This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Master, Doctor La Thi Thuy - Interventional Cardiologist - Cardiovascular Center - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital
Arteriosclerosis and atherosclerosis are sometimes used to mean the same thing, but there is actually a difference between the two terms. For more information, readers can refer to the following article.
1. What is the definition of arteriosclerosis and atherosclerosis?
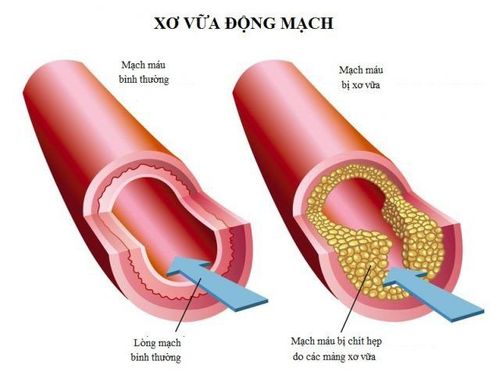
Arteries are blood vessels that carry oxygen and nutrients from the heart to the rest of the body. Arteriosclerosis is a condition in which blood vessels become thickened and stiff – sometimes restricting blood flow to the body's organs and tissues. The arterial system will essentially have good elasticity and stretch, but over time the structures in the arteries become stiffer, a condition commonly referred to as arteriosclerosis.
Atherosclerosis is a special form of hardening of the arteries. Atherosclerosis is the accumulation of fat, cholesterol and other substances on the artery walls. The accumulation process will form atheroma. Atherosclerotic plaques on the artery walls can narrow the artery walls, impeding blood flow. Atheroma can also peel off, forming a blood clot.
Although atherosclerosis is often thought of as a heart problem, it can affect arteries anywhere in your body. Atherosclerosis is treatable. Healthy and active lifestyle habits can help prevent atherosclerosis.
2. Symptoms
Mild atherosclerosis often does not have any symptoms. Atherosclerosis usually won't cause symptoms until an artery is so narrowed or blocked that it can't supply enough blood to organs and tissues. Sometimes a blood clot completely blocks the flow of blood, or even breaks off and can cause a heart attack or stroke.
Symptoms of moderate to severe atherosclerosis depend on which arteries are affected. For example:
In the case of atheroma appearing in the coronary artery (heart artery), you may have symptoms of chest pain or tightness (angina) In the case of plaque appearing in the artery blood supply to the brain (carotid or basilar artery), you may have signs and symptoms such as sudden onset of numbness or weakness in an arm or leg, difficulty speaking, slurred speech, temporary loss of vision one eye or loss of movement of the facial muscles (facial drooping). These signs signal a transient ischemic attack (TIA). If left untreated, it can progress to a stroke. In the case of atherosclerosis in the arteries in the arms and legs, you may have signs or symptoms of peripheral artery disease, such as pain in your legs when walking (claudication) or a drop in blood pressure in your legs. affected limb. In case of atherosclerotic plaque in the renal artery, it can lead to high blood pressure or kidney failure. If you think you have diseases related to plaque, you should be examined by a specialist. You should also be on the lookout for any new symptoms that result from a lack of blood supply, such as chest pain, leg pain, or numbness.
An early diagnosis and treatment can stop the progression of plaque and prevent a heart attack, stroke, or other emergency.
Xơ vữa động mạch có thể tăng nguy cơ đột quỵ
3. Causes
Atherosclerosis is a slowly progressive disease process that can begin in childhood. Although the exact cause is unknown, atherosclerotic plaque can occur as a result of destruction or damage to the inner cell layer of the artery. Destruction can be caused by:
High blood pressure High cholesterol High levels of triglycerides, a form of fat (lipids) in the blood Smoking and other sources from tobacco Insulin resistance, obesity or diabetes Unexplained infection either from arthritis, lupus, psoriasis, or an intestinal infection. Once the inner lining of the artery wall is damaged, blood cells and other substances often gather at the site of injury and accumulate in the inner lining of the artery. Over time, fatty deposits (plaques) made up of cholesterol and other cellular products that also accumulate at the site of injury become hard, causing the vessel lumen to narrow. When that happens, the organs and tissues fed by the blocked artery don't get enough blood to function properly. Eventually, the fatty deposits can break off and enter the bloodstream.
In addition, the outermost lining of plaque can rupture, releasing cholesterol and other substances into the bloodstream. This can lead to the formation of a blood clot, which can block blood flow to a part of the body, such as occurs when blood flow to the heart is blocked, causing a heart attack. The clot can also travel to other parts of your body, blocking blood flow to another organ.
4. Risk factors
Hardening of the arteries occurs over time. Besides aging, factors that increase the risk of atherosclerosis include:
High blood pressure High cholesterol Elevated CRP levels, an inflammatory marker of diabetes Diabetes Obesity Sleep apnea Smoking and use other forms of tobacco Family history of early cardiovascular disease No exercise Unhealthy diet

Bệnh nhân cao huyết áp sẽ có nguy cơ bị xơ vữa động mạch
5. Complications
Complications of atherosclerosis depend on which arteries are blocked. Example:
Coronary artery: angina, acute myocardial infarction or heart failure Carotid artery: TIA (transient ischemic attack) or stroke Peripheral vascular disease: insensitive to heat and cold, increases the risk of burns or frostbite. In rare cases, poor circulation in your arms or legs can cause tissue death (gangrene). Aneurysms: a serious complication that can occur anywhere on your body. An aneurysm is a bulge in the wall of your artery. Symptoms are dangerous if the patient has pain and pulsating pain at the site of aneurysms. If the aneurysm ruptures, the patient can face life-threatening internal bleeding. Although this is usually a sudden, catastrophic complication, oozing blood loss can still occur. If the blood clot in the aneurysm ruptures, it can block the distal artery. Chronic kidney disease: prevents blood from reaching the kidneys. Over time, this can affect kidney function, making it impossible for waste to be eliminated from the body.
6. How to prevent
Some ways to prevent atherosclerosis are as follows:
Quit smoking Eat good, safe foods Exercise regularly Maintain a suitable weight Check and maintain stable blood pressure Check and maintain stable cholesterol, blood sugar Just remember to make changes one step at a time and keep in mind what lifestyle changes can stay with you in the long run.
Vinmec Cardiology Department has always received much praise and satisfaction from domestic and international customers, being pioneers in successfully applying the world's most advanced techniques in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. .
A team of highly qualified and experienced specialists: qualified doctors from Master's to Professor's and Doctor's degrees, reputable in medical treatment, surgery, interventional cardiac catheterization. Intensive training at home & abroad. In particular, Prof. TS.BS Vo Thanh Nhan - Cardiology Director of Vinmec Central Park was recognized as the first and only expert in Vietnam to be awarded the "Proctor" certificate on TAVI. State-of-the-art equipment, comparable to major hospitals in the world: The most modern operating room in the world; The most modern silent magnetic resonance imaging machine in Southeast Asia; The CT machine has a super-fast scanning speed of only 0.275s/round without the use of drugs to lower the heart rate; 16-sequence PET/CT and SPECT/CT systems help to detect early damage to cardiovascular organs even when there are no symptoms of the disease. Applying the most advanced advanced cardiovascular techniques in the world in treatment: Painless open heart surgery; Percutaneous aortic intervention without general anesthesia; Treatment of mitral regurgitation through the catheter has a success rate of 95%; Ventricular-assisted artificial heart transplantation for patients with end-stage heart failure prolongs quality of life beyond 7 years. Cooperating with leading cardiovascular centers in Vietnam and the world such as: National Heart Institute, Cardiology Department of Hanoi Medical University, University of Paris Descartes - Georges Pompidou Hospital (France), University of Pennsylvania (France), University of Pennsylvania United States)... with the aim of updating the most modern cardiovascular treatments in the world. To register for examination and treatment with leading doctors of the Cardiology Department at Vinmec International General Hospital, please click the "Contact Us" button on the website, or register online HERE.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.