This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Doctor Emergency Resuscitation Department - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.
Bile is a green or yellow liquid with a pH around 7 - 7.7. Bile is very important for the digestion of food, especially fat. Humans cannot live without bile.
1. What is bile translation?
Bile is secreted in hepatocytes and then enters the bile ducts into the second part of the duodenum (below the stomach) and participates in the digestion of food, especially the digestion of fats. Every day the body secretes about 600ml - 1 liter of bile. However, the excretion of bile in the liver is also dependent on the amount of bile salts in the enterohepatic circulation. The greater the amount of bile salts, the greater the liver's ability to excrete bile.
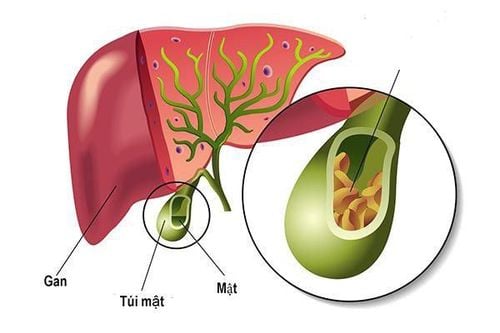
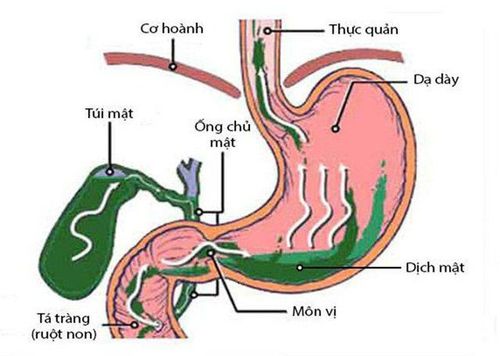
2. The process of storing bile in the gallbladder
The gallbladder is a very important part of the body, where it stores bile secreted by the liver until it is needed by the duodenum. When eating, the gallbladder will contract to push bile through the bile into the small intestine to help digest food. When not eating, the bile secreted will be stored in the gallbladder.
The volume of the gallbladder is about 20-60ml, the amount of bile stored in the gallbladder includes water, Cl-, Na+ and many other electrolytes. The gallbladder is responsible for storing and concentrating bile. The gallbladder mucosa continuously absorbs inadvertently, causing other components of bile such as bile salts, lecithin, bilirubin, cholesterol to be concentrated in the gallbladder. Usually bile will be concentrated about 5 times or the degree of concentration is up to 12, 20 times. However, the gallbladder still plays a minor role, in some cases related pathology can still be surgically removed if necessary.
3. Composition of bile
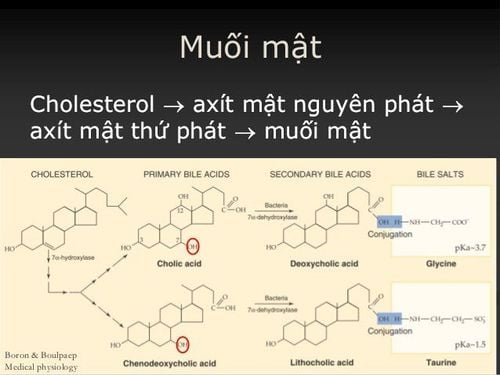
As mentioned above, the active ingredient of bile is bile salts (accounting for 50% of the composition) and has added cholesterol, lecithin, bilirubin as well as electrolytes, specifically:
Cholesterol: Is the main raw material for production produce bile salts. Cholesterol is insoluble in water but is emulsified by lecithin and bile salts to prevent its precipitation. The amount of cholesterol present in bile will depend on the amount of lipids consumed on a daily basis. Therefore, if we eat a lot of lipids for a long time, it can lead to gallstones. Bile salts: An important component of bile that has the effect of digesting food and absorbing lipid digestive products such as fatty acids, cholesterol, monoglycerides and lipids in the small intestine. Bile salts play an important role in the absorption and transport of fat-soluble vitamins such as A, D, E and K. Every day the liver excretes about 0.5g of bile salts. Bile salts are not lost and are usually reabsorbed after use 80-90% will be transferred to the liver in the blood and stimulate the liver to produce more bile. Bile pigment: Produced by the liver from the protein hemoglobin during the breakdown of red blood cells in the liver. Stercobilin in bile pigment will yellow the substances and fluids containing it. This explains why normal stools are yellow. When bile pigments are stasis, they cannot enter the intestines due to biliary obstruction, cirrhosis or other diseases... it will cause the stool to lose its yellow color.
4. What is the effect of bile?
Bile juice plays a major role in supporting the body's digestive process. Specifically:
Stimulates the production of digestive enzymes in pancreatic and intestinal juices, and at the same time activates these enzymes. Helps stimulate intestinal peristalsis thereby creating an alkaline environment in the intestine, preventing the attack of bacteria on the upper part of the small intestine. When eating, bile will be pushed down the duodenum to do the task of digesting food. Without bile, fat cannot be digested, making it impossible for the body to absorb fat as well as fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E and K. In addition to supporting the digestive process such as: On top of that, bile also helps to remove the degradation products in red blood cells, forming the color of bile.
If the body has some problems that affect the bile fluid (such as gallstones, malformations of the biliary tract, tumors, cholecystectomy ...) it can lead to difficult eating and drinking. digestion, slow digestion, bloating.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.