This is an automatically translated article.
Soda is a drink high in caffeine and sugar and is an addictive drink. If you are really addicted to soda then many other health problems can occur including both physical and mental problems. The first is unwanted weight gain, then there are more serious consequences such as type 2 diabetes, fatty liver, dental disease, weak bones, cardiovascular disease and depression.
1. What is soda addiction?
Addiction is a mental and physiological disorder characterized by continued use of a substance even though it negatively affects you. People can be addicted to many substances and to some behaviors. For example, drug addiction, alcoholism, some medications like corticosteroids, sex addiction, and even smartphone addiction.
Soda addiction does not have an official definition, and currently there is not enough scientific evidence to suggest that it is a real disorder.
For this article, soda addiction, or soda dependence is defined as drinking too much soda without being able to quit or control your daily soda intake even though it has already had negative effects on you. .
Food addiction, including soda addiction, has many states and behaviors similar to drug addiction. Because soda contains a number of potentially addictive substances such as caffeine, sodium, and sugar or artificial sweeteners, drinking soda is much more addictive than you might think.

Soda chứa nhiều chất có khả năng gây thèm nên dùng lâu rất dễ bị nghiện
2. Symptoms
The symptoms of soda dependence are mainly related to the function of your brain and nervous system. For example, symptoms you may experience include:
Extreme cravings A thirst that can only be satisfied with soda A feeling of dependence on drinking soda An inability to control how much soda you drink Some other symptoms are similar to those of withdrawal such as headaches, irritability, depressed mood or sluggishness when there is no soda to drink.
3. Consequences of soda addiction
Soda dependence can have a number of side effects.
Effects on teeth: soda is acidic, and over time it can discolor your teeth and wear down enamel, thereby weakening your teeth making you more susceptible to cavities and other dental problems. If you drink full sugar soda instead of diet soda, your dental problems will get worse because sugar feeds bacteria and forms plaque, thus accelerating tooth decay.
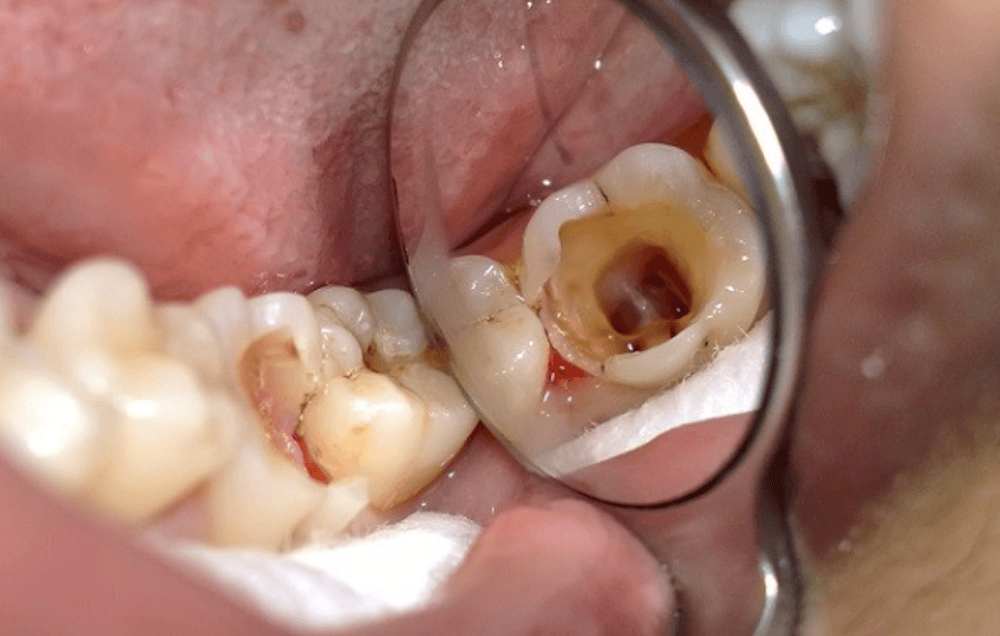
Lạm dụng soda khiến tình trạng răng miệng trở nên tồi tệ hơn
Effects on bones: Phosphoric acid in dark sodas can also contribute to osteoporosis, brittle bones. Unwanted weight gain: Drinking too much soda, both regular and diet soda, leads to unwanted weight gain. Diet soda may still contain artificial sweeteners that make it easy to become addicted to this drink and still gain weight as usual. A regular cup of soda with a capacity of about 240ml will provide about 100 calories - including sugar. And if you drink a large 480ml cup with each meal, you've added 600 calories to each meal. Obviously, whatever the reason, consuming large amounts of sugar can cause unwanted weight gain, increase the risk of type 2 diabetes and even cardiovascular disease. Drinking sugary sodas also increases the risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in both adults and children.
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline here for support.
Articles refer to the source: healthline.com