This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Do Van Manh - Emergency Department - Vinmec Ha Long International Hospital.
Traumatic brain injury is a trauma to the head that damages the skull and other internal structures. Without proper emergency treatment of traumatic brain injury, the victim is very likely to die or experience many serious sequelae.
1. Overview of traumatic brain injury
Traumatic brain injury is a life-threatening risk, especially childhood trauma is always a potential danger. The main causes of traumatic brain injury include:
Traffic accidents. Labor accident. Life accident. Accident when there is a disaster. Careless accident. Sports accident. Head trauma during childbirth... There are two common types of traumatic brain injury:
Closed traumatic brain injury: There is traumatic brain injury but not yet causing a dura, not opening the brain to the lips. outside school. Injury to the skull can cause skull depression, skull fracture, concussion, brain contusion, brain compression due to hematoma, cerebral edema, pneumothorax... Open traumatic brain injury: Causes dural tear, opens the brain to the outside world and have a high risk of encephalitis. In addition, there are many ways to classify other traumatic brain injury complications such as according to the nature or location of brain damage, focal and diffuse brain trauma, or both types at the same time.
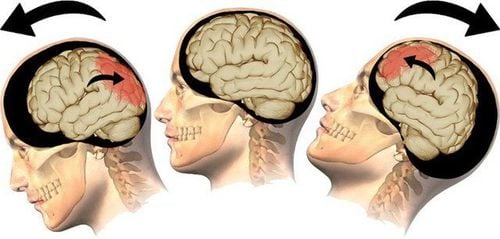
Chấn thương sọ não do nhiều nguyên nhân khác nhau gây ra
2. Symptoms of traumatic brain injury
The mechanism of generating traumatic brain injury is due to a direct blow to the head. Depending on the site of impact, the speed and the cause of the injury, symptoms can range from mild to severe. In general, symptoms of traumatic brain injury often manifest in two forms:
2.1. Primary injury Is an injury that occurs immediately after an accident, with specific manifestations at the site of contact, including:
Scalp tear causing a lot of blood loss. Fracture of the skull along the crow's foot, or rupture of the brain and inserted into the meninges and brain tissue. Injury to the meninges causes cerebrospinal fluid to leak. External and subdural hematoma, bleeding in the brain. Brain organization is crushed or escaped. In addition, there are inertia-related injuries due to the skull being shaken or twisted, the head moving, so the brain is subject to sudden acceleration / deceleration. This condition damages the diffuse axis, making the victim comatose for a long time, while the subclinical symptoms are much more severe.

Máu tụ dưới màng cứng
2.2. Secondary injuries Formed after an accident occurs, including:
Intracranial hematoma: The bleeding blood accumulates in a mass, occupying space in the skull and increasing intracranial pressure, causing brain cell damage. . Cerebral edema: Damage to the blood-brain barrier and cell membranes leads to abnormal accumulation of water in the interstitium and in the cells. Ventricular dilation: Blood flow obstructs the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid.
3. First aid for traumatic brain injury
3.1. When to be hospitalized? In case of head injury, parents need to take their child to the hospital immediately if they see one of the following signs:
Unconscious for more than 1 minute right after the fall. Still awake after the collision, but then there are unusual signs such as: fussy, difficult to comfort, sleep a lot, lethargy, poor interaction or unconsciousness; Vomiting more than 5 times or vomiting lasting more than 6 hours after a head injury. The fontanelle is swollen, stretched, accompanied by a pale face. There are injuries in other places, bleeding profusely. In adults, there may be additional manifestations such as confusion or loss of consciousness, prolonged headache and vomiting, mental confusion, seizures,...
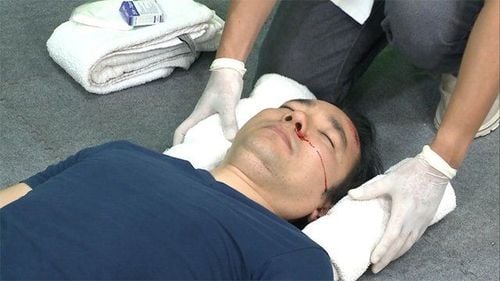
Cấp cứu chấn thương sọ não cần đảm bảo an toàn cho người
3.2. Care plan Emergency and immediate care on admission Immediately after an injury, the victim must be given first aid promptly, quickly transferred to the nearest medical facility for initial treatment, and then taken to a specialist. neurosurgery department.
Comprehensive examination A comprehensive examination is required when the victim comes to the emergency room, especially if there is multiple trauma such as internal bleeding, hemothorax, pelvic fracture, femur fracture...
Urgent treatment Acute and prioritized airways When performing a neurological examination, the following sequence is required: Perception, neurologic findings, vital signs (pulse, blood pressure, temperature, and respiratory rate). The victim's breathing and circulation must be controlled.
Confirm the diagnosis and choose the treatment method Examine, re-evaluate the lesion through clinical and subclinical. Treat traumatic brain injuries as soon as possible to avoid blood loss and infection.

Người bệnh cần đưa đến bệnh viện để cấp cứu và theo dõi tình trạng bệnh
3.3. First Aid Priority Immobilize the cervical spine while waiting for X-ray results. Clear the airways by aspirating fluid in the mouth and through the nose. Intubation or tracheostomy in the presence of jaw fracture. Ensure adequate ventilation and breathing. Control bleeding and circulation; Aggressive shock treatment to improve cerebral perfusion. Stop the external source of bleeding (if present). Rapid neurological assessment. In general, all measures of initial examination and resuscitation of the victim must be performed in parallel. For intracranial hematomas causing brain compression, emergency surgery is required immediately after detection to relieve the brain. If the victim has impaired consciousness, dilated pupils on one side or is paralyzed, the emergency treatment of traumatic brain injury late will be life-threatening.
3.4. Indications for subclinical X-ray of the skull: Bone surface, skull subsidence, cracks, skull fracture... CT Scan of head: Weakness, hemiplegia, strabismus, dizziness, confusion, headache prolonged and vomiting, seizures, skull fractures,... In addition, to evaluate the prognosis, the patient must perform a full range of electroencephalogram (EEG), cerebral angiogram (DSA) or vascular Doppler tests. Brain. In order to minimize the degree of disability left by sequelae, patients are forced to undergo a long rehabilitation process.
In general, emergency management of traumatic brain injury is a top priority and must be opened quickly. Doctors also need to comprehensively evaluate all injuries to avoid missing out, affecting the hope of saving the patient. For victims who do not need to be hospitalized, a written instruction from a specialist is required for convenient monitoring at home.
Specialist Doctor I Do Van Manh has more than 10 years of experience in the field of Critical Care - Anti-poison. He used to be the Deputy Head of the Intensive Care Unit at Quang Ninh General Hospital before working at Vinmec Ha Long International Hospital.
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health System nationwide for medical examination and treatment or contact to book an appointment online HERE.
Recommended video:
Cerebral aneurysm - essential knowledge
SEE ALSO:
How to deal with severe traumatic brain injury? Injuries caused by traumatic brain injury