This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Van Huong - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec International General Hospital Da Nang.Abdominal radiographs are often used as an imaging tool to look for signs of bowel obstruction. Although this diagnosis cannot be ruled out if radiographic findings are normal, it is a first-line clinical indication because of its ease, speed, and prevalence. The main radiographic findings of bowel obstruction are dilated loops of bowel in the presence of an air-fluid level. Furthermore, an upright abdominal radiograph can also be used to screen for bowel perforation.
1. What is the indication for bowel obstruction X-ray?
Imaging plays an important role in the diagnosis of intestinal obstruction as well as in helping to determine the appropriate choice and timing of management. Indications for X-ray bowel obstruction are:Differentiate true mechanical obstruction from bowel obstruction due to paralytic ileus or constipation Determine the site of obstruction, whether small bowel obstruction or colonic obstruction Determine cause underlying bowel obstruction Evaluate complications of intestinal obstruction, such as perforation Assess viability of the bowel segments involved
2. General features on X-ray film of intestinal obstruction
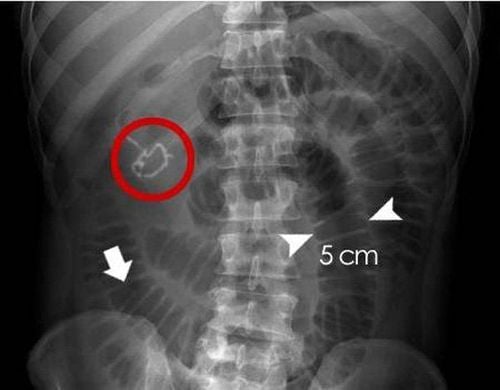
Therefore, the clinician should order an unprepared abdominal radiograph before the patient's initial suspicion of bowel obstruction. Those subjects were hospitalized because of symptoms of intermittent abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, abdominal distension and constipation, and bowel obstruction.
The following unprepared abdominal radiographs assist in the diagnosis of intestinal obstruction:
Dilated loops of bowel in the presence of a typical slightly water level In the supine position, an estimate of bowel distension is made is based on the width of the bowel loops. In the lateral position (horizontal X-ray), the water level is more clearly seen Distal atelectasis image Distal small bowel obstruction must cause dilation of more than 2.5cm in bowel diameter to be visible Visible on radiographs Abdominal distention with gas The "string of pearls" sign when observed on the intestinal wall contains partial fluid and air bubbles accumulate along the surface
3. Features of X-ray film of small bowel obstruction
Imaging means with abdominal radiographs are only 50-60% sensitive for small bowel obstruction. In most cases, abdominal radiographs will have features suggestive of small bowel obstruction as follows:Dilated loops of small bowel proximal to obstruction Dilated loops of bowel centered in the midline The diameter of the loop of bowel is dilated from 2.5 to 3 cm, which is essential for the diagnosis of intestinal obstruction Observed with small bowel loops, running around the bowel circumference Having a slightly central water level In the same bowel circle but the water level is slightly different at different heights (height difference from more than 2 cm). Stomach bloating. However, if radiographs of small bowel obstruction do not show this finding, the diagnosis cannot be ruled out. This is because in small bowel obstruction, which is a high bowel obstruction, the abdomen may be less likely to develop gas than in a low bowel obstruction such as a colonic obstruction, because the gas is released through the patient's vomiting reflex or has been cleared. pressure during nasogastric tube insertion.
The "string of pearls" sign: small air sacs in the intestinal wall when the lumen of the small intestine is filled with fluid
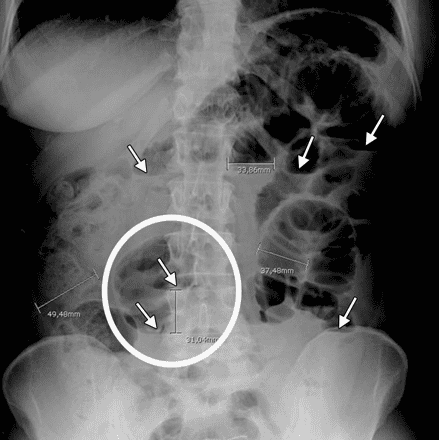
4. Characteristics of X-ray film of colonic obstruction
Belonging to the low bowel obstruction category, the radiograph of colonic occlusion, although having some features of general intestinal obstruction, also has some differences:Distended bowel loops, secondary to gas-producing organisms in the bowel. stool Collapse of the colon in the distal segment, because usually there is little or no fluid in the large intestine because water has been reabsorbed mostly in the small intestine. However, the appearance of this sign on radiographs depends on the duration of obstruction and the function of the ileal valve. Absence of air or no air in the rectal balloon If the bowel obstruction is late in the colonic framework, radiographs can detect ischemic colon complications and intestinal perforation due to necrosis such as: gas in the intestinal wall, gas portal vein or free air in the abdomen (pneumoperitoneum).
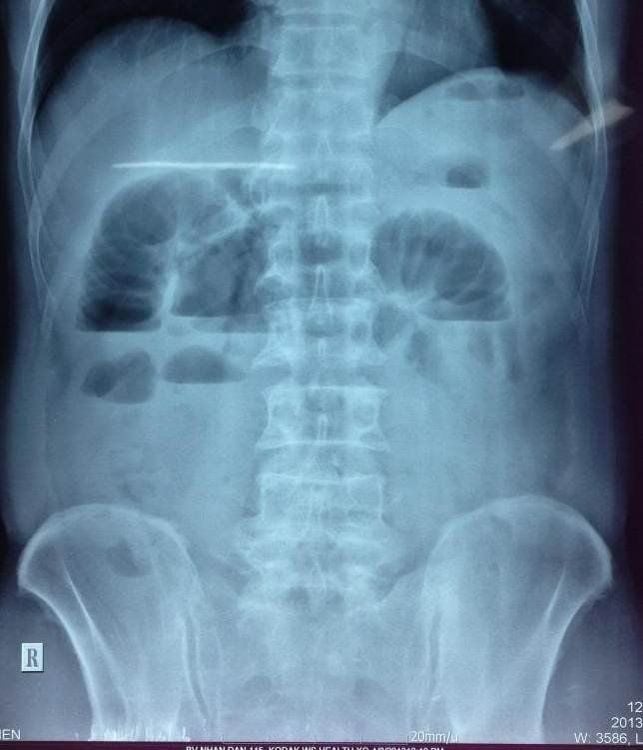
5. Limitations of abdominal radiographs in bowel obstruction
Because it is a rudimentary imaging tool and is simply performed in the initial approach of patients with suspected bowel obstruction, abdominal radiographs have some limitations, with limited sensitivity and specificity. may be worse than computed tomography.Accordingly, the location and etiology of bowel obstruction often cannot be clearly identified on radiographs, especially in the area between the proximal dilated segment and the non-dilated distal loop of the small intestine. Furthermore, radiographs may also present difficulties in distinguishing small bowel loops from large bowel loops in some cases.
In addition, when more specialized investigations are needed, conventional X-ray images on unprepared abdominal films are of poor value in helping to differentiate organic bowel obstruction from paralytic ileus.
In summary, to confirm the diagnosis of bowel obstruction quickly, your doctor may recommend an abdominal X-ray. However, some obstructions in the intestinal tract cannot be seen using conventional X-rays. Therefore, radiographs of intestinal obstruction are only useful towards the suspected diagnosis. When further investigation or surgical intervention is needed, the role of computed tomography will be the next step after radiography.
In order to improve the examination and treatment process, Vinmec International General Hospital has applied gastrointestinal X-ray technique in examination and diagnosis of many diseases. X-ray technique at Vinmec is carried out methodically and according to standard procedures by a team of highly skilled doctors and nurses, modern machinery system, thus giving accurate results, making a significant contribution to the determine disease and disease stage.
For consultation and examination at Vinmec medical system nationwide, please register at the Website for the best service.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.