This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Van Huong - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec International General Hospital Da Nang.An arteriovenous malformation (AVM) is an abnormality of high-flow blood vessels, in which there is a connection between the artery and the vein. Some AVMs are asymptomatic and cause no obvious signs. CT, MRI, and ultrasound are of great significance in the diagnosis of arterial malformations. Treatment of AVMs can be accomplished by monitoring the condition or disabling the AVM with surgery, radiation therapy, or embolization.
1. What is arteriovenous malformation?
Vascular malformations are abnormal connections or passages between arteries and veins. They occur most commonly in the brain, neck, and spine but they are also found in the hands, feet, lungs, liver, and reproductive system. AVMs cause blood to pass through capillaries, which are the smallest blood vessels and go directly from arteries to veins. Some AVMs don't cause problems, but in some people they can rupture and bleed, causing serious problems.Most episodes of bleeding are not severe enough to cause permanent damage but significant bleeding can occur. If the AVM is in the brain, this bleeding can cause a stroke or brain damage. If a peripheral AVM develops outside of the head, neck, and spine it can reduce blood supply to surrounding tissues and over time this can damage tissue, causing pain and ulcers or sores. open on the skin. AVMs can also force the heart to work harder to circulate blood.
Most AVMs are present at birth and some AVMs are present after surgery. AVMs in the head, neck, and spine can cause headaches, neck pain, seizures, unusual sounds, vibrations or wobbles in one ear, double vision, increased pressure in the ear. eyes (glaucoma), eye swelling, decreased vision, redness and congestion in the eyes, problems with voice, vision or movement, prominent blood vessels on the scalp and on the ears.
Symptoms of peripheral AVM include dyspnea on exertion, hemoptysis (if the AVM is in the lungs), bleeding, abdominal pain, melena (if the AVM involves the digestive system), anemia, and swelling painful lumps on the trunk and sores on the skin.
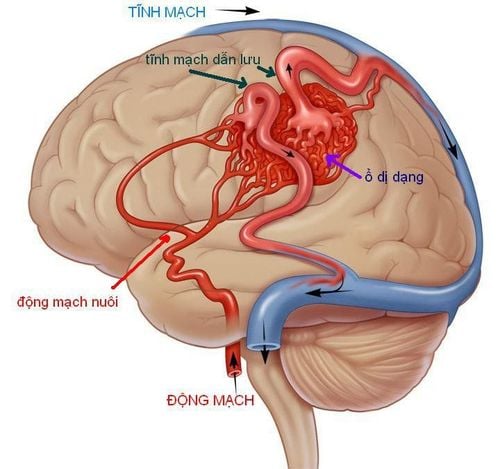
Dị dạng mạch là những kết nối hoặc lối đi bất thường giữa động mạch và tĩnh mạch
2. How are arteriovenous malformations diagnosed and evaluated?
AVMs tend to be found during the treatment of unrelated disorders. Doctors may perform the following imaging tests to diagnose brain AVMs:Head computed tomography (CT): This is a CT scan that combines special X-ray equipment with a machine. sophisticated computer to create multiple images or images inside the body. CT angiography (CTA) may be performed to detect and characterize the AVM. During CTA, contrast material can be injected into a vein while images of the blood vessels are obtained. The combination of these scans can help doctors decide on the best therapy for patients with AVMs. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): An MRI is a procedure that uses a strong magnetic field, radiofrequency pulses, and a computer to create detailed images of organs, soft tissues, bones, and virtually all structures. structure inside another body. MR is also used to visualize vessels. This is an MR angiogram (MRA) procedure that combines intravenous contrast injection to get the best images. A procedure called MR perfusion (MRP) that creates an image of the blood stream may also be done. Doctors may perform the following imaging tests of peripheral AVMs:
Ultrasound : An ultrasound image is created using sound waves to create pictures of the inside of the body. Ultrasound is often the first procedure used to image the peripheral AVM. Angiography: Angiography is a method of creating images of the main blood vessels supplying the AVM by inserting a thin plastic tube called a catheter into the blood vessel, and contrast material is injected into the vessel supplying the AVM while X-ray. This provides a very detailed image of the AVM. Computed tomography (CT): CT can show AVMs in different parts of the body. As with head CT, a full-body CT scan may include an injection of contrast material. Whole-body CT may also include CT angiography (CTA) and CT perfusion (CTP). Magnetic resonance imaging: Doctors may use an MRI to help diagnose AVMs in other parts of the body. MR angiography (MRA) and MR perfusion (MRP) may be used as part of this test. These imaging tests can provide information about the location and size of the AVM and can also reveal the extent of bleeding in the area.
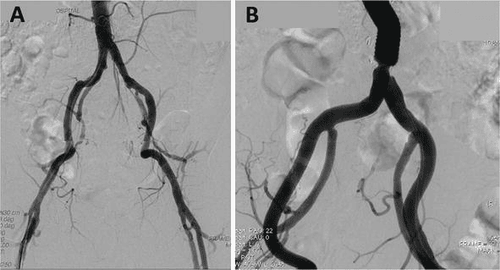
Chụp động mạch là phương pháp tạo ra hình ảnh của các mạch máu chính cung cấp AVM
3. How is AVM treated and treated?
Most AVMs do not require immediate treatment, however, all AVM patients should consult a specialist. It's important to know that AVMs don't go away on their own, and treatment options depend on various factors, including symptoms, the location of the AVM, and the individual's overall health. The decision to treat AVM requires careful weighing of benefits and risks.The main treatment options include:
Medical management of symptoms: The use of medications to treat symptoms such as headaches, back pain, and seizures caused by AVMs. For peripheral AVMs, compression sleeves can reduce swelling in the arms or legs. However, these are often not helpful. Patients with peripheral AVMs should seek care in a vascular malformation clinic with interventional radiologists experienced in the treatment of AVMs. People with brain AVMs should have regular check-ups with a neurologist, interventional neuroradiologist, or neurosurgeon. Surgery: Surgical removal is an option if the brain AVM is bleeding and located in an area that can be easily operated on. The procedure is performed under general anesthesia, then the doctor approaches the brain AVM by removing part of the skull. Some peripheral AVMs can be treated surgically if they are small enough. Removal of the AVM when possible will often eliminate the possibility of further bleeding. Stereotactic radiosurgery: Sometimes the brain AVM can be located in an area that is difficult to reach with surgery, and stereotactic radiosurgery is an option in these cases. In this procedure, a focused beam of high-energy radiation is focused on the brain AVM and will damage the vessels and form a blood clot to seal the AVM. Embolization of AVMs: Embolization is a much less invasive procedure than surgery. In this procedure, a thin plastic tube is inserted into an artery. The doctor directs it to the position of the AVM under image guidance. Then, a special liquid glue is placed or released to stop blood flow to the AVM. This method may require a variety of accompanying treatments. Some AVMs may be embolized before surgical removal. After treatment, you may need follow-up imaging to make sure the AVM has been completely removed or destroyed. There is still a risk of bleeding if some AVMs remain after treatment. Therefore, patients need to go to a reputable hospital to conduct examination and treatment as soon as there are signs of arterial malformations (AVMs). Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the leading prestigious hospitals in the country, trusted by a large number of patients for medical examination and treatment. Not only the physical system, modern equipment: 6 ultrasound rooms, 4 DR X-ray rooms (1 full-axis machine, 1 light machine, 1 general machine and 1 mammography machine) , 2 DR portable X-ray machines, 2 multi-row CT scanner rooms (1 128 rows and 1 16 arrays), 2 Magnetic resonance imaging rooms (1 3 Tesla and 1 1.5 Tesla), 1 room for 2 levels of interventional angiography and 1 room to measure bone mineral density.... Vinmec is also the place to gather a team of experienced doctors and nurses who will greatly assist in diagnosis and detection. early signs of abnormality in the patient's body. In particular, with a space designed according to 5-star hotel standards, Vinmec ensures to bring the patient the most comfort, friendliness and peace of mind.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference sources: radiologyinfo.org, slideshare.net