This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with Master, Doctor Nguyen Van Huong - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec International General Hospital Da Nang.Gallstones are one of the most common gastrointestinal diseases. Imaging techniques play an important role in assessing the location, size, and number of gallstones, and the effects of gallstones on other organs. The most commonly used diagnostic techniques for gallstone disease today are abdominal ultrasound, abdominal CT scan, and MRI.
1. Overview of gallstone disease
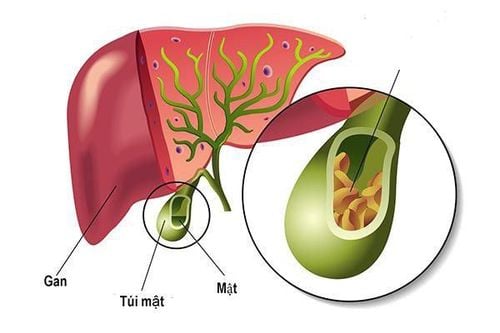
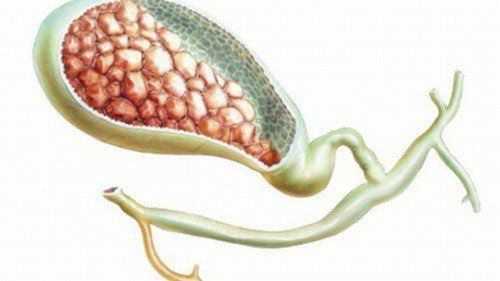
The normal gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped sac located below the right lobe of the liver, connected to the biliary tract via the cystic duct. The function of the gallbladder is to store and concentrate the bile secreted by the liver. When we eat, the gallbladder contracts to push bile through the common bile duct into the intestines to help digest food, especially fats.Gallstones are one of the most common diseases in the digestive tract. Gallstones are solid entities arising from crystallized bile that may occur in the gallbladder, common bile duct, or intrahepatic bile ducts. In developed countries, the majority of gallstones are composed mainly of cholesterol. In Vietnam, most are pigment stones, originating from eggs and intestinal parasites.
Gallstones can be very small, only a few millimeters in diameter, or they can be large, several centimeters in diameter. Pebbles can be round, oval, or many other shapes. The patient may have only a few stones, but there are also many stones. The incidence of gallstone disease in women is higher than in men because the female sex hormone progesterone reduces gallbladder motility, while the hormone estrogen increases cholesterol and reduces cholesterol-soluble bile acids. Some other factors that can increase the risk of gallstones are: obesity, poor nutrition, diabetes, medical conditions that limit gallbladder function or slow bowel movements. including spinal cord injury,...
2. Role of abdominal ultrasound, abdominal CT scan, MRI in diagnosing gallstone disease
Imaging techniques play an extremely important role, helping to provide doctors with valuable information about the condition of gallstones such as the location and size of the stone, and the effect of the stone on other organs. Some of the commonly used diagnostic techniques for gallstone disease today include:2.1. Abdominal ultrasound
Abdominal ultrasound produces images of the gallbladder and biliary tract, helping to detect gallstones with high sensitivity and specificity. Ultrasound helps to determine the nature of stones such as number and size, detect signs of inflammation, obstruction of bile flow, anatomical information such as liver, biliary tract, gallbladder polyps, ... Abdominal ultrasound is the most common method used to evaluate gallbladder abnormalities today.Ultrasound of gallstones is best done when the patient is fasting and not taking any diuretics. Typical images of gallstones are:
Stones are round or oval hyperechoic, sometimes arc-shaped, with a shadow, and move when the patient changes position.
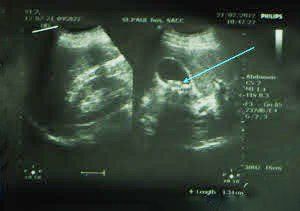
The gallbladder is filled with stones, shrinking to form two arcs. One arc of the gallbladder wall and a second arc with the shadow of the stone. Gallbladder sludge: Part or all of the gallbladder capacity is filled with bile sludge, sometimes bile sludge with many very small stones without a shadow.
2.2. Abdominal CT scan
Abdominal CT scan, also known as abdominal tomography, is a method that uses X-rays and a computer system to create three-dimensional cross-sectional images of the abdomen. Abdominal CT scans quickly create detailed images of the gallbladder and biliary tract, helping the doctor to accurately detect gallstones, signs of inflammation, and signs of bile flow obstruction.Abdominal CT scan is indicated in case the doctor suspects that gallstones are formed or stones cause complications such as perforation of the common bile duct, gallbladder cancer,...
2.3. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in the evaluation of gallstones
Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRI) is a technique that uses magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to create images of the liver, gallbladder, biliary tract, pancreas, and pancreatic duct.Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography is very valuable in the investigation of pancreatic biliary tract diseases, can help accurately determine the presence and nature of gallstones, showing inflammation, obstruction of the gallbladder or ducts secret.
Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography has many advantages such as safe, non-invasive, non-radioactive, patients do not need anesthesia, better identify the biliary tract above the obstruction, accurately assess external lesions. honey,...
Gallstones do not need treatment if there are no symptoms. Patients need to follow up with an appointment for the doctor to monitor the progress of the stone. If you have cholecystitis or complications related to gallstones, your doctor may prescribe antibiotic treatment and remove your gallbladder. In most cases, your doctor will remove your gallbladder with laparoscopic surgery. If gallstones obstruct the bile duct, other procedures can be performed such as: endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP), percutaneous gallstone lithotripsy, etc.
Gallstones are quite common. , and usually cause no symptoms. But when there are complications such as cholecystitis - acute cholangitis due to stones will be very serious. Should have a healthy diet and regular health check-ups to detect stones early to help monitor easily and know the signs of acute cholecystitis due to stones early to go to the hospital for timely treatment
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: radiologyinfo.org