This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Cao Thanh Tam - Cardiologist - Cardiovascular Center - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Atherosclerosis is a condition in which the walls of the arteries become hardened and plaque builds up in the lumen, causing narrowing or blockage of the arteries. These plaques are created from the deposition of cholesterol, fats, calcium, fibrin and other deposits...
Complications of the disease are often heart attacks, strokes, peripheral blood diseases. .. Atherosclerosis is a very dangerous disease if not treated promptly. However, to prevent this disease, it is advisable to have regular health check-ups and maintain a healthy lifestyle.
1. What is atherosclerosis?
Arteriosclerosis occurs when the blood vessels that carry oxygen and nutrients from the heart to the rest of the body (arteries) become thick and stiff. Sometimes restricting blood flow to organs and tissues. Healthy arteries are soft and elastic, but over time, the vessel walls in the arteries can harden, a condition commonly known as arteriosclerosis.
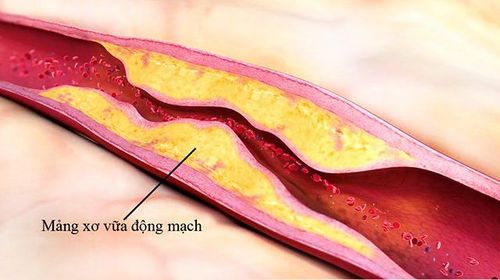
Atherosclerosis is a specific type of hardening of the arteries, but the terms are sometimes used interchangeably. Atherosclerosis refers to the buildup of fat, cholesterol, and other substances in and on artery walls (plaque), which can restrict blood flow.
Plaques can break off, causing blood clots. Although atherosclerosis is often thought of as a heart problem, it can affect arteries anywhere in the body. Atherosclerosis is preventable and treatable.
2. Symptoms of atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis progresses silently. Patients will often have no symptoms of the disease until the artery is so narrowed or blocked that it cannot supply enough blood to organs and tissues. Sometimes a blood clot can completely block blood flow, or even break off and cause a heart attack or stroke.Symptoms of moderate to severe atherosclerosis depend on the arteries affected. For example:
● If you have atherosclerosis in your coronary arteries, you may have symptoms such as chest pain or pressure (angina).
If you have atherosclerosis in the arteries leading to the brain, you may have signs and symptoms such as sudden numbness or weakness in your arms or legs, difficulty speaking or slurring, temporary loss of vision in one eye or sagging facial muscles. These signals are a transient ischemic attack (TIA), which, if left untreated, can progress to a stroke.
If you have atherosclerosis in the arteries in your arms and legs, you may have symptoms of peripheral artery disease, such as leg pain when walking (claudication).

3. Causes of atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is a slowly progressive disease that can begin as early as childhood. Although the exact cause is unknown, atherosclerosis can begin with damage to the inner layer of the artery wall. Atherosclerosis can be caused by:● High blood pressure
● High cholesterol
● High triglycerides - a type of fat (lipid) in the blood
Smoking and other sources of tobacco
● Insulin resistance, obesity obesity or diabetes
Inflammation from conditions such as arthritis, lupus, or an infection or unexplained inflammation
Once the inner wall of an artery is damaged, blood cells and other substances normally clot at the site of injury and accumulate in the inner lining of the artery wall. Over time, plaques formed from cholesterol and other cellular products also accumulate at the site of injury and harden and narrow the lumen of the arteries. Organs and tissues associated with blocked arteries will not receive enough blood to function properly.
Plus, the smooth lining of plaque can rupture, spilling cholesterol and other substances into the bloodstream. This can cause a blood clot, which can block blood flow to a specific part of the body, such as occurs when blocked blood flow to the heart causes a heart attack. A blood clot can also travel to other parts of the body, blocking flow to another organ.
4. Risk factors for atherosclerosis
Hardening of the arteries occurs over time. Besides aging, factors that increase the risk of atherosclerosis include:
High blood pressure High cholesterol Diabetes Obesity Smoking and other tobacco use Family history of cardiovascular disease Lack of exercise An unhealthy diet.

5. Complications of atherosclerosis
Complications of atherosclerosis depend on the blocked arteries. For example:
Coronary artery disease: When atherosclerosis narrows the coronary arteries, the heart will cause coronary artery disease and can cause chest pain (angina), heart attack or heart failure, arrhythmia.
Carotid artery disease: When atherosclerosis narrows the arteries near the brain, carotid artery disease can develop and can cause a transient ischemic attack (TIA) or stroke.
Peripheral artery disease: When atherosclerosis narrows the arteries in the arms or legs, there can be reduced perfusion in the arms and legs known as peripheral artery disease. This can make the body less sensitive to heat and cold, increasing the risk of burns or frostbite. In rare cases, poor circulation in the hands or feet can cause tissue death (necrosis).
Aneurysms: Atherosclerosis can also cause aneurysms, a serious complication that can occur anywhere in the body. An aneurysm is a bulge in the wall of an artery. Most people with an aneurysm have no symptoms. Pain and stinging in the area of the aneurysm can occur and is a medical emergency. If an aneurysm ruptures, you may face life-threatening internal bleeding. Although this is usually an unexpected, catastrophic event, the leak can be slow. If the blood clot in the aneurysm dislodges, it can block the artery at a distant point.
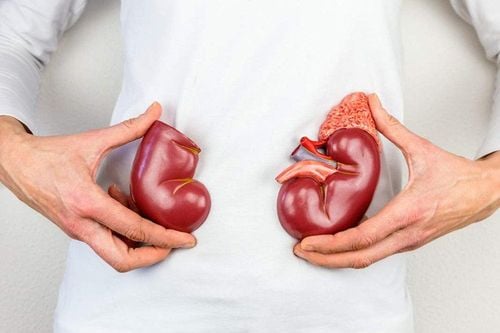
Chronic kidney disease: Atherosclerosis can cause the arteries that carry blood to your kidneys to narrow, preventing blood from getting oxygen and nutrients to the host kidney tissue. Over time, this can affect kidney function.
6. Prevention of atherosclerosis
The healthy lifestyle changes recommended to treat atherosclerosis also help prevent the disease. Includes:
Quit smoking Eat healthy foods Exercise regularly Maintain a healthy weight Just making the above changes one step at a time can manage the disease in the long run.
If you have unusual symptoms, you should be examined and consulted with a specialist.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: mayoclinic.org; healthline.com; webmd.com.