This is an automatically translated article.
The brain governs most of the body's vital activities, including controlling and processing emotions. Currently, scientists are still learning about the role of specific brain organs in controlling basic human emotions such as fear, anger, happiness and love.1. How does the brain control emotions?
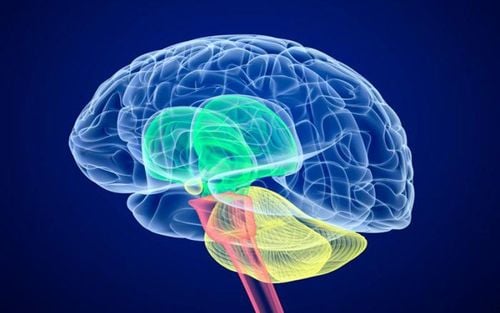
The limbic system is a group of interconnected structures deep in the brain that control emotions and behavior. Scientists do not yet agree on a complete list of organs in the limbic system. Structures generally accepted as part of the system include:Hypothalamus: In addition to controlling emotions, the hypothalamus is involved in sexual responses, hormone release, and body temperature regulation. . Hippocampus: The hippocampus helps to store and retrieve memories. It also helps people visualize spatial dimensions. Amygdala: The amygdala helps the body produce a variety of different responses to things and phenomena in the environment, especially situations that cause intense emotional stimulation. It plays an important role in controlling fear and anger. The corpus callosum consists of two structures, the cingulate gyrus and the parahippocampal gyrus. Together, they affect a person's mood, motivation, and judgment.
2. What part of the brain controls fear?
From a biological point of view, fear is an emotion that helps the body create a response to situations that are “possibly” unsafe or that warn of danger.This response is produced by the amygdala, followed by the hypothalamus. This is why some people with amygdala damage sometimes react inappropriately to dangerous situations.
When the amygdala stimulates the hypothalamus, it produces a “fight or flight” response. This is a physiological response that occurs while the body senses an event that threatens, attacks, or endangers life. Then, the hypothalamus sends signals to the adrenal glands to produce hormones like adrenaline and cortisol.
When these hormones enter the bloodstream, you may notice a number of physical changes, such as an increase in:
Heart rate Breathing rate Blood sugar Sweat In addition to triggering the “fight or flight” response, the amygdala Individuals also play a role in repeating fear responses to certain situations in life.
Trắc nghiệm: Bài kiểm tra chỉ số trí tuệ cảm xúc (EQ) của bạn
Chỉ số trí tuệ cảm xúc Emotional Quotient (EQ) là một chỉ số dùng để nói lên trí tưởng tượng, đánh giá và cảm xúc của một con người. Hãy làm bài trắc nghiệm sau để biết chỉ số EQ của bạn là bao nhiêu?
Nguồn tham khảo: webmd.com

3. What part of the brain controls anger?
Anger is an emotion that helps the body respond to threats or environmental stress. It is the "fight" part of the "fight or flight" response. For example, feeling frustrated when there's trouble in achieving a goal can trigger feelings of anger.The amygdala stimulates the hypothalamus similarly to the fear response. In addition, anger is also controlled by the prefrontal cortex. People with trauma in these areas will have difficulty controlling emotions, especially anger.
4. What part of the brain creates feelings of happiness?
Happiness is a state in which the body feels satisfied and happy. It helps stimulate positive thoughts and emotions.Imaging studies show that feelings of happiness originate in part in the hippocampus. In addition, it is also affected by the quadrilateral lobes (precureus) with the function of recalling memories, storing emotions and enhancing concentration.
A 2015 study found that greater gray matter volume in the right quadrilateral lobe helps people feel happier. Scientists think that the quadrangular lobe helps process certain information and convert it into a feeling of happiness.

5. What part of the brain produces emotions in love?
The onset of romantic love is related to feelings of tension produced in the hypothalamus. When in love people are often excited and nervous when thinking about the person they love or standing in front of them.When these feelings become intense, the hypothalamus stimulates the release of many hormones (dopamine, oxytocin, and vasopressin). Dopamine is linked to a "reward" system that elevates emotions in love.
A small 2015 study found that when volunteers were shown pictures of their favorite person, activity in certain areas of the brain increased, and dopamine was stimulated to produce more.
Oxytocin known as the love hormone, is produced in the hypothalamus and released through the pituitary gland. It increases when you hug someone or have an orgasm. Oxytocin also helps increase social bonds, create trust, and build relationships. It also promotes feelings of calm and contentment.
Similar to oxytocin, vasopressin is produced in the hypothalamus and secreted by the pituitary gland. It also helps to strengthen social relationships.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: healthline.com