This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with Master, Doctor Nguyen Thi Nhat - Infectious Diseases Doctor - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.Pulmonary schistosomiasis is a chronic, highly contagious disease in the community. Although the mortality rate is low, the impact of the disease on organ function is quite large. So how to treat lung schistosomiasis?
1. What is pulmonary schistosomiasis?
Schistosomiasis or snail fever is a parasitic infection, caused by several species of freshwater flukes in tropical and subtropical regions, of the genus Schistosoma. Among them, the most pathogenic species are S. japonicum, S. mansoni, S. mekongi, S. hamatobium, and S. intercalatum.As noted, the mortality rate from schistosomiasis is always very low, but the disease is often chronic and can cause damage to other organs in the body, especially the lungs. Pulmonary schistosomiasis is not an uncommon disease that can occur in people with hepatosplenomegaly infected with S. japonicum, S. mansoni or S. haematobium.
Schistosomiasis is recognized as a common disease in freshwater and brackish water areas, so people who are constantly in contact with water will be at high risk of infection. The larvae penetrate the skin through the skin and then develop and cause disease.
2. The life cycle of schistosomiasis in the human body
Immediately after contact with human skin, the schistosomiasis tail larvae have the ability to adhere, penetrate the skin and rely on blood vessels to move. In the larval stage, penetrating the skin will cause an itching sensation for the patient, but the vast majority of cases of tapeworm infection do not notice this symptom.When traveling to the lungs, the schistosomiasis larvae will take the necessary development steps to be able to migrate to the liver. It takes about 7 weeks for the tail larva to change and develop into an adult male/female fluke.
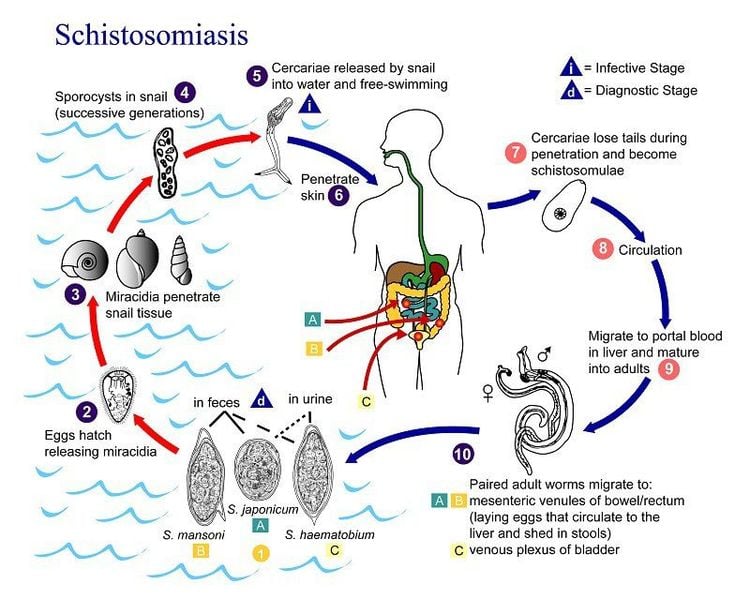
Vòng đời của sán máng trong cơ thể con người
3. Diagnosis of pulmonary schistosomiasis
3.1. Implementing the quadrants
To be able to confirm the diagnosis of pulmonary schistosomiasis requires a combination of 4 factors: epidemiology, clinical manifestations, immunological tests and imaging.Epidemiological factors:
Patient lives or travels in areas where schistosomiasis is endemic. Have been exposed to contaminated water. Clinical manifestations:
When the parasite penetrates through the skin, the patient's body appears red; Shortness of breath, coughing up blood; Headache, abdominal pain, leg numbness; Have a febrile reaction, feeling chills; Portal venous pressure increases due to damage to the liver parenchyma; Swollen lymph nodes, swelling of the liver and spleen; Painful urination, urinary frequency, blood in urine; Gastrointestinal bleeding, diarrhea, black and bloody stools; Dizziness, dizziness. Laboratory tests:
Eosinophilia, possibly with thrombocytopenia, anemia; Use a microscope to look for schistosomiasis eggs in patient samples: sputum, urine, feces or bronchoalveolar lavage fluid; Diagnostic serology test; X-ray: Image shows nodular infiltrative lesion.
3.2. Differential diagnosis
Need to differentiate lung fluke (Pulmonary Schistosomiasis) with the following pathologies:Diseases of portal hypertension; Chronic bronchitis; Eosinophilic pneumonia; Pulmonary hypertension diseases.
Cần chẩn đoán phân biệt sán máng phổi với các bệnh lý khác
4. How to treat lung schistosomiasis?
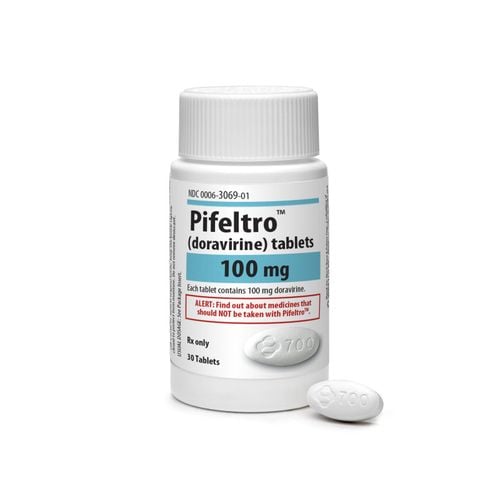
To treat lung schistosomiasis, one of the following drugs can be used:Praziquantel: This is the best drug to treat pulmonary schistosomiasis today. Dosage 40mg/kg/time, success rate from 85-90%. However, the drug can cause some side effects such as: Irritability, dizziness, headache, abdominal pain. Besides, patients may experience nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, rash. In essence, these side effects are caused by the drug, but partly due to the body's immune system reacting to the dead parasites. Besides, the drug is contraindicated in cases of hypersensitivity to the drug's components, pregnant women or people with weakened immune systems.
In addition to Praziquantel, there are 2 other drugs that can be used such as: Oxamniquin, Metrifonat. However, patients should note that these drugs are only used when Praziquantel is not available.
5. Prevention of lung schistosomiasis
Pulmonary schistosomiasis is a dangerous disease, so taking preventive measures is extremely important. You can take measures to prevent this disease by the following ways:Need to boil water before use, filter domestic water before use; In endemic areas with endemic schistosomiasis, contact with water sources contaminated with schistosomiasis should be avoided. Avoid playing, swimming in dirty lakes or standing water because it is easy to have schistosomiasis larvae in the water. Pulmonary schistosomiasis is a very contagious disease and has a high risk of outbreak if subjective. The disease can cause many dangerous complications in the lungs as well as affect many different organs, especially in pregnant women. Therefore, if you yourself have signs of the disease, you need to immediately go to reputable medical facilities for timely examination, diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary schistosomiasis.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.