This is an automatically translated article.
Primary cholangitis is a serious autoimmune disease that usually occurs in people aged 40 years and older. This disease can damage the liver, leading to primary cirrhosis. If not treated early, the disease will cause dangerous complications such as osteoporosis, cholangiocarcinoma, and even death.1. What is primary cholangitis?
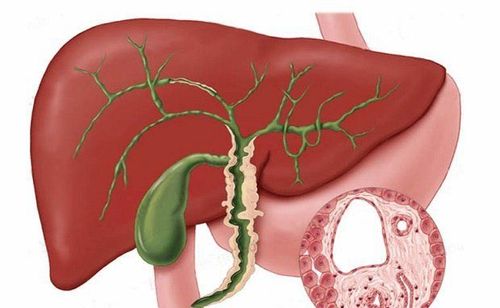
Primary cholangitis (PBC) is a condition in which the bile ducts in the liver are damaged. This disease is also known as primary biliary cirrhosis.
The bile ducts in the liver play a very important role in the human body. They contain a liquid called bile, which is a key player in digestion and is located far from the liver. On the other hand, bile is the liquid that helps the body absorb fats, cholesterol and some essential vitamins. In addition, it also helps to get rid of old damaged red blood cells and other unnecessary things in the body.
When the bile ducts do not work effectively, bile will accumulate in the liver, leading to hepatitis, even leaving scar tissue. Over time, these scar tissue replaces healthy liver tissue and makes it impossible for the organ to function as it should.
However, this process is usually slow so your liver may not be severely damaged at first. The disease can be controlled with medication in combination with other aggressive treatments. If not treated early, the condition can worsen over a few months or years, when the patient is more likely to need a liver transplant surgery.
Viêm đường mật nguyên phát gây ảnh hưởng đến chức năng gan
2. Causes of primary cholangitis
Currently, medicine is still unable to make an exact conclusion about the root cause of primary cholangitis.
However, many studies suggest that primary cholangitis is related to genes. People who have a parent, brother, or sister with primary cholangitis have a higher risk of developing the disease as well. In addition, primary cholangitis can also be related to immune system problems, such as: Thyroid disorders, scleroderma, or pernicious anemia. Several external factors contribute to the disease, including tobacco, toxic chemicals, or infections.
3. Symptoms of primary cholangitis
In the early stages, the patient may not notice any abnormalities related to primary cholangitis. The body can function normally and healthy for many years. As the disease progresses, the patient often has some typical symptoms as follows:
Fatigue Itching skin Urticaria Dry eyes and mouth Jaundice, yellow eyes Swelling in the feet and ankles Pain and swelling in the abdomen Bone, muscle and joint pain Dark skin Unexplained weight loss Poor memory.
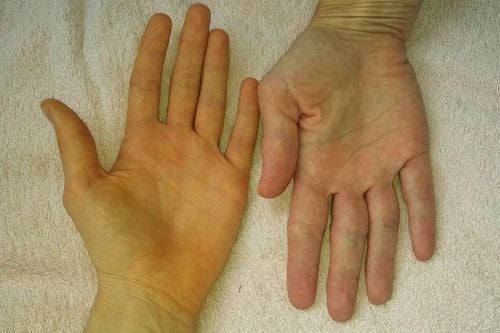
Vàng da là triệu chứng thường gặp của bệnh
4. Complications of primary cholangitis
When primary cholangitis is not detected and treated in time, the disease will cause dangerous complications for the overall health of the patient, including:
Fatigue Lack of vitamins A, D, E and K Fatty urine Osteoporosis Ascites Gastrointestinal bleeding Brain Hepatitis Peritonitis Liver failure complications can occur when primary cholangitis has persisted for 7-15 years, or more. The disease can even lead to the formation of biliary tract tumors, causing cholangiocarcinoma.
Bệnh lý não gan là một biến chứng nguy hiểm của bệnh viêm đường mật nguyên phát
5. Diagnosis of primary cholangitis
To diagnose primary cholangitis, your doctor may recommend a blood test to check your liver's functioning and look for abnormalities in the immune system.
Besides, you can also perform some other tests to diagnose the disease, such as: computed tomography (CT scan), ultrasound, MRI, or endoscopy (ERCP). These tests will give the doctor a more detailed picture of the liver and the areas around it.
In addition, liver biopsy may also be ordered. In this test, a small sample of liver tissue is removed and examined under a microscope in a laboratory to look for lesions and abnormalities associated with primary cholangitis.
6. Treatment of primary cholangitis
Currently, there is no cure for primary cholangitis, but medications can slow the progression of the disease.
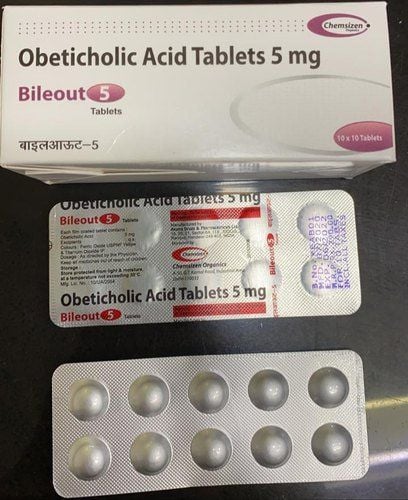
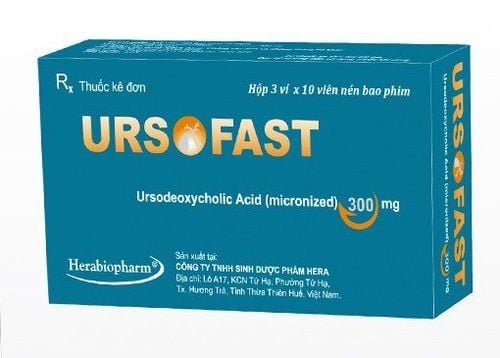
The most commonly used drug is ursodiol (ursodeoxycholic acid), which is effective in promoting bile movement through the liver. Another medication, obeticholic acid (Ocaliva) can also be used in combination with ursodiol or alone to treat primary cholangitis (PBC).
To prevent the disease from developing, you should make some healthier lifestyle changes. If you regularly drink alcohol, it's best to try to limit or give it up, because alcohol is a leading stressor to the liver. Besides, you should also choose low-sodium foods, add lots of green vegetables and fruits rich in vitamins and maintain a regular exercise routine to reduce uncomfortable symptoms caused by the disease.

Thuốc có tác dụng hiệu quả trong điều trị bệnh viêm đường mật nguyên phát
In case the use of drugs does not work, the patient may have to resort to surgical intervention to transplant the liver. However, this is a major surgery, so before choosing, you should consult your doctor carefully.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: webmd.comSEE MORE
Primary sclerosing cholangitis Inflammation of the biliary tree, what to do? Prevention of sclerosing cholangitis