This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor II Ho Viet Le Diem - General Internal Medicine - Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Dyslipidemia, also known as dyslipidemia and diabetes, is a very common metabolic disease today, the disease progresses silently until serious complications appear if it is not diagnosed and treated. timely. Dyslipidemia in people with diabetes is even more dangerous for patients, significantly increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease.
1. Dyslipidemia in diabetics
Dyslipidemia: an increase in cholesterol, plasma triglycerides or both. Disorders of cholesterol include elevated low-molecular-weight lipoproteins (hereinafter referred to as LDL-C) or low-density lipoproteins (HDL-C), or both.Diabetes: is a metabolic disorder, characterized by chronic hyperglycemia, caused by insulin deficiency or insulin intolerance, the disease may be accompanied by lipid and protein metabolism disorders. and glucose, diabetes includes 2 main types, type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes.
Characteristics of dyslipidemia in diabetics
Diabetic patients have a high rate of dyslipidemia, especially in diabetics. In patients with type 2 diabetes, it is reported that about 30 to 60% of patients with type 2 diabetes have dyslipidemia.
Factors that make diabetics more prone to dyslipidemia include:
Chronic hyperglycemia is poorly controlled, insulin resistance, insulin's influence on metabolism, production and metabolism of blood sugars. Enzymes and proteins in the liver are involved in the biosynthesis and metabolism of lipids such as apoproteins, lipoprotein lipase enzymes, cholesteryl ester transfer protein enzymes. Reduces the effect of insulin on fat metabolism in fat and muscle cells. Fat metabolism disorders in groups of diabetic patients are slightly different. Type 1 diabetics often have increased triglycerides and less often decreased HDL-C, good control of blood sugar in this group of patients also helps. quite well control blood lipid disorders. Patients with type 2 diabetes often experience increased triglycerides and decreased HDL-C, besides changes in the structure of LDL-C, in patients with type 2 diabetes, the LDL-C becomes smaller in size, This increases the risk of deposition in the blood vessels, increasing the risk of atherosclerosis. Dyslipidemia in patients with type 2 diabetes is more difficult to control even with good blood glucose control. Dyslipidemia and diabetes significantly increase cardiovascular risk. Dyslipidemia and diabetes themselves are important risk factors for cardiovascular diseases, especially those related to atherosclerosis. coronary artery disease such as myocardial infarction, cerebral infarction., about 1/3 of patients with coronary artery disease have dyslipidemia and about more than 2/3 of diabetic patients die from cardiovascular events, Diabetes increases the risk of cardiovascular disease 2 to 4 times. Dyslipidemia increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases in diabetics, especially cholesterol disorders that play an important role in atherosclerosis. Diabetes causes vascular complications, including macrovascular and microvascular complications. While high blood sugar mainly causes damage to small blood vessels, dyslipidemia mainly causes atherosclerotic lesions of large vessels, the combination of diabetes and dyslipidemia increases the both macrovascular and microvascular events. Dyslipidemia in both type 1 and type 2 diabetics significantly increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
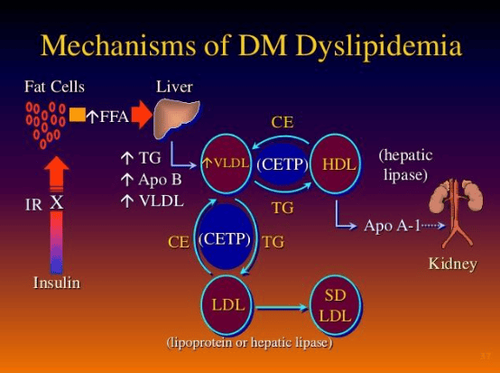
Rối loạn mỡ máu ở bệnh nhân tiểu đường do nhiều cơ chế khác nhau, có những đặc điểm sinh bệnh học riêng
2. Treatment of dyslipidemia in diabetic patients
Treatment of dyslipidemiaPrinciples of treatment of dyslipidemia include Treatment according to the cause Treatment according to the type of dyslipidemia Fully assess cardiovascular risk for appropriate, coordinated treatment goals Management of drug therapy and non-drug treatment, combination treatment of comorbidities, regular monitoring of treatment response.
Non-drug treatment: Including diet adjustment, lifestyle changes, increased exercise, weight control, smoking cessation... Drug treatment: There are many drugs available to help treat For the treatment of dyslipidemia, each group of drugs has different mechanisms of action, effectiveness, and treatment costs. It is necessary to choose the right drug for each specific patient population. In many cases, it is necessary to combine several groups. drugs together for maximum effectiveness for the patient. The drug groups currently used to treat dyslipidemia include: Statins, Fenobibrate, Ezetimibe, Niacin, PCSK9 inhibitors.. Notes when treating dyslipidemia in diabetics
With With the above-mentioned pathological characteristics, the treatment of dyslipidemia in diabetics should note the following.
People with both dyslipidemia and diabetes will significantly increase the risk of diseases Cardiovascular disease, therefore, it is necessary to have a complete and accurate risk stratification to have an appropriate treatment goal, the goal of blood lipid lowering treatment in this group of patients is also more stringent than in people without diabetes. Dyslipidemia in people with diabetes is often more complicated, combining many types of disorders such as: Increase in triglycerides, decrease in HDL-C, Increase in LDL-C, decrease in LDL-C size, so treatment often requires treatment. combination of many measures including: good control of blood sugar, non-pharmacological treatment and often a combination of different drug groups to treat dyslipidemia Patients with dyslipidemia Blood and diabetes will have to be well treated for both diseases, so many drugs will often have to be used at the same time, drugs for dyslipidemia and diabetes can both affect liver and kidney function. Therefore, regular monitoring is required during treatment to avoid unnecessary drug interactions.
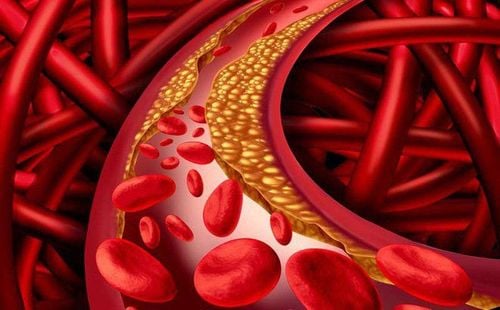
Kiểm soát tốt mỡ máu ở bệnh nhân tiểu đường là hết sức quan trọng để phòng ngừa các biến cố tim mạch, đặc biệt là xơ vữa động mạch
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.