This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Dang Xuan Cuong - Emergency Resuscitation Department - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.The rectum is the last part of the large intestine before the anus, which is susceptible to diseases. In order to diagnose and detect the disease in time, rectal endoscopy cannot be ignored. It is a simple, quick and accurate way to detect the disease.
1. What is rectal endoscopy?
Rectum, the last part of the large intestine, about 20 to 30 cm long. The rectum is the bridge between the anus and the colon. The main function of the rectum is to store waste, along with bowel movements, to expel stool through the anus. Due to many reasons, the rectum often suffers from diseases such as ulcers, rectal polyps, rectal cancer, ...
Rectal endoscopy is a procedure to insert a flexible endoscope through the anus into the rectum to detection of lesions, diagnosis and treatment of diseases. This method is highly appreciated in detecting rectal pathology thanks to its accuracy and simple procedure.
There are two types of rectal endoscopy:
1.1 Hard tube rectal endoscopy The endoscope is a straight, rigid tube with a diameter of 1 - 2cm and a length of 25 - 50 cm depending on age and physical condition with a camera, light light and a manual inflator to expand the lumen. Before, when there was no flexible endoscope, rigid endoscope was commonly used. However, rigid bronchoscopy has some disadvantages such as difficulty in performing polypectomy because the hard tube when opening the glass cover to put the instrument into the tube will open, causing air to escape, the bowel lumen collapses, making it difficult for the endoscope to observe the damage. sorry, can't record.
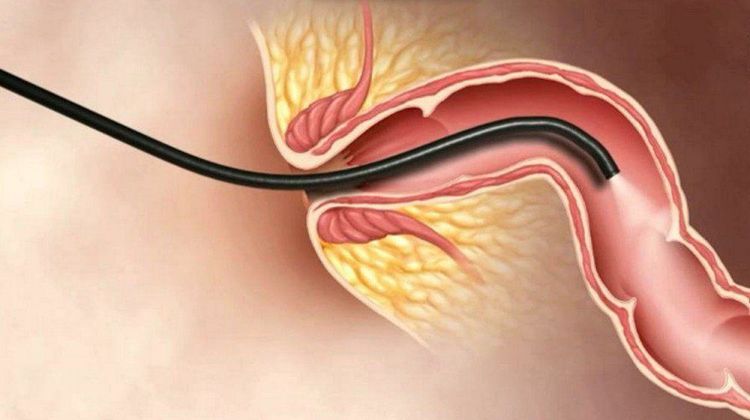
Nội soi trực tràng
1.2 Flexible rectal endoscopy The flexible bronchoscope has a small diameter of about 1.3cm, a length of about 65cm, the end of the scope is covered with smooth plastic, and the body of the flexible bronchoscope can be bent according to the bends of the intestine. Flexible bronchoscopy causes less pain, the patient only needs to lie on the left side, the doctor stands straight behind the patient's back, controls the bronchoscope and observes the image on the screen, if necessary can take or record images. when looking.
In addition, the endoscopic treatment technique is made easy thanks to the biopsy channel and the closed system of suction pump by machine. The advantage of flexible endoscopy is that the small, flexible design makes the patient comfortable, the flexible tube is made of specialized materials, so it does not hurt the rectal mucosa. The image of the endoscope will be displayed directly on the screen.
2. When is a colonoscopy needed?
Rectal endoscopy is indicated for the diagnosis of hemorrhoids, anal fistula, tumor pathology, cancer, rectal ulceration, polyps,... and also to monitor the disease progression of cases that have undergone regional surgery. anterior anorectal. Especially valuable in screening, early diagnosis of rectal cancer helps patients receive early treatment, prolonging the survival time for cancer patients.
When there are the following signs, it is necessary to perform a rectaloscopy to diagnose the disease
Abdominal pain. Abdominal pain below the navel, abdominal pain in the left iliac fossa, abdominal pain with contractions of bowel movements. Bloody mucus stools, bright red blood need to be endoscopically to detect the disease early. Bowel disorders: Abnormal bowel movements with diarrhea and constipation also require endoscopy. Stool disorder, difficulty defecation. Anal itching. Anal pain. When there is a burning pain in the anus, the anal canal or outside the anal canal has an abnormal discharge. Because these are very likely to be manifestations of dangerous diseases in the rectum. Indications for rectal cancer screening for people with a family history of colon cancer Cases of anemia of unknown cause Test positive for erythrocytes in stool Check for abnormalities on X-ray -Oposcopy to periodically check patients with polyps, colorectal cancer Diverticulosis Diseases of the colon Inflammatory bowel diseases Patients with ulcerative colitis bleeding, Crohn's, cancer, polyps, anal fistula, anal fissures subjects need endoscopy to monitor In addition, during endoscopy, the doctor can biopsy the lesion to look for malignant cells
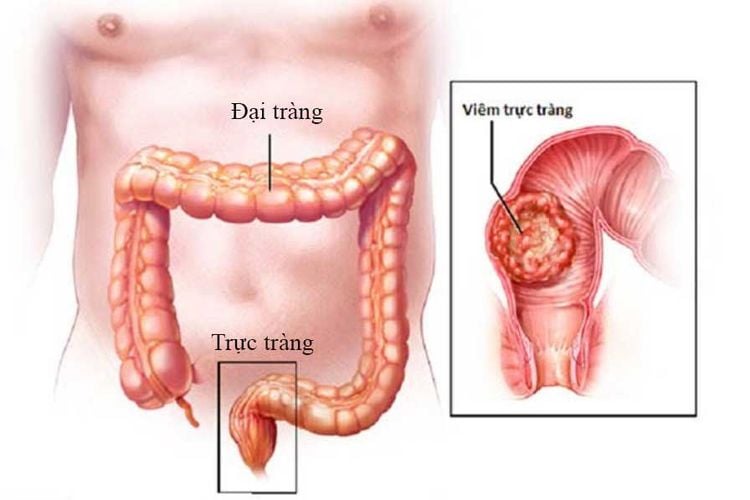
Người bệnh bị viêm trực tràng cần nội soi trực tràng
Rectal endoscopy to treat diseases such as:
Removal of polyps Removal of foreign bodies Hemostasis Dilatation of hemorrhoids Treatment of hemorrhoids Rectal endoscopy to monitor disease:
After polypectomy Severe dysplasia
3. Contraindications of rectal endoscopy
There are no absolute contraindications. Be careful when the patient is old and weak, the patient is pregnant or the case of severe acute inflammation prevents the bronchoscope from being inserted. Do not do rectal endoscopy if the patient does not agree or when the patient has: acute heart failure, arrhythmia, peritonitis, coagulopathy...
Người bệnh suy tim, loạn nhịp tim không nên nội soi trực tràng
4. What should the patient monitor after endoscopy?
Patients during and after endoscopy are continuously monitored on monitoring of hemodynamic status and oxygen saturation If the patient is on pre-anesthetic, monitor until fully awake Monitor pulse and blood pressure symptoms such as: abdominal pain, abdominal distension, nausea, Patients undergoing the procedure should be monitored for alarm symptoms: Abdominal pain, bloody diarrhea Although colonoscopy is a fairly common and common technique, used in the diagnosis of colorectal diseases, but this is still an intervention method and has certain risks. Therefore, consider choosing to perform at a reputable medical facility.
In particular, Vinmec Times City International General Hospital has been equipped with the most modern gastrointestinal endoscopy system of Olympus with the method of endoscopy with narrow light frequency band (NBI). This is a breakthrough method in screening and diagnosing cancers of the gastrointestinal tract (esophagus, stomach, duodenum and colon and rectum) at early and very early stages. NBI endoscopic images have high resolution and contrast, making it easy for doctors to detect small changes in color, morphology of cancerous and precancerous lesions that are difficult to detect with conventional endoscopy. .
Master. Doctor Dang Xuan Cuong received intensive training in the field of emergency resuscitation and poison control at Hanoi Medical University and Bach Mai Hospital. With 14 years of experience in the field of emergency resuscitation and poison control, Dr. Cuong Nguyen is the Head of Functional Exploration Department, Deputy Head of Emergency Resuscitation Department, .. at Hai Duong Provincial General Hospital and participates in lectures. Clinical teaching at Hai Duong University of Medical Technology. Currently, Dr. Cuong is an Emergency Resuscitation doctor at Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.