This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Pham Manh Chung - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Ha Long International Hospital
Colonoscopy, also known as virtual colonoscopy. This is an imaging technique that does not require an endoscope. This technique is much superior to other traditional diagnostic methods, so it is widely applied in modern medicine.
1. What is a colonoscopy?
The colon, also known as the large intestine, is the last part of the digestive system. The colon has the function of receiving digested food and absorbing nutrients from the small intestine, then continues to carry out the process of absorbing mineral salts and water, breaking down the remaining substances to form feces. CT scan of the colon helps to check for abnormalities in this part of the intestine.Colonoscopy can provide information normally only obtained by colonoscopy. A CT scan is less invasive than a colonoscopy because the procedure does not require the entire colon to be inserted. Therefore, a CT colonoscopy is sometimes called a virtual colonoscopy. This method helps doctors see the entire colon lumen without the need for a colonoscope like traditional methods.
CT colonography uses a CT scanner to create detailed images of the colon. This technique can be used instead of colonoscopy to help detect cancer and other intestinal abnormalities, thereby making a quick and accurate diagnosis.
2. When should a colonoscopy be performed?
The main purpose of this method is to find polyps or tumors in the colon. If there are symptoms such as: change in bowel habits, weight loss or blood in the stool, over 50 years old, anemia of unknown cause... you should have a CT colonoscopy or colonoscopy.
CT colonography can also be used to screen/screen for colon cancer in people at risk (family history of colorectal cancer or polyposis, family history of have ulcerative colitis, have familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) or have colorectal cancer syndrome without familial adenomatous polyposis (HNPCC)). In addition, CT colonoscopy is often used in people who are too weak or unable to have a colonoscopy.
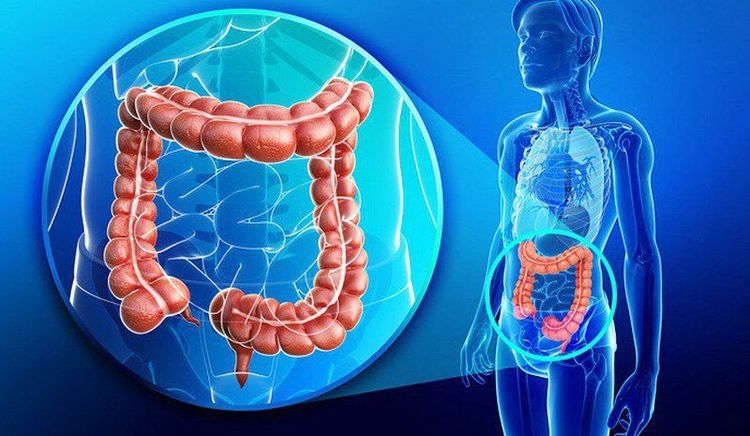
3. Advantages and disadvantages of colon tomography method
Advantages: Clear, high-resolution images support more accurate diagnosis and diagnosis. It is possible to monitor organs such as the small intestine, intestinal wall and abdominal organs. The implementation time is short, fast and accurate, detecting small-sized polyps in the colon lumen. No anesthesia, less invasive technique is used because the endoscope is not inserted into the body. Creates a feeling of comfort, less anxiety, no pain and very low complication rate. Cons: The image shows the location of the lesion but cannot be intervened, not immediately cutting like the endoscopic method. Using X-rays, the body is exposed to a little radiation, the level of influence is within the limits and is underestimated compared to the benefits that this technique brings. Surgery cannot be performed when needed, but other surgical techniques must be used.
4. Principle of CT colon scan
The CT scanner is like a giant thick ring, the side of the scanner has an X-ray source. The patient lies on a long table and slides in until the part of the body to be scanned is inside the machine. The source will rotate around the body, rotating and emitting a penetrating X-ray beam.
At each certain position of the imaging table (also called a slice), the receiver/transducer detects and records the intensity of the X-ray beam after passing through the body. The denser the tissue, the less penetrating the X-ray and vice versa. X-ray detectors feed this information into the computer. Tissue types with different densities will form images on a computer screen through different shades of gray (gray scale). An image of the inside of the body is created after each step, forming an image of a slice. As the table moves, the X-rays will pass through the next part of the body and the computer will create new slices.
5. Colon scan procedure
The doctor examines and conducts pre-scan tests. Ask the patient to fast for 4-6 hours. Cleanse the intestines. Intestinal spasmolytics or contrast injections may be given, depending on the reason for the test. Place the patient on the bed, and inject air into the rectum through the anus. For the patient to lie on the tomography machine, keep the position, hold the breath when required, the doctor conducts tomography to obtain the necessary images. The doctor receives the results, diagnoses the disease, and advises the patient on treatment.
6. Notes on CT colonography

Notify your doctor when you are pregnant, suspect pregnant or have diabetes, kidney failure, allergies... Pregnant women, if possible, should not have CT scans because X-rays can cause birth defects. If contrast injection is required, the patient must stop some of the previous medications, especially those taking metformin (for diabetes). If the patient is taking this medicine, the doctor will give instructions on what to do. Do not bring metal objects when shooting. Follow a suitable diet the days before and after the scan, fasting 4-6 hours before the scan. When performing the technique, air will be pumped into the anus, if you want to fart or bloat, don't worry because this is a normal expression and will quickly end. Consult a doctor if it is used in children, as children are much more affected by X-rays than adults, which may increase the risk of cancer later in life. If you're breastfeeding and may need to give up milk for 24 hours after your scan, ask your doctor for specific advice.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.