This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Dr., Doctor Tran Nhu Tu and Master, Doctor Le Thi Hong Vu - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Danang International Hospital.
Due to its fast, safe, low cost, and relatively high accuracy, abdominal ultrasound is the first-line imaging technique used when patients suspect acute appendicitis.
1. What is acute appendicitis?
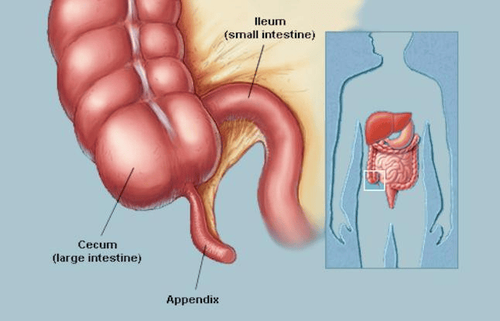
The appendix is a finger-shaped structure of the digestive tract that attaches to the first segment of the large intestine (the cecum). The appendix has an immune function, helping B lymphocytes to mature and make antibodies. However, the role of the appendix is not too important, the body does not increase the risk of infection or immunosuppression if the appendix is removed.Acute appendicitis is a very common abdominal surgical emergency. The disease can occur at any age, from the elderly to children. There are many causes of appendicitis, such as: fecal stones, lymphoid enlargement due to infection, parasites, gallstones, appendiceal tumor, etc. , reduce the perfusion of appendiceal tissues, creating conditions for bacteria to grow, causing inflammation, and the appendiceal tissues are damaged and die. If not detected and treated in time, the appendix can burst, bacteria can be released into the abdomen, causing dangerous complications, which can be life-threatening such as localized or generalized peritonitis. , appendiceal abscess,...
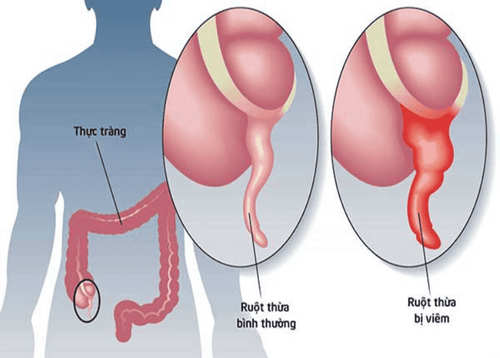
Hình ảnh viêm ruột thừa cấp
2. Why is it necessary to perform abdominal ultrasound in the diagnosis of acute appendicitis?
When suffering from acute appendicitis, the patient will have symptoms such as dull abdominal pain above the navel then moving to the lower right corner of the abdomen, low fever (high fever from 39oC when appendix has complications), digestive disorders. such as anorexia, diarrhea, nausea,... If only based on clinical symptoms and blood and biochemical tests, the disease will be easily confused with many other gastrointestinal, urinary, and genitourinary tract diseases. symptoms similar to right renal colic, right adnexitis, cecal ileitis, right ovarian tumor torsion, right ovarian cyst hemorrhage, right ectopic pregnancy, acute cholecystitis,. ..According to studies, if only based on clinical manifestations and biochemical and hematological tests, the rate of laparotomy but without appendix ranges from 16-47%. If imaging facilities are used, this rate drops to 6-7%. Thus, the use of imaging tools is extremely important in the definitive diagnosis of acute appendicitis. The imaging tools that can be used in the diagnosis of acute appendicitis are abdominal ultrasound, computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI),... in which abdominal ultrasound is the First-line method, safe, highly sensitive, easy to implement, widely used in medical facilities.
Siêu âm ổ bụng giúp chẩn đoán viêm ruột thừa cấp
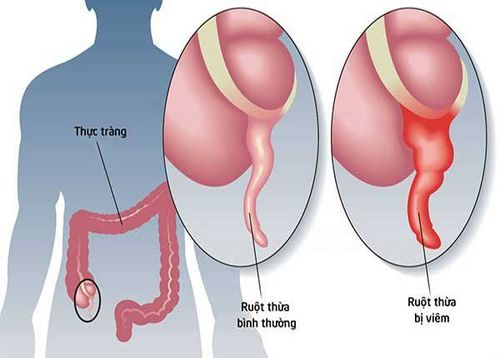
When the appendix is inflamed, the ultrasound image is a tubular structure filled with fluid, similar to the intestines, incompressible, thicker than normal, larger than 6-7mm in diameter. Using color doppler and power doppler ultrasound to detect the wall of a tubular structure showing hyperperfusion. Using a transducer, it is possible to distinguish a movable loop from a fixed inflamed appendix. Diseases of gastrointestinal, genitourinary and urinary tract origin with appendicitis-like manifestations can be detected on ultrasonography of the right lower quadrant of the abdomen.
3. What are the advantages of ultrasound for acute appendicitis?
Although not as accurate as CT or MRI, in diagnosing acute appendicitis, ultrasound has many advantages, such as:Compared to computed tomography (CT), ultrasonography of acute appendicitis has the advantage of not having radioactive ions, which is very important for women, children and adolescents, who often suffer from acute appendicitis and are also vulnerable to radiation. Patients do not need to drink sedation, perform general anesthesia, drink or inject contrast when performing ultrasound, so they will not experience side effects, risks, allergies when taking or injecting drugs. this. Ultrasound has the advantage of being able to examine the appendix in different positions, surveying it dynamically and easily repeating it many times without radiation, without harm to the body, and at a lower cost than CT or MRI. Although the sensitivity is not as high as that of CT, given the prevalence of the disease and if the abdominal ultrasound technique is performed by a skilled clinician, the sensitivity and specificity in the diagnosis of acute appendicitis in children are not as high. are 98.5% and 98.2% respectively. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) method avoids radiation exposure for patients, but the cost is high, the implementation time is long, the delay in diagnosis and treatment will increase the risk of appendicitis appearing. complications. Ultrasound has the advantage of being fast, low-cost, and helping patients to be diagnosed and treated promptly.
Phương pháp chụp cộng hưởng từ (MRI)
Therefore, according to current assessment, ultrasound is the first-line procedure in patients with suspected appendicitis. Clinical manifestations consistent with the ultrasound findings of appendicitis are sufficient to proceed with surgery. Only when the patient has clinical symptoms and the ultrasound images are not clear, if the physician is still in doubt, other techniques should be performed. In normal, non-pregnant adult patients, the next indicated technique after ultrasound is computed tomography (CT), in pregnant women, the technique used is magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). ).
Dr. Tran Nhu Tu with over 20 years of experience, of which 3 years as Deputy Head of the Paraclinical Department - Hoa Vang Hospital, 16 years as Deputy Head of Imaging Department at Da Nang Hospital, 4 years as Head of Department Diagnostic imaging at Da Nang Obstetrics - Pediatrics Hospital; Dr. Tu makes accurate diagnoses, minimizes errors based on acquired images, and is ready to serve patients 24/24 in emergencies and emergencies.
Dr. Tu has participated in domestic and foreign training courses such as: Master of Radiology, Research Fellow in Diagnostic Imaging at Hanoi Medical University, Diagnostic Imaging at CHU Reims - France, Electricity interventional radiology at Winterthur hospital - Switzerland, interventional radiology at Singapore General Hospital... before being the head of the Department of Diagnostic Imaging at Vinmec Danang Hospital as it is now.
Master doctor Le Thi Hong Vu has good English, has participated in many short-term and continuous training courses on annual diagnostic imaging. The doctor has more than 7 years of experience as a doctor in the field of diagnostic imaging, especially ultrasound.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.
SEE MORE
Treatment of appendicitis requires surgery or not? Handbook of things to know about acute appendicitis Children with fever, abdominal pain, vomiting: Beware of appendicitis