This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by a doctor from the Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.The peritoneum is the largest serosa in the body, and has the function of covering and protecting all the organs in the abdomen. In addition, the peritoneum also makes the structure of the organs more solid.
1. What is the peritoneum?
The peritoneum is the largest serosal membrane in the body. The peritoneum covers all organs in the abdominal cavity and pelvis, lining the inner wall of the abdomen, the inferior surface of the diaphragm, and the superior surface of the pelvic diaphragm.The peritoneum consists of two leaves, the parietal peritoneum lining the inside of the abdominal wall, the pelvic wall, and the visceral peritoneum that cover the organs and become the serosa of these organs. The space between the visceral peritoneum and the parietal peritoneum, called the peritoneal cavity, contains a small amount of serous fluid for the purpose of reducing contact between organs.
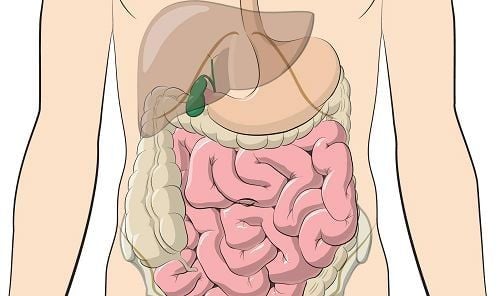
Phúc mạc bao bọc tất cả các cơ quan trong ổ bụng và hố chậu
2. Structure
2.1 Some related structures The abdominal cavity is a closed cavity bounded by the abdominal wall, above the diaphragm, and below the perineum. The abdominal cavity contains organs and the peritoneum.The peritoneal cavity is the space between the visceral peritoneum and parietal peritoneum. Under normal circumstances, the two peritoneal leaves are close to each other, the peritoneal cavity is then a virtual cavity. In case of pathology, there is accumulation of fluid, blood, and gas, we have a true peritoneal cavity. The peritoneal cavity is a closed cavity in men, and in women, the peritoneal cavity communicates with the fallopian tubes.
Classification of abdominal organs as follows:
Intraperitoneal viscera are ovaries, not completely covered by the peritoneum. An intraperitoneal viscera is an organ that is almost entirely covered by the peritoneum. For example, stomach, liver, spleen... Extraperitoneal organs are organs located in the back wall of the abdomen like the kidneys, or in the pelvis like the bladder and uterus. The transformed organ is an embryonic organ located in the peritoneum but during development becomes extraperitoneal such as the duodenum, pancreas, and ascending colon. descending colon. 2.2 Structures of the Peritoneum As discussed above about the visceral peritoneum and parietal peritoneum, there are still some intermediate structures that do not fall under the definition of the upper two peritoneum. Through these medial structures, blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatics enter the intraperitoneal organs. The mesentery is two peritoneal leaves that hang the digestive tract to the abdominal wall, between the two leaves are blood vessels to the small intestine, lymphatics and nerves. Ligaments are two folds of the peritoneum that go from the parietal peritoneum to the visceral peritoneum of an organ that is not part of the digestive tract, for example, the crescent ligament, the coronary ligament. The omentum consists of two peritoneal leaves connecting the organs together: the small omentum and the great omentum.
3. Structure and function of the peritoneum
3.1 Structure The peritoneum is composed of two layers:The serosa is the peritoneal surface made up of a layer of squamous epidermal cells, the cell layer that makes the peritoneum smooth and iridescent. On the other hand, this epidermis also secretes fluid that wets the peritoneum. Due to trauma or peritonitis, the epithelium is damaged, the viscera become sticky and obstruct the functioning, especially of the small intestine. The subserosal plate is a layer of connective fibrous tissue and has high elasticity, thanks to this layer, the peritoneum can firmly protect the organs. The size of the peritoneum is quite large, although it is located in the abdomen, it has many folds. An area equal to that of the body's skin.
3.2 Functions The peritoneum has the following functions:
Encloses the organs, protects and stabilizes the structure of the organs.
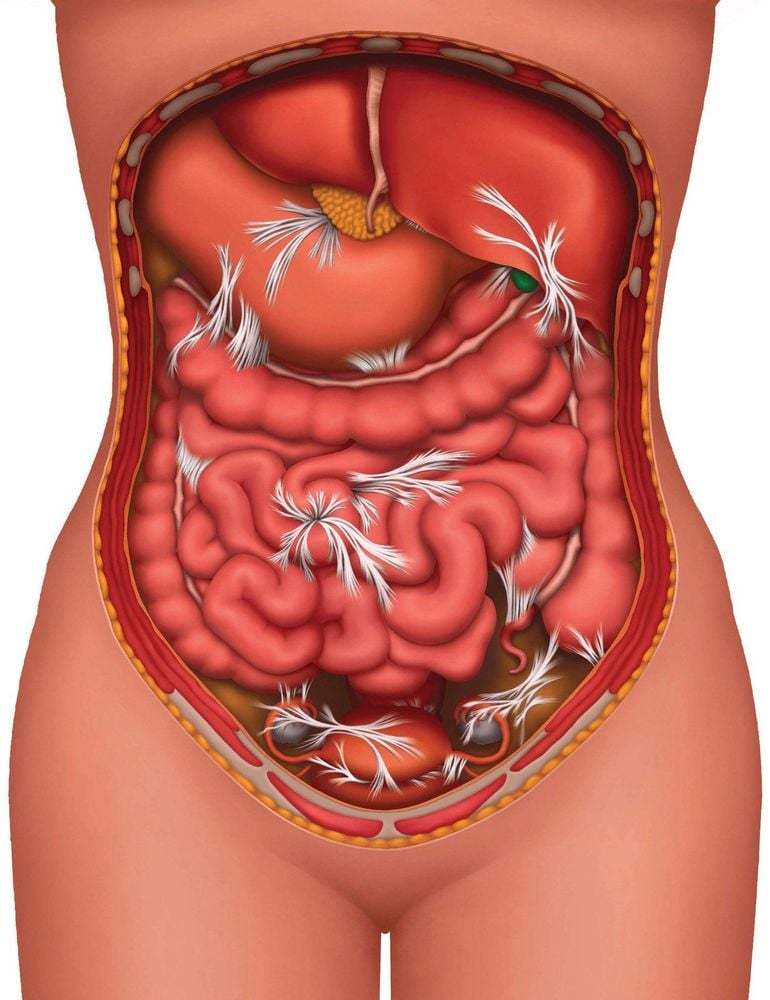
Phúc mạc có các chức năng bao bọc các tạng, che chở và vững chắc cấu trúc của các tạng
4. Abdominal subdivision
The peritoneal folds divide the abdominal cavity into zones. The omentum rotates within the peritoneal cavity forming the omental sac. The transverse mesentery divides the peritoneal cavity into two layers: the upper layer of the transverse mesocolon and the lower layer of the transverse mesocolon. The upper layer of the transverse mesocolonHas liver, stomach, spleen, duodenum, pancreas. The falciform ligament of the liver is divided into two cells called the right subdiaphragm and the left subdiaphragm. The right subdiaphragm or right liver cell descends through the left colonic fissure. The cell below the left diaphragm or the left liver cell, connecting with the stomach and spleen cells.
Lower layer of transverse mesocolon
Mainly jejunum and ileum. The mesentery of the small intestine runs from left to right from top to bottom and divides the lower floor into two cells: right and left.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination, consulting and service services. comprehensive and professional medical treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.