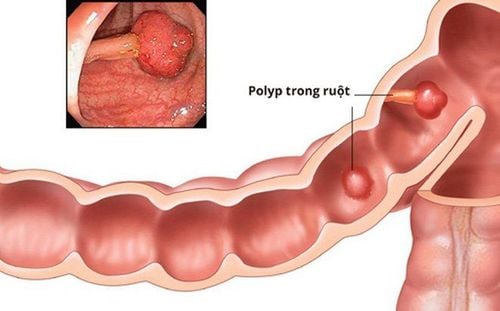
Colonic polyps are defined as protruding masses on the surface of the colonic epithelium, often with broad stalks or legs. Histopathologically, colon polyps are of epithelial origin, which can be adenomatous polyps, hyperplastic polyps or stromal polyps. There can be 1 or more colon polyps per patient, the vast majority of which are benign, but there are also cases where polyps grow and become cancerous. Anyone can get colon polyps.
Colon polyps include 3 main types: hyperplastic polyps account for the vast majority of cases with a rate of 90%, adenomatous polyps account for 10% and very rare polyposis syndrome with an extremely small rate.
Common hyperplastic polyp is colon polyp 5mm or less than 5mm with polyp shape is round, small, sessile and not capable of turning into malignant colon polyp. Polyps are classified into 3 types: ductal, villi and tubular-villi, this is a polyp that can appear anywhere on the colon, usually has a stalk and is less than 1.5cm in size. Colon polyps, if they are larger than 2cm in size and have villi, have a high risk of turning into malignant colon polyps. Polyposis colon syndrome includes hereditary polyps and polyposis syndrome unrelated to genetic factors. Among hereditary polyps, familial adenomatous polyposis is the most common and has the potential to transform into a malignant form.
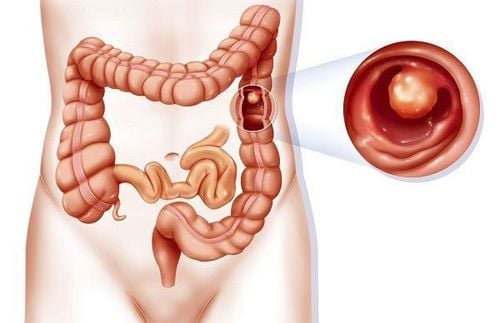
2. Familial colon polyps
Familial colon polyp is a condition in which there are many adenomatous polyps in the colon, which should be treated as soon as possible to prevent the possibility of turning into cancer when the patient reaches the age of about 35-40. Familial colon cancer is caused by a clonal mutation in the adeno polyp gene, also known as the APC gene, which is responsible for inhibiting the occurrence of colon tumors. When a child receives this mutated APC gene from one of the parents, there is a 50% chance of having inherited polyps at birth. According to some studies, this type of gene mutation can appear randomly during conception, then develop into familial adenomatous polyposis at a certain age in life, usually during pregnancy. 35-40 years old.
For the symptoms of familial colon polyps, patients often do not have obvious clinical manifestations, but the disease only progresses silently inside the body. Many patients do not discover any symptoms until the disease has progressed to the stage of colon cancer, so it is important to have regular health checkups, cancer screening to have Familial adenomatous polyposis can be detected as early as possible. There are some symptoms also sometimes appear that help the patient to suspect the possibility of having colon polyps of family nature such as: abnormal rectal bleeding, diarrhea, abdominal pain... When the patient is Performing colonoscopy will result in many images of colon polyps or polyps of the stomach and duodenum... In addition, genetic testing also contributes greatly in supporting the diagnosis of pathology. this.

This is a disease that proliferates colon polyps continuously, so it is very difficult to completely remove these polyps from the body in a short time. One of the effective methods applied to treat familial colon polyps is total colectomy, which is usually performed on adult patients. In some cases, after surgery, colon polyps continue to form and grow, so medical treatment is required to prevent the growth of these polyps. After surgery, patients will be prescribed drugs to help colon polyps shrink or can't continue to grow such as: Sulindac, Celecoxib...
Complications of colon polyps are familial if not treated. timely progress to colon cancer, rectal cancer, stomach cancer, duodenal cancer, thyroid cancer, tumor appearance in the central nervous system as well as in the liver. In addition, another complication is quite serious for familial adenomatous polyposis, which is diffuse mesenteric fibroids affecting some organs and blood vessels inside the abdomen, namely the condition of the gastrointestinal tract. Among the hereditary polyposis diseases in the colon, familial adenomatous polyposis is the most common colon polyp condition, related to genetic factors. transmitted from family, should be detected early and intervention measures to prevent these colon polyps from developing into colon cancer.
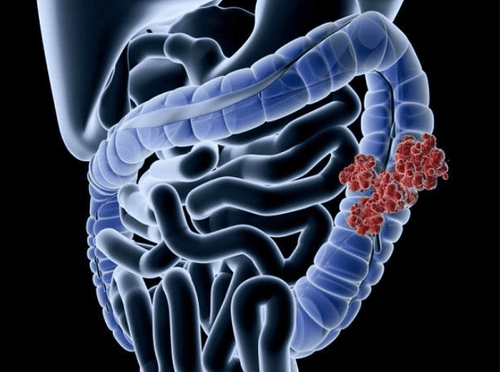
Gastrointestinal cancer screening is a scientific and effective measure to detect gastrointestinal cancer early (esophageal cancer, stomach cancer, colon cancer) and provide a good treatment plan. best. Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital has a package of screening and early detection of cancers of the gastrointestinal tract (esophagus - stomach - colon) combined with clinical and paraclinical examination to bring the most accurate results. maybe.
When screened for gastrointestinal cancer at Vinmec, you will receive:
Gastrointestinal specialty examination with an oncologist (by appointment). Gastroscopy and colonoscopy with an NBI endoscope with anesthesia. Peripheral blood cell total analysis (by laser counter). Automated prothrombin time test. Automated thrombin time test. Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time (APTT) test using an automated machine. General abdominal ultrasound
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.