This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Doctor Tran Quoc Tuan - Head of the ICU - ICU - Emergency Resuscitation Department - Vinmec Phu Quoc International General HospitalInflammation occurs frequently to fight harmful agents for the body. However, prolonged, aggravated or frequent inflammation also affects organs in the body.
1. Definition of inflammation
Inflammation plays a protective role and is generally beneficial for the body. Inflammation is the biological response of the whole body against inflammatory agents such as microorganisms, chemical and physical agents) or internal agents (ischemic necrosis, autoimmune diseases). ...). The manifestations of inflammation commonly seen at the site are swelling, heat, redness, pain. There are also inflammatory manifestations inside the body that are invisible to the naked eye to fight inflammatory agents. Diseases are inflammatory conditions such as: hepatitis, appendicitis, colitis, gastric mucosal inflammation, encephalitis, nephritis...Inflammation of the body can be divided into acute inflammation and inflammation chronic. Inflammation can suddenly attack in a short time called acute inflammation, while agents that attack silently for a long time cause chronic inflammation.
Acute inflammation occurs when the inflammatory agent affects the tissue for a short time, causing a short and not long-lasting inflammatory response. Acute inflammation lasts from a few hours to a few days. Acute inflammation can turn into chronic inflammation. The main reaction in acute inflammation is the oozing reaction, in addition, there is often a destructive reaction, if mild, the lesions are degenerative, but in severe cases, they may be necrotic lesions of cells and tissues. Chronic inflammation usually begins with an acute inflammation, however, some chronic inflammation progresses to an acute phase usually manifesting a dull, slow, long-lasting attack as in tuberculosis, the patient only presents with fatigue. Fatigue and low-grade fever, undetermined time of occurrence, onset of symptoms, and no recollection of the acute phase. In addition, it can also be seen in people who are exposed to dust containing siliceous particles, which will lead to chronic silicosis, and this disease is of unknown acute stage.
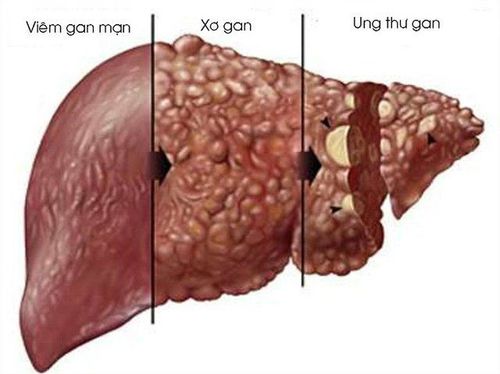
Viêm gan là biểu hiện viêm diễn ra bên trong cơ thể
2. Causes of inflammation
Bacterial infections: Bacteria, viruses, protozoa, fungi and parasites. Chemical agents: Organic, inorganic in industry or in medicine. Physical agents: Foreign bodies, radiation, trauma... Immunity: Hypersensitivity reactions are severe and excessive reactions of the body to foreign antigens such as furs, pollens, and substances. In foods or drugs, the products of hypersensitivity reactions cause inflammatory lesions. In autoimmune diseases such as Hashimoto's thyroiditis, rheumatoid arthritis... Some of the endogenous causes of inflammation are: closed necrotic tissue causing aseptic inflammation, inflammation around cancer tissue, metabolic products Inflammatory chemicals such as blood urea increased causing inflammation of the pleura and pericardium.3. How does inflammation affect the body?
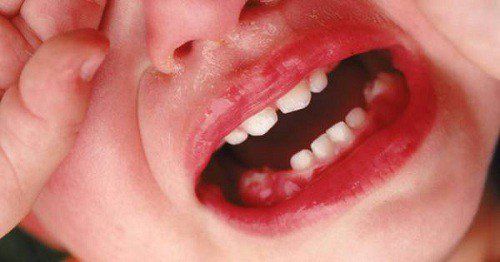
Viêm cơ có thể ảnh hưởng nghiêm trọng đến nướu, lợi
Inflammation can affect a number of problems. Body problems:
Inflammation is not good for the lungs. When inflammation occurs in the lungs, it can lead to fluid buildup in the lungs and narrowing of the airways, making it difficult to breathe. Infections, asthma, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) are all conditions characterized by inflammation in the lungs. Inflammation can damage the gums (gingiva): Inflammation is the cause of periodontal disease – a chronic inflammation of the gums caused by a long-term accumulation of bacteria. Periodontal disease will cause the gums to recede and make the bone structure around the teeth weak and damaged. Inflammation damages the bones: Inflammation throughout the body can impede bone growth and even promote bone loss. Inflammation of the digestive system can also be particularly damaging to bone health, as inflammation in the gut prevents the absorption of nutrients needed for bone growth, such as calcium and vitamins. D. Inflammation Related to Depression: Inflammation can be a cause of depressive symptoms, such as moodiness, loss of appetite, and poor sleep. Inflammation helps the body fight infection: Inflammation is a visible response to help heal a wound or fight an illness. Symptoms of inflammation include: Fever, sore throat, or an open wound that becomes infected and becomes hot, red, and painful to the touch. Swelling, heat, redness, and pain are characteristic of the immune process as the body fights off harmful agents. In this case, inflammation is a healthy response and is necessary to help you heal. However, this type of inflammatory response should only be temporary, once the infection clears up or if you get better, the inflammation should go away as well. Inflammation helps prepare mentally: Instead of blood cells going to part of the body, inflammatory factors release a protein called C-reactive protein (CRP) into the bloodstream and CRP will through the blood throughout the body. This response will greatly increase the body's adrenaline levels and will help the person get out of a potentially life-threatening situation. However, if you are under stress for a long time, the amount of CRP in the body will often stay high. This is a risk factor for many other chronic diseases. Inflammation can damage the gut: Immune cells can start to react to bacteria that are naturally present in the gut, causing chronic inflammation. These immune cells can also attack the digestive system on their own, causing autoimmune diseases such as inflammatory bowel disease, which includes ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. Inflammation can damage joints: When inflammation occurs in joints, it can lead to very serious damage such as rheumatoid arthritis which is also an autoimmune disease that is associated with various medical factors. gene. Inflammation associated with cardiovascular disease: When the body is injured or damaged, it can also lead to inflammation including the blood vessels. The formation of atherosclerotic plaques in the arteries can lead to chronic inflammation. These fatty plaques attract white blood cells and become larger, causing blood clots and leading to a heart attack. Inflammation linked to higher cancer risk: Chronic inflammation has been linked to lung cancer, esophageal cancer, cervical cancer and gastrointestinal cancer. When immune cells initiate an inflammatory response, immune regulation deteriorates and creates a favorable environment for cancer cells to thrive. Inflammation can affect sleep: Inflammation can be the cause of poor sleep or sleeping more than usual.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.