This is an automatically translated article.
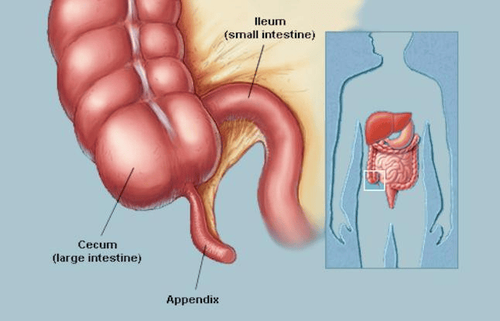
The article was professionally consulted by Dr. Ngo Viet Thang - Gastroenterologist, Department of General Surgery, Vinmec Ha Long International Hospital.The appendix is a small, finger-shaped tube-shaped structure that arises from the first part of the large intestine called the cecum. Appendicitis is when the appendix becomes infected and inflamed. When the appendix becomes inflamed, it swells and in some cases ruptures. Anyone can get appendicitis, but ages 10 to 30 are most common. The standard treatment is resection of the inflamed appendix.
1. Symptoms of appendicitis
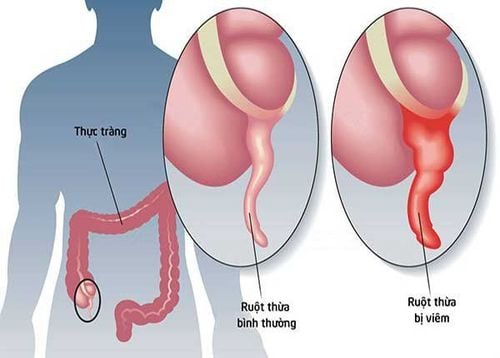
Abdominal pain is the first and always present symptom. Abdominal pain in appendicitis due to inflammation typically has the following characteristics: The pain begins around the umbilicus or epigastrium accompanied by nausea or vomiting. After about 2-12 hours, the pain gradually increases and moves down to the right iliac fossa region, continuous dull pain, increases when coughing or when changing position,... This is the most reliable symptom to recognize. 1 case of acute appendicitis.Depending on the location of the appendix, the patient will feel very differently about the location of abdominal pain in appendicitis: hip pain (postcecal appendix), hypogastric pain (pelvic appendix) , pain under the right flank (appendix under the liver), ...
In addition, the nature of abdominal pain in appendicitis depends on many other factors: Medication being used, patient's tolerance , the patient's resistance, the patient's medical condition.
In new-onset cases, or in atypical cases, it is easy to confuse with other diseases. For example, at the beginning of the pain, the patient may have stomach pain with nausea, which many people mistake for gastritis, or the pain in the lower abdomen with frequent loose stools, mistaken for enteritis or dysentery, back pain in appendicitis. After the cecum is mistaken for a kidney-urinary pathology, right upper quadrant pain in the appendix below the liver is mistaken for a gallstone disease, ... This can make you subjective and easy to miss. Therefore, when you have symptoms of abdominal pain, you should be fully examined and evaluated with a specialist to avoid missing the disease. You should avoid self-medication and self-administration because this will obscure the symptoms, leading to a late diagnosis, which can lead to complications of appendicitis.
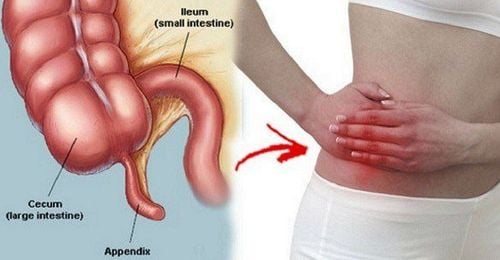
Vị trí đau của viêm ruột thừa khá đa dạng, nhưng thường bắt đầu từ phần dưới bên phải của bụng.
Anorexia Anorexia, though not constant, is nearly always present in acute appendicitis, so much so that many experts consider the absence of this symptom to warrant reconsidering the diagnosis of appendicitis.
Nausea, vomiting Nausea, vomiting are signs of acute appendicitis. It always comes after abdominal pain. However, this symptom can deceive patients as well as doctors with other diseases such as gastritis or food poisoning.
Diarrhea Diarrhea is only seen in some special cases such as appendicitis of the pelvis or appendix with complications that have ruptured, creating inflammation in the sac of Douglas (lowest area of the abdomen when standing) causing irritation defecation
It should be noted that there are many diseases of the abdomen and pelvis that mimic appendicitis. For that reason, in order to diagnose appendicitis, a patient should be fully evaluated with laboratory tests, imaging studies, and a thorough examination by a gastroenterologist.
Trắc nghiệm: Làm thế nào để bảo vệ lá gan khỏe mạnh?
Làm test trắc nghiệm kiểm tra hiểu biết về gan có thể giúp bạn nhận thức rõ vai trò quan trọng của gan, từ đó có các biện pháp bảo vệ gan để phòng ngừa bệnh tật.2. Causes of appendicitis
Appendicitis is caused by obstruction of the lumen of the appendix for many reasons, with fecal stones being the most common cause. This obstruction increases intra-appendiceal pressure due to bacterial growth and increased secretion of the inner lining of the appendix. As a result, the appendix becomes inflamed, swollen, and filled with pus. If not treated promptly and properly, the appendix can gangrene, or rupture, causing widespread inflammation in the abdomen called peritonitis.3. Complications of appendicitis
Appendicitis, if not diagnosed and treated promptly, can lead to complications such as:Perforated appendix: When the appendix ruptures, bacteria will spread throughout the abdomen and can be dangerous to the body. live. Surgery to remove the appendix and clean the abdomen is required immediately. Intra-abdominal abscess: When the appendix is left for a long time or improperly treated, the abdominal organs such as the great omentum, small intestine,... come to cover the pus-filled cavity, forming a localized pus-filled pocket. in the abdomen is called an abscess. Treatment for this case is to prioritize drainage under the guidance of ultrasound in combination with antibiotic treatment according to the protocol. Then an appointment for appendectomy after 6 months.
Viêm ruột thừa có nhiều biến chứng nguy hiểm.
Diagnosis is based on:
Physical examination: including a thorough history, careful abdominal examination is necessary for a definitive diagnosis. Blood tests: Helps assess inflammation and infection to aid in diagnosis and treatment. Imaging: Patients can have X-ray, ultrasound, or CT scan of the abdomen to help confirm the diagnosis of appendicitis as well as differentiate it from other causes of pain other than appendicitis. .
4. Treatment of appendicitis: Does appendicitis require surgery or not?
Until now, the standard treatment for appendicitis was surgical removal of the inflamed appendix. This is the classic treatment and is accepted by all clinicians worldwide ever since. From 2004 to now, there have been a number of studies on non-operative treatment of uncomplicated appendicitis with antibiotics.Results from these studies show that the success rate of antibiotic therapy for uncomplicated appendicitis is 90%, 10% are unresponsive and have complications requiring surgical intervention. Follow-up of patients who successfully treated for uncomplicated appendicitis within 1 year had 30% recurrent appendicitis.
So treatment of uncomplicated appendicitis with antibiotics cannot completely treat appendicitis and the disease will have a very high risk of recurrence in a short time. Therefore, the gold standard of treatment for appendicitis remains surgical resection of the inflamed appendix. This is an effective method to help definitively treat appendicitis.
Currently, emergency non-operative treatment is considered in special cases when the appendix ruptures and creates an abscess. Treatment for this case is to prioritize drainage under the guidance of ultrasound in combination with antibiotic treatment according to the protocol. Then an appointment for appendectomy after 6 months.
For patients with appendicitis with indications for surgery, before surgery, the patient must be completely fasted from food and drink, given enough intravenous fluids, and corrected for electrolyte disturbances if any, before being transferred to the room. Surgery must allow the patient to urinate to avoid the need for a urinary catheter. Patients will be given prophylactic antibiotics before surgery for uncomplicated appendicitis to prevent wound infection and intra-abdominal infection. Complicated appendicitis cases will be treated with antibiotics according to the regimen.
Inflammatory appendectomy can be performed in 2 ways: laparoscopic or open surgery. However, laparoscopic surgery is the method of first choice for appendectomy in all cases unless there are contraindications to laparoscopic surgery such as patients with severe cardiovascular or respiratory disease unable to tolerate surgery. laparoscopic surgery, or patients with a history of previous laparotomy,... Laparoscopic surgery is most commonly used in the treatment of appendicitis because of its many outstanding advantages. These include faster recovery time, less pain, very small incisions and no scars, especially good for people with obesity and the elderly. In cases where the appendix has ruptured and the infection is inside the abdomen, or the patient with ruptured abscess cannot perform well and safely with laparoscopic surgery, it will be converted to open surgery. It's not a failure with laparoscopic surgery but for safety reasons.
So the answer to the question: “Can appendicitis go away on its own? “is that surgery is needed to treat it.
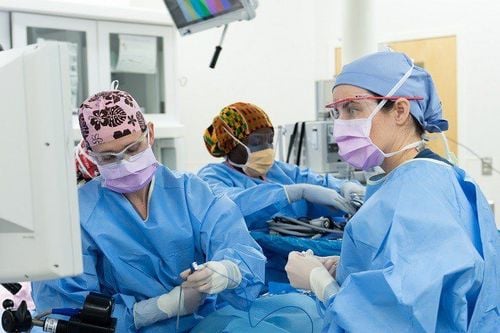
Nội soi là phương pháp phổ biến trong điều trị viêm ruột thừa vì có nhiều ưu điểm vượt trội.
5. Lifestyle and home treatment after surgery
Recovery time after surgery depends on the method of laparoscopic or open surgery, appendicitis has complications or not. For uncomplicated appendicitis cases, patients recover faster with laparoscopic surgery. Usually, you can be discharged from the hospital 1-2 days after surgery, and quickly return to daily activities after 2-3 days. For cases of appendicitis with complications, the recovery time may be longer. To help the recovery process faster:Avoid vigorous activity: If the patient has laparoscopic surgery, the period of abstinence will be from 3 to 5 days. If the patient undergoes open surgery, the period of abstinence will be from 10 to 14 days. Always ask your doctor about your health and when you can resume normal activities. Need help with a cough: Place a pillow on top of your stomach, and press down when coughing, laughing, or moving to relieve the pain. Contact your doctor if pain relievers don't work: Pain increases the body's inertia and slows down the healing process. If you still have pain while taking pain relievers, call your doctor. Get up and work out when you're ready: Start slowly and gradually increase the amount of activity. Let's start with a short walk. Sleep when you're tired: During your recovery, you may feel more sleepy than usual. This is normal, take a break if you think it's necessary. Consider returning to school or working with your doctor: You can return to normal work if you feel well enough. Children can return to school within 1 week.

Tập thể dục nhẹ nhàng và chế độ dinh dưỡng tốt sẽ giúp bệnh nhân bình phục nhanh hơn.
6. Medications that can be prescribed
Certain pain relievers can help relieve pain after surgery. However, there are a few options to help manage pain better, for example:Activities such as listening to music, talking with friends will make you forget the pain, especially effective for The subject is children. Visualize images, like closing your eyes and thinking about a place you love. Conclusion: Appendicitis is the most common surgical emergency. Surgery is a mandatory method to definitively treat and prevent dangerous complications of appendicitis. And of course, post-operative therapy is an important part of the patient's recovery.
Department of Endoscopy - Gastroenterology is one of the key specialties at Vinmec International General Hospital. For timely examination, advice and treatment of digestive diseases, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide or register online on the website for service.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.