This article was professionally consulted by a Gastroenterologist, Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital and Master, Doctor Vu Tan Phuc - Gastroenterologist - Department of Examination & Internal Medicine, Vinmec Phu Quoc International General Hospital.
Acid reflux causing shortness of breath not only brings discomfort in daily life, but it is also a warning sign that the condition of the disease is at risk of worsening.
1. What is gastroesophageal reflux?
Gastroesophageal reflux (GERD), also known as gastric acid reflux, is a phenomenon in which gastric juice, pepsin or food refluxes into the esophagus. This disease occurs when the stomach increases acid secretion, causing excess acid in gastric juice, leading to a tendency to reflux into the esophagus.
The main causes of this disease are due to esophageal sphincter failure, diaphragmatic hernia, increased pressure in the abdomen or food stagnation in the stomach.
In addition, some factors that increase the risk of gastroesophageal reflux disease are: obesity, pregnancy, smoking, asthma, improper diet, diabetes, and excessive alcohol consumption.
2. What are the symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux?
The most common symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux include:
- Burning, heartburn: Belching is an early sign of gastroesophageal reflux. Acid reflux is often accompanied by heartburn, belching, leaving a sour feeling in the mouth;
- Pain in the epigastric region: The feeling of pain and pressure in the epigastric region occurs due to acid reflux affecting the nerve endings;
- Excessive salivation;
- Bitter mouth: Gastroesophageal reflux is often accompanied by the phenomenon of increased bile secretion, causing a bitter mouth;
Asthma, difficulty swallowing, cough, hoarseness.

3. Does gastroesophageal reflux cause shortness of breath?
Usually, when having difficulty breathing, the first cause thought of is respiratory problems, but this is also a common symptom in patients with gastroesophageal reflux. Or more precisely, shortness of breath is one of the serious symptoms of gastric reflux. More than 45% of patients with gastric reflux will feel shortness of breath.
According to the most recent studies, shortness of breath when suffering from gastric reflux is due to excess acid in the stomach, affecting the breathing tube. Normally, when there is excess acid, the body will automatically adjust to produce base to neutralize it. But in patients with the disease, the amount of acid produced is too much, causing the base to not be enough to neutralize, leading to excess. This amount of acid causes the esophagus to dilate, not close tightly, thereby leading to shortness of breath.
The mechanisms leading to shortness of breath include:
- Excess acid in gastric juice flows into the esophagus, causing irritation of the esophageal mucosa. Here, pressure appears on the trachea. At this time, the patient will begin to have difficulty breathing;
- When food is pulled up to the pharynx, the airway is also blocked, causing difficulty breathing and chest tightness;
- The amount of acid refluxed into the esophagus not only causes blockage, but also causes inflammation. At that time, the nervous system in the esophageal mucosa will affect the muscles in the chest, thereby causing a reflex contraction, directly compressing the airway, causing difficulty breathing;
- Stomach acid enters the esophagus, potentially penetrating the lungs, causing swelling of the airway. This phenomenon mainly occurs when the patient is sleeping.
4. Is gastric reflux causing difficulty breathing dangerous?
As mentioned above, when the patient experiences difficulty breathing, it is also a warning sign that the patient's condition is getting worse. At this time, dangerous complications can arise at any time if the patient is not treated promptly:
- Respiratory problems: When acid refluxes into the stomach too many times, it will cause ulcers. Not only does it affect the airways, it also causes phenomena such as pharyngitis, laryngitis, bronchitis, bronchitis, pneumonia. These problems are very difficult to treat and have very complicated developments.
- Barrett's esophagus: This is a disorder that often occurs when gastric juice refluxes into the esophagus for a long time, causing the esophagus to change color. About 5% of subjects with Barrett's esophagus will have a very high risk of esophageal cancer, 30 to 125 times higher than normal people.
- Esophageal stricture: The process of acid reflux into the esophagus repeatedly will cause irreversible damage to the esophagus, forming scar tissue, narrowing the esophagus.
- Esophageal ulcer: This is the most common complication of gastroesophageal reflux disease. When the mucosal layers are eroded, bacteria will attack and cause an inflammatory reaction, activating inflammation. If not intervened promptly, ulcers will form.
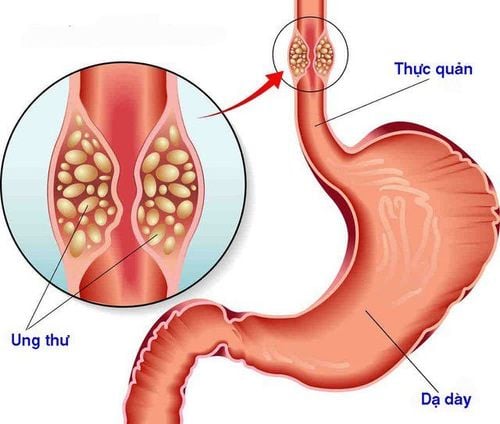
- Esophageal cancer: although this complication is not common, there is still a risk of it occurring. When a patient has this complication, the condition will worsen very quickly, even causing death if not treated promptly.
5. How to overcome gastroesophageal reflux leading to shortness of breath
Shortness of breath for a long time is a very bad and dangerous feeling. Therefore, patients need to see a doctor regularly to detect and treat the disease, avoiding difficulty breathing before going to the doctor. Thus, there is a risk of serious complications arising.
In addition, patients can note the following advice:
- Change your lifestyle to a healthy state: Patients need to change their eating habits, should not eat too much before going to bed or eat too much in one meal. Should exercise regularly, give up bad habits, no alcohol, tobacco, reduce stress. Along with that, add good foods such as yogurt, bread, apples, ginger, oats, and green vegetables. Knowing what to eat with gastric reflux will help patients reduce uncomfortable symptoms.
- Using Western medicine for treatment: The groups of drugs recommended by doctors include: H2 blockers (Cimetidin, famotidine), proton pump inhibitors (lansoprazole, omeprazole...), drugs that increase the tone of the lower esophageal sphincter (metoclopramide, domperidone), drugs that protect the gastric mucosa (alginate, dimetico, misoprostol...).
- Use natural herbs: 9 recommended herbs include Roman Chamomile, Licorice, Atractylodes, CurmaNano, Coptis, Magnolia officinalis, Pinellia, Atractylodes Rhizome, Ginger.

To arrange an appointment, please call … or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.