This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Duong Xuan Loc - Gastroenterologist - General Surgery Department - Vinmec Danang International General HospitalFamilial polyposis (FAP) is an inherited disease caused by an abnormality in the APC gene structure. The disease manifests with many polyps growing mainly in the colon, even the duodenum and small intestine. If left untreated, polyps can become cancerous.
1. What is familial polyposis (FAP)?
Familial polyposis (FAP) is a rare genetic disease caused by structural abnormalities of the APC (adenomatous polyposis coli) gene. Most cases of the disease are inherited, only 25 - 30% are spontaneous gene mutations.Familial polyposis causes polyps to form in the colon, rectum, and even the upper digestive tract (small intestine, duodenum). If left untreated, polyps in the colon and rectum are more likely to become cancerous by the age of 40.
Most people with familial polyposis need a colonectomy to remove the colon. prevent cancer. Duodenal polyps also carry a risk of developing into cancer, but they can be controlled with careful monitoring and regular polyp removal.
The milder form of the disease is called impaired familial polyposis (AFAP). People with AFAP often have fewer colon polyps (average 30), and are also less likely to develop cancer than people with FAP.
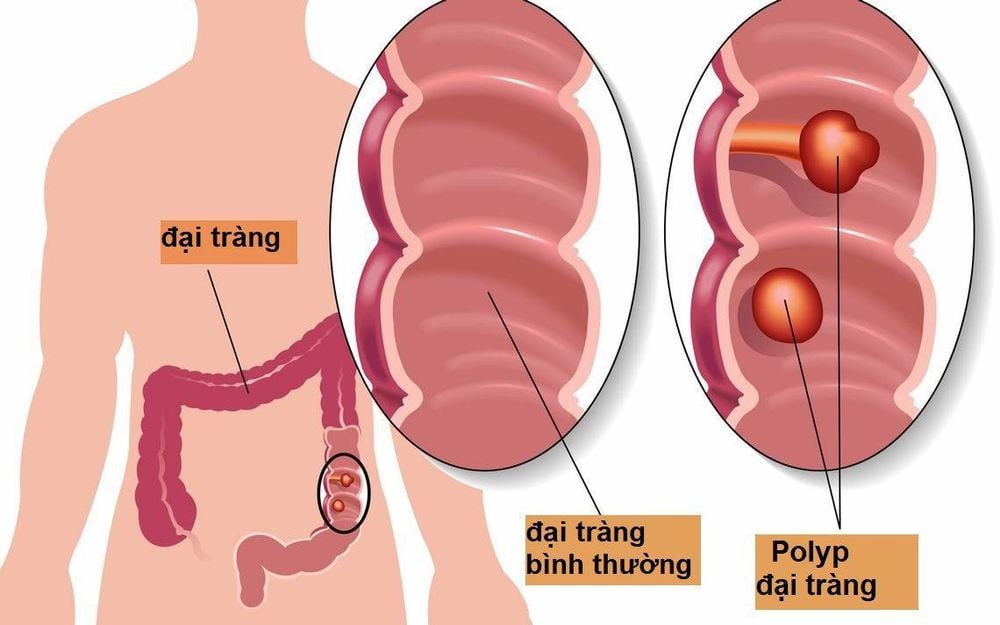
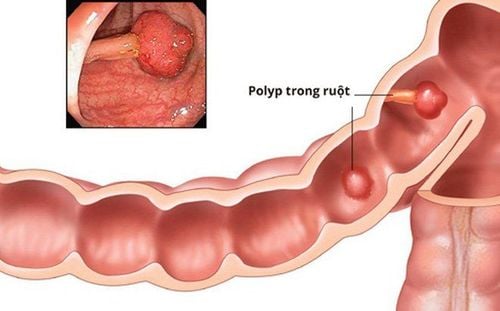
Bệnh đa polyp gia đình gây hình thành các polyp tại đại tràng
2. Symptoms of familial polyposis (FAP)
The symptom of familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) is that hundreds or even thousands of polyps develop in the colon and rectum. The disease usually begins in adolescence, polyps almost 100% will develop into colon cancer and rectal cancer by the age of 40.3. Causes of familial polyposis (FAP)
Familial polyposis (FAP) is caused by an abnormal structure of the APC (adenomatous polyposis coli) gene, which is usually inherited from parents. However, in some people, the gene mutation is spontaneous, unrelated to genetic factors.4. Risk factors for familial polyposis (FAP)
The risk of familial polyposis is higher if a parent, child, or brother has the disease. If someone in your family has FAP, other family members should be screened.For typical familial polyposis (FAP), screening is performed annually between 10 and 12 years of age by colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy. If the disease has not been detected by the age of 40, consider discontinuing follow-up.
For mild polyps (AFAP), screening is initiated at age 25-30 with a complete colonoscopy every 1 to 2 years. If colonoscopy shows polyps, it should be removed and biopsied. If the results are benign, endoscopy will be performed annually.

Bệnh đa polyp gia đình (FAP) mang tính di truyền
5. Complications of familial polyposis (FAP)
In addition to colon cancer, familial polyposis also has the potential to cause the following complications:Duodenal polyps : Polyps that develop in the duodenum have the potential to become cancerous. However, if carefully monitored, duodenal polyps are often detected and removed early before they develop into cancer. Balloon of Vater Polyp: Polyp of the ampulla of Vater occurs in the region where the terminal portion of the bile duct and pancreatic duct empty into the duodenum. It can develop into cancer but can often be detected and removed before it develops into cancer. Stomach polyps: Stomach polyps are developed in the lining of the stomach. Desmoid tumors: Desmoid tumors can arise anywhere in the body but usually develop in the abdominal wall. It can cause serious problems if it grows on nerves or blood vessels or puts pressure on organs in the body. Other cancers: FAP rarely causes cancer in the thyroid, central nervous system, adrenal glands, liver, or other organs. Benign skin tumors Benign osteosarcoma Congenital pigmented epithelial hypertrophy (CHRPE): These are benign pigmentary changes in the retina of the eye. Dental Abnormalities: Includes extra teeth or missing teeth. Low red blood cell count (anemia).
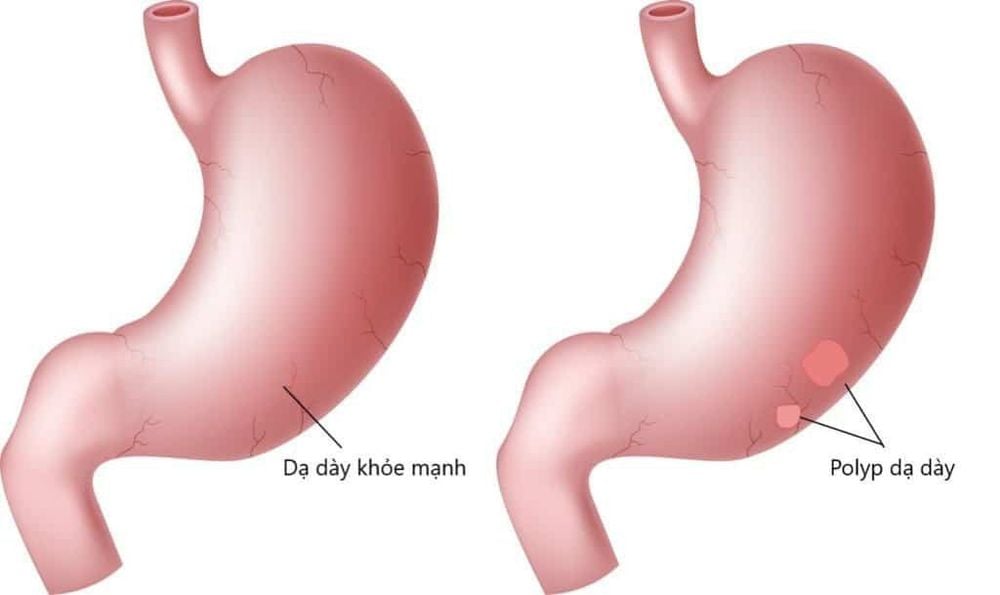
Đa polyp gia đình (FAP) có thể gây polyp dạ dày
6. Prevention of familial polyposis (FAP)
If someone in your family has familial polyposis, you need to bring your family members in for genetic testing and counseling. This is necessary to screen for and prevent the development of the disease.If you have FAP, you need to go to the doctor for regular monitoring, then surgery if necessary. Surgery can help prevent the growth of colorectal cancer and other complications.
Familial polyposis is a complex disease that can turn into many other cancers. Therefore, when a person is diagnosed with familial adenomatous polyposis, family members should be tested for the disease. If so, it needs to be treated early, to reduce the risk of colorectal cancer.
Screening for early detection of colon cancer brings high treatment efficiency. The 5-year survival rate is very high up to 90% for those detected and treated early.
Một trong những phương pháp điều trị đa polyp gia đình là phẫu thuật
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: mayoclinic.org