Some contraceptive methods are better than others and have fewer side effects. You may wonder whether to choose a brand-name or generic option, whether to use a hormonal or non-hormonal method, or whether you should opt for an injection, implant, or pill. No contraceptive method is without side effects, and these side effects vary depending on the individual, so you should choose the contraceptive method that best suits you.
1. Which contraceptive method has the fewest side effects or the most suitable method?
Some contraceptive methods are better than others and have fewer side effects. You might wonder whether to choose a brand-name or generic option. Should you opt for a hormonal or non-hormonal method? Should you get an injection, use an implant, or take a pill?
As you also know, each woman’s physiology is different – it’s hard to assess which contraceptive option has the most side effects for a particular woman. That’s why it’s important to try different methods and change them to find the one that has the fewest side effects and is most suitable for you.
Therefore, the answer to the question of which contraceptive method has the fewest side effects depends on the individual. Instead, you should be advised on the effectiveness of the contraceptive method and whether it is suitable for you.
If your current contraceptive method isn’t suitable for you or if you're considering trying a different method, you can consider the methods below that doctors consider having the most side effects.
2. What is the effectiveness of current contraceptive methods?
The list below shows the effectiveness of each of the 15 methods and the frequency with which they need to be used or considered (frequency of use).
The effectiveness of each method is calculated by determining how many women get pregnant if 100 women use this method for one year.
For example, if a specific contraceptive method is 99% effective, then 1 woman out of every 100 using it will get pregnant within a year.
Some methods listed below, such as pills, include the phrase "if used correctly." This is because individuals using these methods must use them every time they have sex, or remember to take or apply them daily, weekly, or monthly.
If not used correctly, they will not be as effective as desired.
Contraceptive methods with more than 99% effectiveness:
- Contraceptive implants (up to 3 years)
- Hormonal intrauterine devices (IUDs) (up to 5 years)
- Non-hormonal IUDs (up to 5 to 10 years)
- Female sterilization (permanent)
- Male sterilization or vasectomy (permanent)
Contraceptive methods with more than 99% effectiveness if always used correctly, but often less than 95% effective with typical use:
- Birth control injections (renewed every 8 or 12 weeks, depending on the type)
- Combined oral contraceptives (taken daily for 3 weeks each month)
- Progestogen-only pills (taken daily)
- Birth control patches (changed weekly for 3 weeks each month)
- Vaginal rings (replaced every month)
Contraceptive methods with 99% effectiveness if used according to instructions:
- Natural family planning methods (tracking body temperature and cervical mucus daily)
Contraceptive methods with 98% effectiveness if used correctly:
- Male condoms (every time you have sex)
Contraceptive methods with 95% effectiveness if used correctly:
- Female condoms (every time you have sex)
Contraceptive methods with 92-96% effectiveness if used correctly:
- Diaphragms or caps with spermicide (every time you have sex)
3. The Most Common Side Effects of Some Birth Control Methods
Depo-Provera, an injectable birth control, has been reported to have the most side effects. Oral contraceptives are reported to have the second-highest number of side effects, while the IUD and NuvaRing have the least reported side effects.
3.1. Depo-Provera
Depo-Provera is an injectable birth control that you receive every three months. This form of contraception contains the hormone progestin, which typically prevents ovulation by stopping the ovaries from releasing eggs. Progestin also thickens cervical mucus, preventing sperm from reaching the egg.
Studies report that patients using Depo-Provera in clinics experience the highest number of side effects compared to any other birth control method. Doctors say these side effects can be very uncomfortable and have caused many women to stop using this form of birth control. The most common side effects include:
- Hair loss
- Weight gain
- Acne
- Mood swings
- Bloating
- Increased appetite
- Injection site reactions
- Numbness or tingling
- Decreased libido
- Joint pain
- Decreased breast size
3.2. Oral Contraceptives
Oral contraceptives, or "pills," have been around for many decades. These are pills taken once a day, or nearly every day, on a regular cycle to prevent pregnancy. There are many different brands of oral contraceptives, and each contains varying dosages of estrogen and progesterone (two types of female sex hormones).
Oral contraceptives are reported to have the second-highest number and severity of side effects after Depo-Provera. Some of the more common side effects include:
- Breast tenderness
- Nausea
- Mood changes
- Headaches
- Vomiting
- Bloating
- Diarrhea
- Weight changes
- Spotting or bleeding between periods
- Changes in menstrual flow
- Vaginal discharge
3.3. IUD (Intrauterine Device)
No form of contraception is without side effects, but the IUD (intrauterine device) seems to have the least. This is why it is a popular choice among women of all ages.
An IUD is a small device that a doctor places in your uterus to prevent pregnancy. It is meant to be a long-term form of contraception but can be removed at any time.There are two types of IUDs: copper (non-hormonal) and hormonal. Both have their own side effects, but generally, they have fewer side effects compared to other forms of contraception.
Studies show that nine out of ten women prefer the IUD, although one in ten may experience acne, depression, and request its removal. Some of the reported side effects by women include:
- Pain during IUD insertion
- Heavier menstrual cycles (for women using a copper IUD)
- Abdominal cramping
- Spotting between periods
- Irregular periods
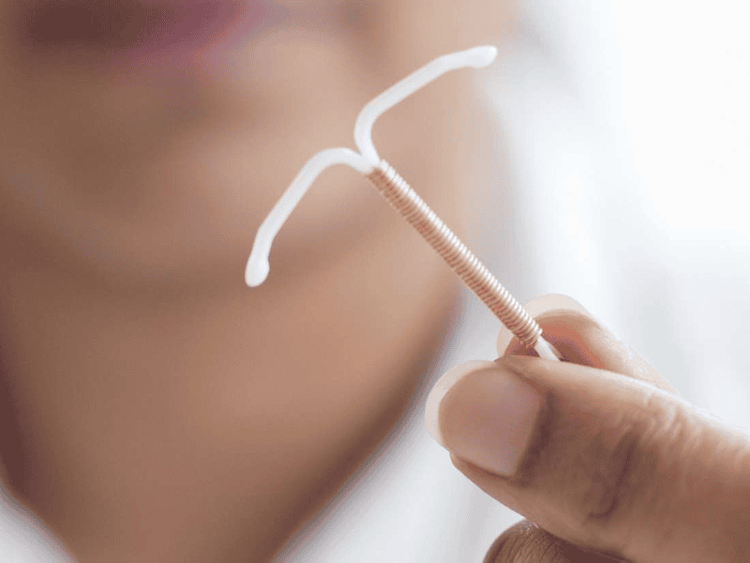

3.4. NuvaRing
NuvaRing is a combination of low-dose estrogen and progesterone and has very few side effects. You insert the ring into your vagina for 21 days, then remove it for 7 days to allow for menstruation.
NuvaRing is well tolerated by many women, as long as the patient is comfortable with inserting it into the vagina.
Although it is usually well tolerated, some side effects may occur, including:
- Spotting or breakthrough bleeding
- Headaches
- Mood swings
- Decreased libido
- Breast tenderness
- Vaginal infections, irritation, or increased vaginal discharge
4. How to Choose the Most Suitable Birth Control Method
4.1. Can You Make Birth Control Part of Your Daily Routine?
If you are an organized person with a consistent daily routine, you have many birth control options. This is because you are less likely to forget to take a pill or reapply a patch.
You might prefer a method that you only need to use during sex, such as male or female condoms, or you might prefer a method that you need to use daily, such as the pill.
Alternatively, you might want to consider methods like patches, injections, or implants, which don’t require daily or per-intercourse usage.
The list below shows how often each method needs to be used, replaced, or performed.
- Methods to use every time you have sex: Male and female condoms, diaphragm or cap
- Methods to use daily: Oral pills (combination or progestogen-only), with some types having a 21-day regimen and a week off every month
- Methods to replace weekly: Birth control patch
- Methods to replace monthly: Vaginal ring
- Methods to replace every 2-3 months: Birth control injection
- Methods to replace every 3 years: Implant
- Methods to replace every 5 to 10 years: IUD or hormonal IUS
4.2. Do You Want a Method That Doesn’t Require You to Remember Every Day?
Not all birth control methods need to be taken daily or every time you have sex. Some methods you don’t need to think about for months or even years.
These methods are inserted by a healthcare professional into your uterus (IUD or IUS) or arm (implant):
- IUD (can last 5-10 years, depending on the type)
- IUS (can last 3-5 years, depending on the type)
- Implant (can last 3 years)
You can also get birth control shots in one of two ways: a muscle injection into the buttocks or a subcutaneous injection in the thigh or abdomen. This is done every 8 or 12 weeks, depending on the type. A healthcare professional can administer the injection, or you may be taught how to inject yourself.
4.3. Are You Comfortable Inserting Birth Control Into Your Vagina?
If you are a woman, are you comfortable inserting birth control into your vagina?
If so, you might want to consider using:
- Vaginal ring
- Female condom
- Diaphragm or cap
If you want a more long-term method and are comfortable with a healthcare professional inserting birth control into your uterus via the vagina, you may consider using:
- Non-hormonal IUD
- Hormonal IUD
4.4. Do You Mind if Your Period Changes?
Some birth control methods can affect your menstrual cycle. Some may make your periods lighter or less frequent. Other methods may make your periods heavier or more irregular.
The methods that may make your periods lighter include:
- Oral pills (combination or progestogen-only)
- Birth control patch
- Birth control injection
- IUS
- Vaginal ring
4.5. Do You Smoke?
Smokers can use most forms of birth control. However, if you are a smoker and over 35, some methods of contraception (such as combined oral pills, patches, or vaginal rings) may not be suitable for you.
If you are over 35 and smoke, you might want to consider these methods of contraception:
- IUD
- Implant
- Birth control injection
- Progestogen-only pill
4.6. Are You Overweight?
Your weight will not affect most types of birth control, and most methods won’t cause weight gain.
However, birth control injections are associated with a slight weight gain if used for 2 years or longer.
4.7. What If You Can’t Use Hormonal Birth Control?
Some methods of birth control work by using hormones similar to the ones women produce naturally: estrogen and progestogen.
Hormonal birth control is not suitable for some women, such as those with conditions like breast cancer.
Not all birth control methods use hormones. Some work in other ways, including:
- IUD
- Male or female condoms
- Diaphragm or cap
4.8. What If You Can’t Use Birth Control Containing Estrogen?
Birth control containing estrogen is not suitable for women who are:
- Over 35 and smoke
- Very overweight
- On certain medications
- Have certain medical conditions, such as circulation issues or migraines
If you cannot use birth control containing estrogen, there are many other options, including:
- IUD
- IUS
- Implant
- Birth control injection
- Progestogen-only pill
4.9. Do You Plan to Have Children Soon?
All forms of birth control can be stopped if you want to have children. You can become pregnant right after stopping birth control.
A woman’s fertility usually returns to normal within the first month after stopping combined pills, the vaginal ring, or the patch.
If you want your fertility to return quickly after stopping birth control, consider the following methods:
- Implant
- IUS
- IUD
- Progestogen-only pill
- Diaphragm or cap
- Male or female condoms
Your fertility may take longer to return to normal after stopping birth control shots.
Most women’s fertility will return after a few months, but it may take up to a year for fertility to return to normal.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: insider.com, nhs.uk, plannedparenthood.org