Diet for people with gastrointestinal bleeding plays an important role in protecting the patient's health. Below is a list of foods that should be prioritized and foods that should be avoided during this condition.
1. Important principles for developing a diet for individuals with gastrointestinal bleeding.
Before discussing what to eat when experiencing gastrointestinal bleeding, it's essential to understand the key principles in creating a suitable diet for this group.
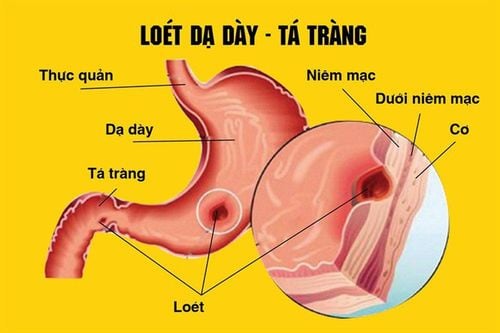
When gastrointestinal bleeding occurs, the gastrointestinal mucosa is often severely damaged. Patients may experience various issues, including abdominal pain, vomiting blood, and black stools, as well as other serious complications. In addition to following the treatment methods prescribed by specialists, diet plays a crucial role in determining the patient's recovery ability.
Effectively using food and dishes can help alleviate disease symptoms and provide the necessary nutrients to maintain a patient's health. When developing a menu for individuals with gastrointestinal bleeding, it's essential to consider the following factors:
- Do not allow the patient to eat while experiencing gastrointestinal bleeding, even if they are awake.
- Once the danger has passed and the bleeding is under control, the patient can resume a normal diet, starting with liquid, soft, and easy-to-digest foods. After that, the consistency of the foods can gradually be increased by introducing soft rice.
- When preparing porridge for the patient, include animal protein to provide extra energy. It is important to chop the food into small pieces and stew it to make it easier to digest and to lessen the strain on the intestines.
- Limit the use of green vegetables, as foods high in fiber, particularly insoluble fiber, can irritate the gastrointestinal mucosa, leading to more pain and bleeding.
- Patients can benefit from increased fruit intake, which helps supplement essential vitamins and minerals, thereby strengthening their resistance.
- If a patient is experiencing gastrointestinal bleeding, it is important to avoid serving them large meals at once. Family members should provide small meals approximately every 2 to 4 hours, ensuring the patient eats a moderate amount of food. This approach helps keep the stomach in a balanced state—not too full and not too hungry.
- It is crucial to monitor the temperature of the food. Avoid serving cold food that is below 5 degrees Celsius or freshly cooked food that exceeds 60 degrees Celsius, as these temperatures can irritate the intestines, leading to strong contractions and increased pain or damage.
2. What Should Patients with Gastrointestinal Bleeding Eat?
Patients experiencing gastrointestinal bleeding are encouraged to incorporate the following foods and drinks into their diet:
- Honey: Honey is an essential food for individuals with gastrointestinal bleeding due to its potential to effectively combat inflammation and neutralize stomach acid. Consuming honey can help eliminate harmful bacteria, reduce inflammation in the intestinal tract, and facilitate the healing of intestinal ulcers. Additionally, honey is rich in vitamins A, C, and E, which can enhance overall health and boost the immune system. For optimal benefits, patients can consume 2-3 tablespoons of honey daily or mix it with warm water and drink it upon waking to promote digestion.
- Porridge: Eating porridge can provide an adequate supply of water, starch, protein, sugar, and fiber, helping patients quickly restore their health without putting additional strain on their intestines. Options such as lotus flower porridge and lotus seed porridge are recommended and should be included in the diet for individuals experiencing gastrointestinal bleeding.
- Milk: During episodes of gastrointestinal bleeding, patients can benefit from drinking milk. This beverage is rich in essential nutrients, including vitamins K and D, calcium, vitamin E, selenium, zinc, magnesium, and phosphorus, all of which are vital for maintaining overall health.
- Foods that absorb stomach acid: Patients can eat bread to help absorb and reduce stomach acid, which can prevent local ulcers. However, these foods should only be consumed once the patient's health is stable and there is no longer active bleeding from the stomach.
- Low-fiber vegetables: When selecting green vegetables, prioritize young and tender varieties, as they are easier to digest and gentle on the intestines. Fiber plays a crucial role in reducing gastric secretions, which helps promote digestion and creates an ideal environment for beneficial bacteria to thrive in the intestinal tract.
- Ginger: This well-known spice is effective for pain relief, reducing bloating and indigestion, and healing gastrointestinal ulcers. Patients can benefit from ginger tea combined with honey or by adding a small amount of ginger to their porridge or other dishes.
- Soft Fruits: Incorporate easily digestible soft fruits like apples, pears, and papayas. These fruits are not only gentle on the intestines, but they also provide soluble fiber along with essential vitamins and minerals for overall health.
- Fish oil: This product is rich in omega-3, a natural anti-inflammatory that helps protect cells in the gastrointestinal mucosa, enhancing the body's ability to heal damage.
Patients experiencing gastrointestinal bleeding are encouraged to incorporate the following foods and drinks into their diet:
3. What should you avoid eating if you have gastrointestinal bleeding?
In addition to prioritizing certain foods, individuals with gastrointestinal bleeding should limit the consumption of the following foods:
- Sour foods: This category includes pickles, salads, and certain fruits like mangoes and lemons, which are high in acid. These acidic foods can significantly increase stomach acid production, potentially leading to the worsening of ulcers in the digestive tract. Patients consuming these foods may experience a variety of negative effects.
- Fast food: Fast food encompasses items such as sausages and bacon, which typically offer low nutritional value and contain high levels of preservatives that can be harmful to the intestines.
- Fatty foods: Fried and stir-fried dishes, such as fried chicken, fried meat, and potato chips, etc, can elevate blood fat levels and increase the risk of atherosclerosis. Additionally, these foods can result in indigestion and bloating, negatively impacting the intestines' ability to regenerate.
- Spicy foods: Dishes that contain a lot of chili, curry, and pepper can irritate the digestive tract and worsen ulcerated areas in the intestines. Therefore, individuals with gastrointestinal bleeding should limit the use of these spices in their diet.
- Raw vegetables: Consuming unsafe raw vegetables increases the risk of gastrointestinal infections, which can lead to more severe diarrhea and ulcers for patients.
- Soft drinks and Stimulants: Carbonated soft drinks, alcohol, and coffee can stimulate intestinal motility and contractions, potentially causing abdominal pain and increased bleeding.
In summary, you have just learned some information about what you should eat when suffering from gastrointestinal bleeding. Patients need to pay attention to strictly comply with the above principles until the disease is completely cured. Be cautious to avoid consuming inappropriate foods, as they can diminish the effectiveness of your treatment and increase the risk of complications associated with this serious condition.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.