This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Phan Ngoc Toan - Emergency Medicine Doctor - Emergency Department - Vinmec Danang International Hospital. The doctor has a lot of experience in the treatment of Resuscitation - Emergency.Retroperitoneal hematoma is a life-threatening condition. Early diagnosis and correct treatment are extremely important, helping patients avoid the risk of dangerous complications.
1. What is extraperitoneal hematoma?
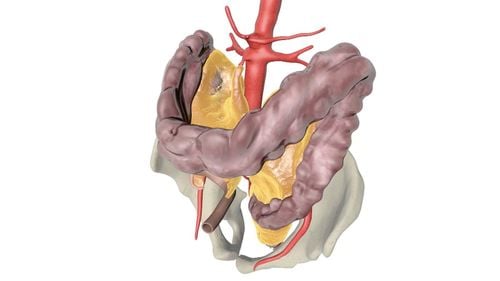
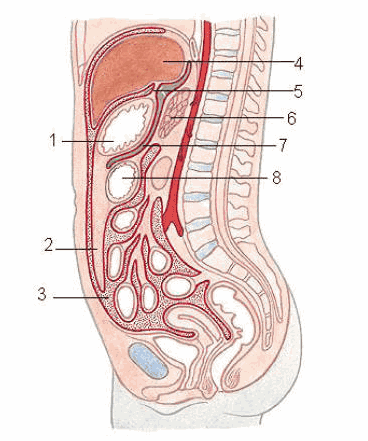
The largest serosa in the body is called the peritoneum. All organs in the abdominal cavity and pelvis, lining the inner wall of the abdomen, the inferior surface of the diaphragm, and the superior surface of the pelvic diaphragm are covered by the peritoneum.Traumatic extraperitoneal hematoma (retroperitoneal hematoma) is a common complication of abdominal or pelvic trauma. The mortality rate due to retroperitoneal hematoma is quite high.
To reduce the mortality rate of extraperitoneal hematoma, early diagnosis and proper treatment are very important.
2. Causes of extraperitoneal hematoma
Some common causes of extraperitoneal hematoma, including:
Spontaneous, post-traumatic, including pelvic trauma, or secondary to other causes such as: ruptured aortic aneurysm, surgery, ruptured tumor. Spontaneous bleeding usually originates from the pararenal space and extends to the preperitoneal, pelvic, and abdominal muscles. Due to the trauma causing bleeding, it is difficult to control when it spreads to the submucosa. Rupture of an abdominal aortic aneurysm limited to the posterior left renal space causes bleeding. Blood flowing from the inferior vena cava flows directly into the posterior right renal space

3. Signs of extraperitoneal hematoma
Signs of extraperitoneal hematoma include:
Abdominal pain Abdominal distention Abdominal muscle mass, back pain, severe lower flank pain Fetal neuropathy However, all symptoms of extraperitoneal hematoma are absent Specifically, this is the cause leading to the difficulties in the diagnosis of post-traumatic hematoma due to the clinical features.
Traumatic extraperitoneal hematoma is a common, life-threatening complication of patients. Therefore, early diagnosis and urgent surgical intervention are extremely important.
4. Diagnosis of extraperitoneal hematoma
CT and ultrasound play an important role in the evaluation of retroperitoneal organs, facilitate the diagnosis of traumatic retroperitoneal hematoma, and help surgeons make surgical decisions. treat. In some cases, ultrasound cannot accurately detect the extent or exact location of visceral trauma, and in addition, its sensitivity to directly demonstrate abdominal trauma is relatively low. Therefore, hemodynamically stable patients with a negative ultrasound diagnosis and high clinical suspicion of abdominal trauma should undergo routine CT. Although there are many advantages in CT, several factors such as the size and location of the hematoma, the radiologist's experience, and the resolution of the CT can affect the accuracy of the diagnosis. Multi-slice CT and angiography are important for the diagnosis of extraperitoneal hematoma.
5. Treatment of extraperitoneal hematoma
If not treated properly, the mortality rate of patients with retroperitoneal hematoma remains high.
There are two treatments for extraperitoneal hematomas:
5.1. Surgery
In the case of penetrating trauma, most retroperitoneal hematomas can be associated with abdominal visceral trauma, and exploratory laparotomy should be performed immediately. In the case of blunt trauma, when visceral trauma cannot be diagnosed with certainty, exploratory laparotomy should be performed, depending on the clinical state of the hematoma. The presence of an enlarged hematoma, an pulsatile mass, and an unexplained abdominal mass suggest the need for surgical exploration. Central retroperitoneal hematoma usually results from trauma to the duodenum, pancreas, or great vessels. The presence of progressive signs and symptoms, increased blood and urine amylase, free gas in the abdominal cavity, and periduodenal or pancreatic effusion suggest duodenal or pancreatic injury, laparoscopic surgery exploration needs to be done. The most common type of retroperitoneal hematoma is located in the pelvis, the main cause is pelvic fracture. Bleeding may cease after appropriate resuscitation and pelvic stabilization, whereas persistent hemodynamic instability may be found in some patients. However, when retroperitoneal hematomas are associated with concomitant damage of the rectum, bladder, or other organs, surgical exploration is important.
5.2. Conservative treatment
Extraperitoneal hematoma in the following cases can be treated conservatively without surgery:
Stable hematomas without causing damage to organs in the central area will be treated with surgical methods conserve. Compared with a central retroperitoneal hematoma, patients with a retroperitoneal hematoma in the lateral region do not necessarily require urgent surgery. Retroperitoneal hematomas due to blunt trauma can be managed conservatively and most patients survive. However, if the hematoma rapidly expands, becomes fragile, or ruptures, it is considered an emergency. In relation to a lateral colonic hematoma, exploratory laparoscopic surgery should be performed to avoid a missed diagnosis of a colonic lesion. In summary, retroperitoneal hematoma is a life-threatening condition, early diagnosis and proper treatment are extremely important. Mandatory exploration should be performed in retroperitoneal hematomas due to penetrating trauma, but the choice of treatment in blunt trauma depends on the anatomical location of the hematoma, visceral trauma and hemodynamic status of the patient.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.