Unlike pulmonary tuberculosis, which is dangerous and highly infectious, lymph node tuberculosis is non-fatal and can be completely cured. However, it remains a relatively common disease, often prolonged and causing significant inconvenience to daily life
1. What is pulmonary tuberculosis?
Pulmonary tuberculosis is an infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which invades and proliferates in the lungs. Among all forms of tuberculosis, pulmonary tuberculosis is the most common, accounting for 80–85% of cases, and it is the main source of community transmission.
1.1. Symptoms
- Cough is the primary and most important symptom of pulmonary tuberculosis. Patients may experience dry cough, productive cough, or hemoptysis. Symptoms persist for more than 3 weeks.
- Shortness of breath and chest pain.
- Fatigue and malaise.
- Low-grade fever, chills in the afternoon.
- Night sweats.
- Weight loss due to anorexia and poor appetite
1.2. Is Pulmonary Tuberculosis Contagious?

- Pulmonary tuberculosis is highly contagious and spreads through the respiratory tract.
- People with pulmonary tuberculosis or laryngeal and bronchial tuberculosis release Mycobacterium tuberculosis into the air when coughing, sneezing, or spitting, through tiny droplets or dust particles. Individuals who inhale these droplets can develop pulmonary tuberculosis
- Additionally, living in damp and polluted environments facilitates bacterial growth and disease transmission
- Consuming food contaminated with Mycobacterium tuberculosis or handling waste containing the bacteria can also lead to infection
1.3. Diagnosis of Pulmonary Tuberculosis
The diagnosis is based on clinical symptoms such as low-grade afternoon fever, night sweats, fatigue, anorexia, and weight loss. Physicians will conduct a lung and full-body examination and may order several tests, including:
Chest X-ray.
- Xpert MTB/RIF test (if available).
- Direct sputum smear microscopy for AFB (acid-fast bacilli).
- Culture for Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
A definitive diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis requires at least one positive AFB sputum sample and chest X-ray findings suggestive of tuberculosis, or two positive sputum samples.
1.4. Treatment for Pulmonary Tuberculosis
- Patients must strictly adhere to the treatment regimen, take medications as prescribed, and avoid discontinuing treatment prematurely, even when symptoms improve.
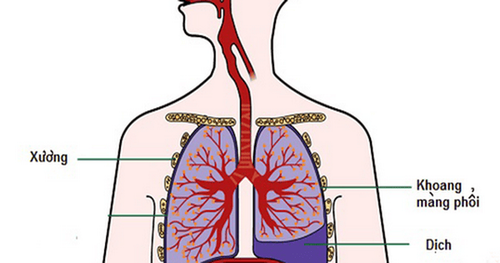
- If left untreated, pulmonary tuberculosis can lead to complications such as pleural effusion, pneumothorax, and hemoptysis.
- Even after successful treatment, patients may experience sequelae such as chronic respiratory failure, bronchiectasis, pulmonary aspergilloma, and recurrent pneumothorax.
1.5. Prevention of Pulmonary Tuberculosis
As pulmonary tuberculosis is an infectious disease, preventive measures include:
- Administering BCG vaccine to children to prevent tuberculosis.
- Wearing a mask when outdoors or in contact with infected individuals.
- Regular handwashing before and after meals.
- Covering the mouth when sneezing or coughing.
- Avoiding sharing personal items with tuberculosis patients.
- Patients with pulmonary tuberculosis should take measures to prevent spreading the infection to others by wearing a mask, covering their mouth when coughing or sneezing, avoiding sharing a room with others, staying away from crowded places, and expectorating sputum only in designated areas. Sputum and any materials that may carry infectious agents must be properly disposed of according to medical guidelines.
- Regularly clean living and working spaces, ensuring they are well-ventilated and exposed to sunlight
- Maintain a healthy diet, adopt a balanced lifestyle, exercise regularly, and avoid substances like alcohol and tobacco. Routine health check-ups are recommended for early disease detection.
2. What is lymph node tuberculosis?
Lymph node tuberculosis is a secondary condition that arises following primary tuberculosis infections elsewhere in the body, such as primary pulmonary tuberculosis. After invading the lungs, Mycobacterium tuberculosis can travel to lymph nodes, causing lymph node tuberculosis.
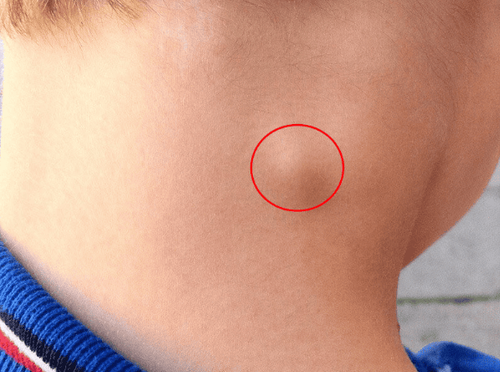
2.1. Symptoms
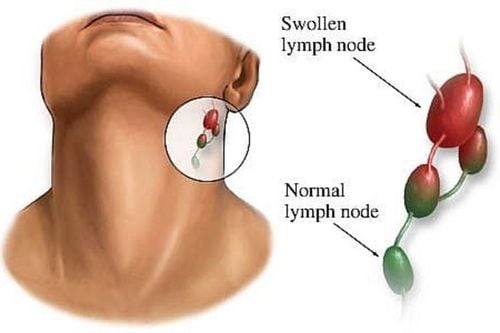
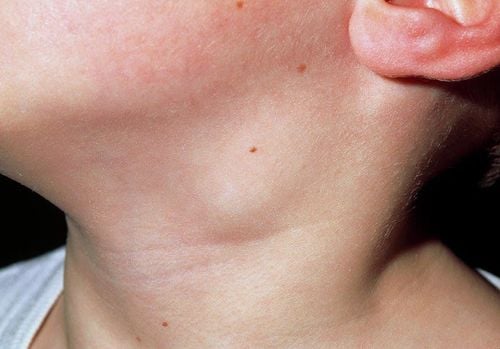
- Enlarged lymph nodes, often forming clusters or chains in specific regions, most commonly in the neck.
- Lymph nodes are irregular in size, non-tender, and non-adherent. The skin overlying the lymph nodes remains smooth, with no signs of redness or warmth.
- Over time, lymph nodes gradually enlarge and may soften, rupture, and discharge caseous pus, which is difficult to heal and often leaves retracted scars with purplish borders.
- Patients may experience fatigue and low-grade fever. Severe symptoms occur in cases of secondary infections or concurrent tuberculosis in other organs, such as the lungs or bones
2.2. Is Lymph Node Tuberculosis Contagious?
Unlike pulmonary tuberculosis, lymph node tuberculosis does not spread directly from person to person because Mycobacterium tuberculosis is confined to the lymph nodes and does not leak outside
2.3. Diagnosis of Lymph Node Tuberculosis
The diagnosis of lymph node tuberculosis is based on clinical manifestations and tests such as:
- Fine-needle aspiration for cytology.
- Lymph node biopsy for histopathological examination.
- Culture for Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
- Chest X-ray.
Differential diagnosis is essential to distinguish lymph node tuberculosis from other conditions, including:
- Bacterial lymphadenitis, characterized by redness, tenderness, and response to antibiotic therapy.
- Hodgkin’s and non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas, diagnosed through lymph node biopsy and bone marrow studies.
- Metastatic cancer with primary tumor signs, confirmed through biopsy.
- Benign lymph node tumors such as lipomas, fibromas, neuromas, and lymphatic cysts.Benign lymph node tumors such as lipomas, fibromas, neuromas, and lymphatic cysts.
2.4. Is Lymph Node Tuberculosis Curable?
- Lymph node tuberculosis can be effectively treated with medical therapy under the supervision of tuberculosis specialists. Patients are prescribed anti-tuberculosis drugs such as rifampicin, isoniazid, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol for a minimum of 9 months, with dosages adjusted based on body weight and treatment protocols
- Whether lymph node tuberculosis requires surgery is a common concern for many patients. Lymph node tuberculosis can be treated surgically by excising the entire lymph node when it forms abscesses that do not respond to aspiration and combined antibiotic therapy, or in cases of tuberculous lymphadenopathy with localized, non-suppurative lymph nodes. Surgical removal and thorough curettage of caseous material in the lymph nodes, followed by the application of anti-tuberculosis antibiotics, is an effective treatment approach.
- Lymph node tuberculosis is also common in children. Early excision of lymph nodes is not recommended, as they play a protective role against Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
- Proper management includes addressing chronic inflammation and completing tuberculosis treatment before considering surgery.
2.5. Prevention of Lymph Node Tuberculosis
- As lymph node tuberculosis is not contagious, prevention focuses on completing treatment for primary tuberculosis to prevent bacterial spread to other organs.
- Boosting the immune system through a nutritious diet, regular physical activity, and adequate rest is crucial, particularly for children, to minimize the risk of infection.
For more health, nutrition, and beauty tips, visit Vinmec International General Hospital to safeguard the health of yourself and your loved ones.
To schedule an appointment at the hospital, please contact the HOTLINE or book directly HERE. Download the MyVinmec App to manage, track, and schedule appointments conveniently anytime, anywhere.