This is an automatically translated article.
Appendicitis is a common acute surgical disease. If not diagnosed and treated promptly, it can have many consequences, even life-threatening.
1. What is appendicitis?
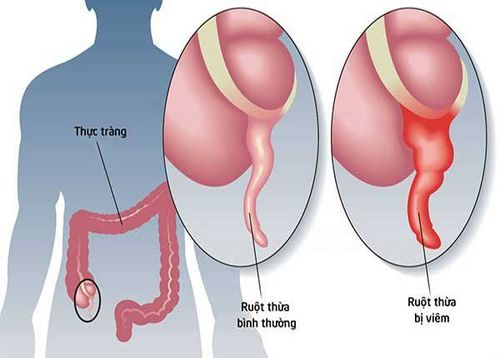
The appendix is a small, narrow piece of intestine located at the end of the small intestine, about a few centimeters long and attached to the cecum (first part of the large intestine). The wall of the appendix contains lymphoid tissue, which is the part of the immune system responsible for producing antibodies.
Appendicitis sometimes has an unknown cause and is often thought to be caused by a blockage at the opening between the appendix and the cecum causing mucus or stool to harden causing the obstruction. This phenomenon is also known as "fecal stones". In some cases, it is possible that the lymphatic tissue of the appendix becomes swollen and obstructs the appendix. The bacteria then proliferate inside, forming pus and swelling, creating pressure that causes abdominal pain. Our body will respond to this phenomenon by attacking to destroy the bacteria. That is the inflammatory response. If the inflammation is high and the infection spreads, the pressure can increase, causing the appendix to burst, causing the infection to spill out and spread in the abdomen. This complication is called peritonitis and can lead to death from sepsis.
Appendicitis can happen to anyone with some of the following risk factors:
Age: Appendicitis usually occurs in young people aged 15 to 30 years; Gender: More male than female; Family history: People with a family history of appendicitis have a higher risk of developing this condition; There is some research that suggests that a low-fiber diet may also increase the risk of appendicitis.
2. Symptoms of appendicitis
Functional symptoms of appendicitis:
Abdominal pain: Starting with severe abdominal pain around the navel or stomach area, after a few hours it will spread to the lower right (right iliac fossa) . The pain is usually dull, rarely severe or sharp pain. When coughing or changing positions makes the pain worse; Loss of appetite: This is a sign of appendicitis that you need to look out for. The reason is that when the appendix is inflamed, it inhibits the production of appetite hormones, making the patient have no interest in eating; Fever: The digital temperature ranges from 38-39 degrees, in the case of high fever, it may have passed the complication stage; There are also some other symptoms such as vomiting and nausea, diarrhea, bloating. Physical symptoms of appendicitis:
In the early stages, the patient's abdomen is still moving with breathing. However, when there are complications, there will be poor mobility; Patients usually have a mild fever, rarely higher than 90 degrees, and a normal or slightly elevated pulse. When there are excessive changes that may already be a complication or should be considered for another diagnosis; Clinically, because there is no definite location, the pain point of appendicitis will not be fixed for all cases, the most common pain point is in the right iliac fossa when the appendix is in an anterior position. Pain is most often felt at or near the Mc Burney pain point; The sign of decompression (Blumberg's sign) is often evident in the right iliac fossa. If the patient is positive for this sign, there is irritation of the peritoneum; Rovsing sign: The patient will experience pain in the right iliac fossa when pressing on the left iliac fossa, which also indicates peritoneal irritation.
Viêm ruột thừa cấp khiến người bệnh gặp những cơn đau tại vùng hố chậu phải
3. Diseases of appendicitis
The clinical symptoms of acute appendicitis vary according to the location of the appendix and the clinical individual. There are several clinical forms such as:
Pediatric Appendicitis: Diagnosis of appendicitis in children is somewhat more difficult than in adults because it is difficult to exploit the symptoms in children accurately. Doing so leads to delays and higher rates of peritonitis. In cases where the disease progresses rapidly to perforation and the characteristics in children have underdeveloped omentum, it is difficult to localize the ruptured appendix, so there are often serious complications. Appendicitis in pregnant women: This is an emergency that requires urgent surgery during pregnancy. Symptoms of appendicitis can be confused with the usual discomforts of pregnancy. During pregnancy, the appendix can move to another location, making diagnosis more difficult. Delayed diagnosis and treatment can lead to appendicitis rupture that is fatal to the mother and fetus. Appendicitis in the elderly: Symptoms of appendicitis in the elderly may be more severe or worse than usual such as low fever, no obvious abdominal wall reaction, white blood cells are not elevated.
4. Subclinical diagnosis of appendicitis
4.1. A complete blood count test To check for signs of infection, your doctor will order a complete blood count test. Patients with appendicitis usually have a mildly elevated WBC count from 10000-18000 with moderate polymorphonuclear leukocytosis of 75-78%. Changes in the blood count are useful in diagnosing acute appendicitis in children, whereas in elderly or immunocompromised patients, white blood cells may not be elevated.
4.2. Abdominal ultrasound This test checks for appendicitis and helps your doctor determine the cause of your symptoms, such as abscesses or fecal stones. The ultrasound image will show the inflamed appendix as a stretchy structure, unable to collapse, without peristalsis, dilated inside, increased echogenicity in the inner margin, and less echogenic edema on the outer border. . In addition, ultrasound also helps in differential diagnosis with gynecological diseases, cecal diverticulitis,..
4.3. Plain abdominal radiograph has low diagnostic value in acute appendicitis
4.4. Pregnancy test There are some cases where an ectopic pregnancy is confused with appendicitis because the pain location and symptoms are relatively similar. An ectopic pregnancy is caused by a fertilized egg implanting itself in the fallopian tube instead of the uterus. This is also an urgent medical emergency, otherwise it will affect the patient's life.
For the differential diagnosis of an ectopic pregnancy, you can perform a blood or urine test to confirm. Alternatively, transvaginal ultrasound can be used to determine the location where a fertilized egg has implanted.
5. Complications of appendicitis
5.1. This is the most serious consequence of appendicitis if it is not detected and treated promptly. The cause is an inflamed appendix that ruptures and leaks fluid into the abdomen, causing an infection.
5.2. Appendiceal Abscess The appendix is surrounded by omentum and bowel loops, if the appendix becomes inflamed and ruptures but has not yet spilled into the abdomen thanks to these protective structures, it will form an appendiceal abscess. The patient has symptoms of high fever and pain when pressing on the right iliac fossa, elevated white blood cells. If not treated promptly, the abscess can burst into the abdomen, causing peritonitis complications as above.
5.3. Appendiceal clumps When the patient has good resistance, the bowel loops and well-functioning mesentery will become a mass of appendiceal clumps enclosing the appendicitis mass. The patient will have improved clinical symptoms, less pain, and the right iliac fossa will have a firm, non-moving mass with mild pain. Blood tests show that the white blood cells are not as high as the two cases above or may be normal. The patient with appendicitis was not indicated for emergency surgery but was monitored and indicated for elective surgery in the following 2 months.
Viêm phúc mạc toàn bộ là một trong các biến của bệnh viêm ruột thừa
6. How is appendicitis treated?
Treatment of appendicitis usually involves surgical removal of the inflamed appendix. Patients will be given antibiotics before surgery to prevent infection.
Drainage before surgery: If the appendix has ruptured and an abscess has formed around the appendix, the doctor will perform a procedure to place a drain through the abdominal wall to bring the pus out. After a few weeks when the infection is under control, surgery can be performed. Surgery to remove the appendix: Depending on the severity of the disease, the patient will have open surgery or laparoscopic surgery. The doctor will make a small incision on the abdomen 5-10cm long to open the abdomen (for open surgery) or several small incisions on the abdomen (laparoscopic surgery). During laparoscopic surgery, the doctor will put into the patient's abdomen a camera to observe and specialized equipment to remove the appendix. This method has the advantage of helping patients recover faster after surgery, with less pain and less scarring. However, in cases where the patient has ruptured appendix and the infection has spread to the outside or has an abscess, open surgery is required to remove the appendix and clear the abdominal cavity.
7. How long will the body recover after surgery?
The recovery time after appendicitis surgery will depend on many factors such as the overall health of the body, whether there are complications or not and the surgical method performed.
If treated laparoscopically, you can leave the hospital a few days after surgery. However, if the surgery is open, the wound will be large and require a longer hospital stay and recovery time.
After surgery, it is necessary to keep the wound clean and dry. When washing your own wound at home, you need to wash your hands thoroughly before touching and follow the doctor's instructions. Do not wear clothing that is too tight to irritate the wound. Keep the area out of the sun to avoid dark scars. The wound will heal gradually in about 4 to 6 weeks and the scar will fade over the next 12 months.
After surgery, the patient will feel more tired than usual, so it is necessary to rest properly.
8. Prevention of appendicitis
Appendicitis can have many different causes, so there is no way to completely prevent it. However, we can limit the risk of developing this disease with a high-fiber diet. There are many studies that have shown that in countries with a high-fiber diet there is a lower incidence of disease.
Increase the intake of foods high in fiber including: Fruits, vegetables, legumes, oatmeal, wheat and other grains. Adding enough water to the body every day helps the intestines be cleaned better, circulates food effectively and limits the blockages that cause appendicitis. Follow a healthy diet, avoid unhealthy foods. Appendicitis is an acute condition and can be life-threatening if not treated promptly. Therefore, when seeing a patient with suspected appendicitis, it is necessary to immediately bring to a medical facility for examination and appropriate treatment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference sources: webmd.com, healthline.com