This article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Lê Thị Minh Hương - Emergency Resuscitation Doctor - Department of Emergency Resuscitation - Vinmec Nha Trang International Hospital. The doctor has over 6 years of experience in examining and treating internal medicine diseases, emergency, and resuscitation.
As we know, there are many different types of medications. Some are taken orally, while others are administered via injection or infusion. Injections are further divided into intravenous, intramuscular, subcutaneous, and intradermal injections. The buttocks are a common site for administering intramuscular injections.
1. Why butt injections?
First, we need to understand that injecting medication involves using a syringe and needle to inject a solution dissolved in oil, water, or a suspension into the body through intravenous, intramuscular, subcutaneous, intradermal routes, or into serous cavities, the spinal canal, etc. Administering medication via injection usually has a faster effect compared to oral administration.
Intramuscular injection involves injecting medication into the patient’s muscle, where it will take effect faster than subcutaneous injection. This is because muscles are well-supplied with blood and are always contracting, which allows for quicker absorption of the medication compared to subcutaneous tissue. Additionally, the sensation of pain in muscles is less sensitive than in subcutaneous tissue, making it possible to inject strong irritants such as Streptomycin, Penicillin, Emetin, Quinine, therapeutic serums, or even blood into the muscle.
Intramuscular injections can be administered in the arm, thigh, or buttocks. So why do we often see buttock injections more frequently? This is because the gluteal muscle is large with a significant muscle mass, and it is also a safe area with few nerves and large blood vessels passing through. Therefore, doctors and nurses often choose the buttocks for intramuscular injections.
2. Indications and contraindications for buttock injections
2.1. Indications for buttock injections
Buttock injections, like intramuscular injections in general, can be used for many different isotonic solutions such as
- Oil-based medications that dissolve slowly and can cause pain.
- Ete, Quinin.
- Colloidal solutions, mercury salts, silver salts, various antibiotics, hormones, etc., which dissolve slowly and cause pain, thus requiring intramuscular injection.
- In theory, all medications that can be injected into subcutaneous tissue can also be injected into muscles, except for Caffeine.
- Some medications should not or cannot be injected intravenously but need a faster effect than subcutaneous injection, so they should be injected intramuscularly.
- Medications that are irritating when injected subcutaneously and are absorbed slowly can be injected intramuscularly.
- In cases where the skin is cracked, subcutaneous injection is not indicated.
2.2. Contraindications for Buttock Injections
Intramuscular injections in general, and buttock injections in particular, are contraindicated for drugs that cause tissue necrosis, such as calcium chloride, ouabain, etc.
3. Technique for Buttock Injections
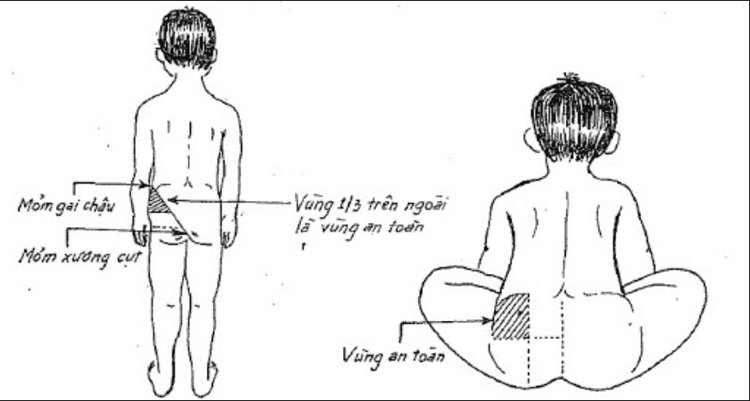
3.1. Identifying the Injection Site
The gluteal region has large blood vessels and the sciatic nerve running through it, so it is crucial to accurately identify the injection site to avoid hitting the sciatic nerve. However, don’t worry, as the gluteal area is quite large, making it easy to determine the correct injection site.
The buttock area is defined by four lines:
Above: Defined by the line connecting the two iliac crests.
Below: The gluteal fold.
Inside: The intergluteal cleft.
Outside: The outer edge of the buttock.
There are two methods to identify the injection site in the buttock:
- Method 1:
Divide one buttock into four equal parts. The injection site is in the upper outer quarter.
Injecting into the lower outer part will hit the hip joint.
Injecting into the inner parts will hit the sciatic nerve and blood vessels.
- Method 2:
Draw a straight line from the anterior superior iliac spine to the coccyx, divide this line into three equal parts. The injection site is in the upper outer third of this line.
Because this area has a thick muscle layer and lacks the sciatic nerve and large blood vessels.
Patient’s position for buttock injection is one of the following two positions:
- The patient lies face down.
- The patient sits on a chair, facing the back of the chair, with their arms hugging the back of the chair, exposing the buttock for the injection.
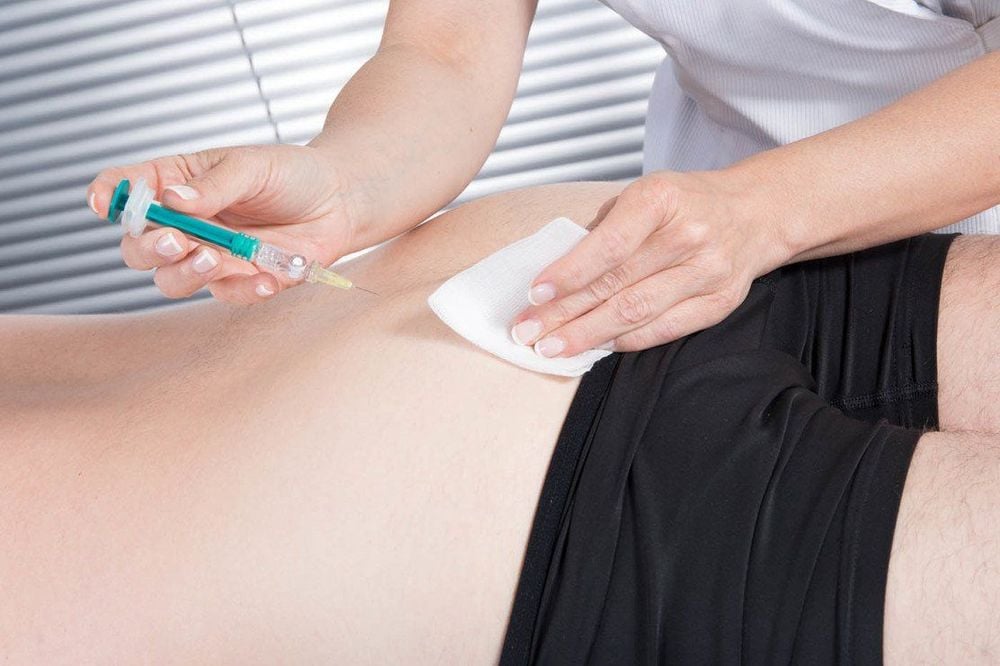
3.2. Buttock Injection Technique
There are two ways
Single-Step Gluteal Injection
- Expose the gluteal area and identify the injection site using one of the prescribed methods.
- Disinfect the injection site with iodine alcohol, followed by 70% alcohol.
- The nurse disinfects their hands with 70% alcohol.
- Left hand: Use the thumb and index finger to stretch the skin at the intended injection site.
- Right hand: Hold the syringe (already filled with the medication and equipped with a needle). Use the pinky finger to support the needle hub, the thumb, middle, and ring fingers to hold the syringe body, and the index finger to support the plunger. Insert the needle perpendicularly into the site swiftly and deeply, but avoid fully inserting the needle hub—leave a gap of about 0.5–1 cm. If the needle contacts bone, withdraw slightly.
- Release the skin with the left hand and gently pull back the plunger to check for blood. If there is no blood, slowly inject the medication. Monitor the patient's facial expression during the injection.
- After the medication has been fully administered, use the left hand to stretch the skin again as before. Gently and swiftly withdraw the needle vertically with the right hand.
Disinfect the injection site again using a cotton ball soaked in alcohol.
Two-Step Buttock Injection Technique
- Expose the gluteal area and identify the injection site using one of the prescribed methods.
- Disinfect the injection site with iodine alcohol, followed by 70% alcohol.
- The nurse disinfects their hands with 70% alcohol.
Step 1:
The left hand stretches the skin at the injection site with the thumb and index finger. The right hand: Hold the needle hub firmly with the thumb and index finger. At this stage, the needle is not yet attached to the syringe.
Curl the remaining three fingers of the right hand and gently tap the patient’s buttock a few times to distract their focus. Then, swiftly insert the needle perpendicularly at a 90° angle into the identified injection site. As before, avoid fully inserting the needle hub; leave a slight gap.
Step 2:
Once the needle is inserted, attach the syringe (pre-filled with medication and air expelled) to the needle hub.Pull back the plunger slightly to check for blood. If no blood appears, slowly inject the medication while monitoring the patient. If blood appears, withdraw the needle and choose a new injection site.
After administering the full dose, use the thumb and index finger of the left hand to stretch the skin again. Swiftly remove the needle vertically with the right hand.
Disinfect the injection site again using a cotton ball soaked in alcohol.
4. Complications of Buttock Injections
Administering intramuscular injections in the gluteal region can lead to several complications, including:
- Needle bending or breaking
- Injury to the sciatic nerve
- Embolism
- Infectious abscess or sterile abscess
- Tissue necrosis
- Anaphylactic shock: This is the most dangerous complication.
Gluteal injections are a commonly used method of intramuscular administration due to the ease of identifying the injection site, which is the large gluteal muscle. However, negligence or a lack of understanding regarding proper site identification and injection techniques can still result in severe complications for the patient.
Vinmec International Hospital is renowned for not only its high standards of medical expertise, with a team of skilled doctors and state-of-the-art technology, but also for its comprehensive, professional consultation and treatment services. The hospital ensures a safe, sterile, and professional environment for patient care.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.