This is an automatically translated article.
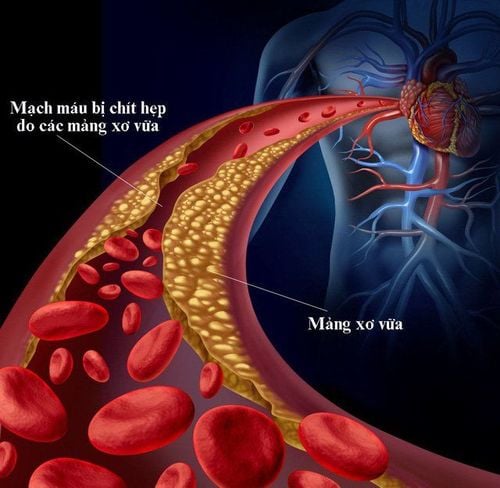
Lopirarator contains the main ingredient Atorvastatin, which inhibits cholesterol biosynthesis in the liver and enhances the catabolism of LDL cholesterol. The drug is indicated in the treatment of hypercholesterolemia, mixed hyperlipidemia and prevention of cardiovascular events.
1. What are the effects of Lopirator?
Lopirator contains the main active ingredient, Atorvastatin - a drug belonging to the Statin group. Atorvastatin reduces serum cholesterol levels by inhibiting HMG-CoA reductase, thereby inhibiting cholesterol biosynthesis in the liver and increasing the number of LDL receptors on the surface of hepatocytes to increase uptake and catabolism of LDL. .
Lopirator is indicated in the following cases:
Patients with hypercholesterolemia: Atorvastatin is indicated as an adjunct to diet to reduce total cholesterol (total-C), LDL-cholesterol (LDL) -C), apolipoprotein B, and triglycerides in patients with primary hypercholesterolemia, heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia, or mixed hyperlipidemia. Prevention of cardiovascular events in patients at high risk of cardiovascular events
2. Contraindications of Lopirator
Lopirator is contraindicated in the following cases:
Patients with hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients in the formulation. Patients with active liver disease or persistent unexplained elevations of serum transaminases (greater than 3 times the upper limit of normal). Patients who are pregnant, lactating and women of childbearing potential are not using appropriate methods of contraception.
3. What is the dose and usage of Lopirator?
How to use:
Patients can take Lopirator with or without food and take it at any time of the day.
Dosage:
Adults:
Lopirator dosage should be individualized according to baseline LDL-C level, treatment goals, and patient response. The usual starting dose of Lopirator is 10 mg once daily. The dose can then be adjusted according to the patient's response. The maximum dose of Lopirator is 80mg x 1 time / day. Primary Hypercholesterolemia and Mixed Hyperlipidemia: Most patients are controlled with Lopirator 10 mg once daily. Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia: Patients are usually started on Lopirator 10mg daily. The dose should be adjusted every 4 weeks to 40 mg/day, possibly increasing to a maximum of 80 mg/day. Homozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia: The dose of Lopirator is usually 10 to 80mg per day. Lopirator should be used as an adjunct to other lipid-lowering treatments in these patients or if such treatments are not available. Prevention of cardiovascular events: The usual dose is 10mg/day. Higher doses may be needed to achieve cholesterol levels according to current guidelines. Children:
Children with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia 10 years of age and older, the starting dose of Atorvastatin is 10 mg daily. The dose may be increased to 80 mg daily, depending on response and tolerability. Dosage should be individualized according to treatment goals and may be adjusted after at least 4 weeks. Other subjects:
Renal failure : No dose adjustment of Lopirator is required. Hepatic Impairment: Lopirator should be used with caution in patients with hepatic impairment. For patients with active liver disease, the use of Lopirator is contraindicated.
4. Side effects of the drug Lopirator
Patients using Lopirator may experience side effects including:
Frequency > 10%:
Gastrointestinal: Diarrhea; Neuromusculoskeletal: Joint pain; Respiratory: Nasopharyngitis. Frequency 1 to 10%:
Cardiovascular: Hemorrhagic stroke. Endocrine and metabolic: diabetes mellitus. Gastrointestinal: Indigestion, nausea. Genitourinary system: Urinary tract infections. Liver: Increased serum transaminases. Nervous system: Insomnia. Neuromuscular: Limbs pain, muscle spasms, musculoskeletal pain, myalgia. Respiratory: Sore throat. Frequency unknown:
Dermatology: Urticaria. Digestive: Abdominal distension, cholestasis, abdominal pain, flatulence. Liver: Hepatitis, increased serum alkaline phosphatase. Nervous system: Irritability, myasthenia gravis, nightmares. Neuromusculoskeletal: Increased blood creatine phosphokinase, joint swelling, muscle fatigue, neck pain. Ophthalmology: Blurred vision. Respiratory: Nosebleeds. Other: Fever, tinnitus. If you experience these symptoms, the patient should stop using Lopirator and notify the doctor for appropriate treatment.
5. Notes when using the drug Lopirator
Liver function tests should be performed prior to initiating treatment with Lopirator and periodically thereafter. Lopirator should be used with caution in patients who drink heavily and/or have a history of liver disease. Patients with recent stroke receiving long-term treatment with high-dose Atorvastatin (ie, 80 mg/day) may have an increased risk of hemorrhagic stroke. Based on current clinical guidelines, statins should be continued in the perioperative period for cardiac arrest and cardiac surgery. Discontinuation of statin therapy before surgery is associated with an increased risk of heart disease and death. Atorvastatin can affect skeletal muscle, causing myalgia, myositis, and possibly progression to rhabdomyolysis (a potentially life-threatening condition characterized by markedly elevated creatine kinase (CK) levels). Women of childbearing potential should use appropriate contraception during treatment with Lopirator. Lopirator is contraindicated during pregnancy. Stop taking the medicine and notify your doctor immediately if pregnancy is found. Lactation: It is not known whether Atorvastatin or its metabolites are excreted in human milk. Due to the risk of adverse reactions in the nursing infant, women taking Lopirator should not breast-feed.
6. Drug interactions
Drug interactions can change the effectiveness and/or increase the serious side effects of the drug. Patients should inform their doctor of all medications and dietary supplements they are using for advice. Here are some interactions to watch out for when using Lopirator:
Strong CYP3A4 inhibitors such as Ciclosporin, Clarithromycin, Delavirdine, Stiripentol, Ketoconazole, Itraconazole, Posaconazole,...have been shown to increase plasma levels. and increased side effects of Atorvastatin. Therefore, caution should be exercised when atorvastatin is co-administered with these drugs. Concomitant administration of Atorvastatin with cytochrome P450 inducers may result in decreased plasma concentrations of Atorvastatin. The risk of muscle side effects, including rhabdomyolysis, may be increased when Ezetimibe or Fusidic Acid is used with Atorvastatin. Several cases of myopathy have been reported when Atorvastatin was administered concomitantly with Colchicine. Concomitant administration of Atorvastatin 80 mg daily with Warfarin resulted in a slight decrease in prothrombin time during the first 4 days of dosing and returned to normal within 15 days of treatment. Concomitant use of Atorvastatin with oral contraceptives increases plasma concentrations of Norethindrone and Ethinyl Oestradiol. Above is information about uses, usage and notes when using Lopirator. Patients should consult their healthcare professional before taking the medication to ensure optimal effectiveness.