This is an automatically translated article.
Article written by Master, Doctor Mai Vien Phuong - Gastroenterologist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.
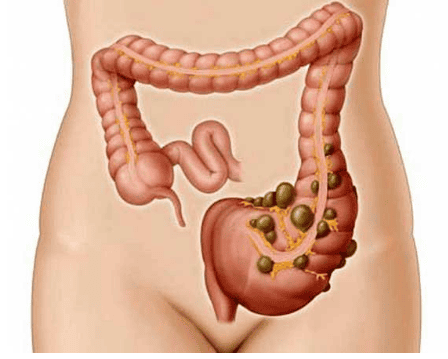
Colon is divided into 3 main parts: cecum, colon and rectum. The small intestine communicates with the large intestine at the cecum and colon boundary. Between the small intestine and the large intestine, there is an ileocecal valve that keeps the contents of the large intestine from flowing back into the small intestine. Colectomy is the removal of part or all of the damaged colon and rectum, possibly with removal of regional lymph nodes.
1. Structure of the colon
The cecum is shaped like a circular bag, its location is just below the jejunum that empties into the large intestine. The cecum is linked to the appendix, which is roughly the same shape as a finger. For an adult, the average height will fall about 9cm and the diameter is about 0.5 to 1cm.The appendix is considered a "relic" left over from evolution in humans and apes. The way to determine the stump of the appendix is that it is located midway from the navel to the right anterior superior iliac spine. Based on that, it is possible to determine whether the abdominal pain is appendicitis or not.
Colon is the main part of the colon, divided into 4 parts: ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon and finally sigmoid colon. The ascending colon ascends from the cecum along the right side of the abdomen until it meets the liver, where it bends at the right angle of the liver. It then becomes the transverse colon, which crosses the abdomen.
As it approaches the spleen on the left side, it turns downward to form the descending colon at a bend called the left angle or angle of the pancreas. When it reaches the pelvis, it is S-shaped forming the sigmoid colon. The colon is the first part of the large intestine, where waste products reach the sigmoid colon and rectum and are excreted.
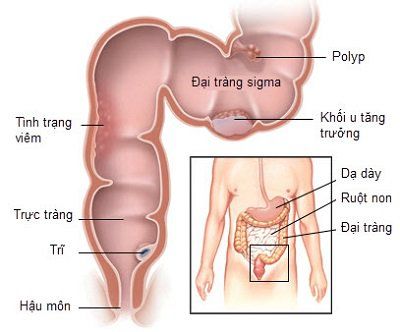
Rectum After being bent twice, the sigmoid colon is connected to the rectum is a straight tube, about 15cm long and ends at the anus opening to the outside of the body. The rectum consists of two sphincter muscles to control the opening and closing of the anus, it is located behind the bladder in men and behind the uterus in women.
The sigmoid colon The sigmoid colon is responsible for strong contractions to maintain a high pressure. This will regulate the movement of stool into the rectum. Because the sigmoid colon is the most high-pressure and narrowest part of the colon, it is also the part of the colon that most often forms diverticula.
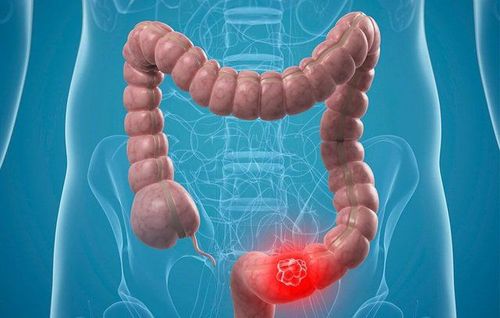
2. What is a colectomy?
Colectomy, also known as a colonectomy, the goal of this surgery is to remove diseased sections of the colon. The large intestine is also known as the colon or colon.During this surgery, your surgeon removes the diseased sections of bowel and then joins the healthy sections of the colon back together. The surgeon may remove all or part of your bowel.
The doctor may perform colostomy if there is not enough healthy bowel after surgery. During a colostomy, your surgeon will move one end of your colon to the outside of your abdominal wall and attach a colostomy bag to your abdomen. As stool passes through your colon, it drains into the pouch. The stool that goes into the bag is usually soft or loose.
Colectomy is usually temporary. You will have an ostomy bag to hold the stool until your bowel heals and opens again. During your next surgery, your surgeon may remove the colostomy and re-perform bowel movements. However, in some cases, a colectomy is permanent.
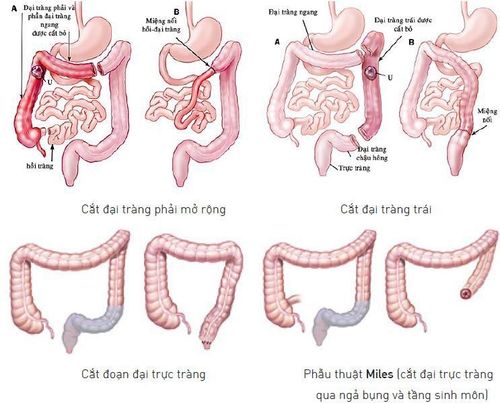
3. Why do I need to have my colon removed?
You may need a colectomy to treat conditions such as:Colon cancer. Intestinal obstruction due to scar tissue or tumor. Diverticulitis, is a disease of the large intestine. Precancerous polyps. Intestinal infection. Bleeding in the intestines. Volvulus, is an abnormal twisting of the intestine. Ulcerative colitis is a type of inflammatory bowel disease. Intussusception, which occurs when one part of the intestine slides into another.
4. What are the risks associated with colectomy?
All types of surgery carry some risks. These risks may include:Infection . Bleed. Heart attack or stroke. Blood clots. Shortness of breath. Pneumonia . Damage to neighboring structures. Oral fistula colonic fistula. Specific risks for a lower bowel resection include:
Bleeding inside the abdomen. Incisional hernia, which occurs when tissue passes through a surgical cut. Damage to the bladder or other nearby organs. Callus. Abdominal wall dissection, which is a surgically opened wound. Problems with the colostomy; such as skin irritation, skin ulcers around the artificial anus. In addition, there are also risks associated with general anesthesia. These include reactions to medications and difficulty breathing.
5. How to prepare for a large bowel resection?
At least two weeks before surgery, tell your doctor about all the medicines you are taking. You should supplement with substances such as vitamins and herbs. You should also tell your doctor if you have had any recent illnesses including colds, hot flashes or herpes.Before surgery, your doctor may ask you to:
Stop taking blood thinners, such as aspirin (Bufferin), ibuprofen (Advil), naproxen (Aleve) or warfarin (Coumadin). Quit smoking. Drink a lot of water. Eat foods rich in fiber. A few days before a colonectomy, you may need to:
Take a laxative to help you pass stools. Take an enema to clean out your colon. Drink only clear liquids; such as filtered water, clear juice and broth. On the day before surgery, follow your doctor's instructions. You may have to abstain from eating or drinking anything for 12 hours before surgery.

6. How is colectomy performed?
You will be given general anesthesia before surgery begins. This will help you sleep during the surgery. It will also keep you from feeling pain. Your surgeon may perform a laparoscopic surgery or a colectomy.During a laparoscopic bowel resection, your surgeon uses a camera to get a clear view of your intestines. Surgery is done through a series of small incisions. It is less invasive than open surgery.
During a colectomy, the surgeon makes a large incision in the abdomen so that the intestines can be seen directly.
The basic structure of both surgeries is the same. The surgeon approaches your intestines with one or more incisions and removes the diseased or damaged bowel. The remaining intestine is stapled or sewn together. This part is called a serial. The surgeon will also perform a colectomy if needed. Then, they will sew the incision closed. In some cases, the surgeon may also need to remove other organs during surgery.
7. What happens after a colonectomy?
Usually, you will be in the hospital for three to seven days. You may need to stay in the hospital longer if you develop complications. You may also need to stay longer if you have a serious underlying health problem.You will have to follow specific instructions on how to eat and drink after surgery. In general, you can drink clear water on the second or third day. As you heal, you'll be able to drink thicker liquids and eat soft foods.
Full recovery can take about two months.
8. What is the long-term outlook?
Most people who have a colectomy make a full recovery. You may have to use a colostomy bag temporarily. You may also need a permanent colectomy. A colectomy usually doesn't prevent you from doing the activities you love. You may need ongoing medical care if you have a chronic intestinal disease; such as cancer, Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis.Laparoscopic colectomy is a modern, minimally invasive technique, small incisions heal quickly, recover quickly, with less damage to nearby organs, especially patients with less pain, and quick recovery of colon function. effective for patients.
Surgery is applied in most of the surgical centers in developed countries and at Vinmec Health System with the most modern machines and equipment along with a team of experienced doctors and nurses.
In particular, Vinmec International General Hospital has been equipped with the most modern gastrointestinal endoscopy system of Olympus with the method of endoscopy with narrow light frequency band (NBI). This is a breakthrough method in screening and diagnosing cancers of the gastrointestinal tract (esophagus, stomach, duodenum and colon and rectum) at early and very early stages. NBI endoscopic images have high resolution and contrast, making it easy for doctors to detect small changes in color, morphology of cancerous and precancerous lesions that are difficult to detect with conventional endoscopy. .
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.