This is an automatically translated article.
Eye electrophysiology includes a wide range of tests that can be used to provide information about the visual system in addition to standard clinical examination of the eye. Accordingly, ophthalmic electromyography (ERG) and ophthalmic electromyography (EOG) are two of the tests conducted in the ophthalmic electrophysiology laboratory. The primary goal of ocular electrophysiological examination is to record electroretinograms, thereby helping to assess the functional integrity of the visual tract.
1. Overview of eye electrophysiology
Vision is the result of electrical signals traveling between the retina and the part of the brain involved with vision (occipital cortex).
Eye electrophysiological tests will help check how well this optic nerve is sending the electrical signals needed for good vision in the brain region. These tests measure the retinal electricity that occurs in the eye when looking at something.
Thus, eye electrophysiology includes various tests to measure retinal activity by electroretinogram recording, which in turn can help check for retinal diseases. These tests can also help diagnose and evaluate various types of problems with vision impairment and general eye health, including:
Electroretinography (ERG)
Electromyography of the eye measures the electrical response of the eye retina when looking at different patterns or flashes of light. The ERG test can check for diseases and problems of the retina.
Full-field ERG can check how well the entire retina is working. Multifocal ERG (mfERG) examines only part of the retina. In addition, this tool can also check for diseases of the macula and loss of central vision.
Electrooculography (EOG)
Electromyography of the eye checks the activity level of electrical currents in the entire eye. This tool is made to check for some eye and retina problems.
Visual Evoked Response (VER)
Evoked potentials test electrical activity in the entire visual pathway, from the eye to the parts of the brain involved with vision.
Like the ERG, this test measures electrical activity as the eye responds to looking at something. The evoked potential test can find problems by showing how brain waves respond to things seen during the test.
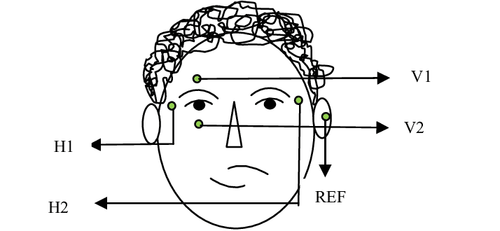
Điện quang mắt là một trong các xét nghiệm điện sinh lý mắt
2. Indications for performance of eye electrophysiological tests
Different eye electrophysiological tests are done for different reasons.
Eye Electromyography (ERG)
Full-field ERG measures the activity of rods and cones. These cells help the body detect light and color. This test also looks at other cells in the retina. As such, an ERG can be done to check for problems such as:
Damage to the retina from drugs or other substances Loss of vision from central or peripheral causes due to retinal damage Night blindness (difficulty seeing) in low light) or color blindness Eye problems caused by whole-field ERG vascular diseases can help find the cause of some retinal problems, such as vitamin A deficiency or metabolic disorders. Multifocal ERG (mfERG) tests for electrical response in the central part of the retina, which can be used to help check for:
Macular diseases for which a full-field ERG is not found Unknown central vision loss cause that a field-wide ERG cannot be found Certain types of retinitis pigmentosa Electromyography (EOG)
EOG is used to help diagnose problems with the retina, may be used to help check for problems topics such as:
Retinal diseases such as Best's disease (congenital macular degeneration) and retinitis pigmentosa
Different forms of macular dystrophy
Evoked potential (VER)
Visual evoked response in VER helps measure how well the entire visual path between the eye and brain is working. The test can be used to check for or evaluate conditions such as retinal problems, optic nerve problems, and multiple sclerosis.
Moreover, the role of VER is also promoted in cases where visual function assessment is required in subjects who cannot respond or have difficulty cooperating in following instructions, such as infants, the elderly.
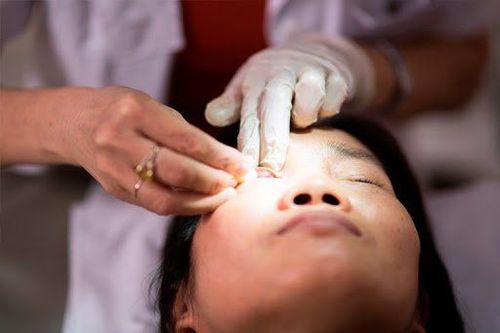
Sau khi thăm khám mắt, bác sĩ sẽ chỉ định đo điện sinh lý mắt tùy theo tình trạng bệnh
3. How to perform eye electrophysiology?
Preparation
The patient hardly needs to do anything special to prepare for the eye electrophysiology test, just prepare the following basic steps:
Follow the doctor's instructions about eating and drinking to prevent blood sugar from falling too low. Avoid caffeine within 12 hours of the test. Wash your hair well before testing. Do not wear any jewelry, such as earrings, near the head. Procedure
How each eye electrophysiology test is performed is different:
Electromyography (ERG)
The position the patient needs to sit or lie down during the test. Eye drops are used to numb the eye, reducing discomfort. A very small electrode is placed on the cornea and on the face. The patient is instructed to look at a screen that displays flashes of light (flash ERG) or an image sample (ERG pattern). The test records the electrical response in the eye when looking at lights and patterns. The electrical activity of the eye is measured on a machine called an electroretinogram. This test is done in both light and dark, known as dark adaptation. Different wavelengths of light are used during the test to check for problems with the cones and rods of the eye. Total execution time is about an hour. Electro-optical measurement (EOG)
Position the patient upright in a chair Very small electrodes are mounted on the inner and outer corners. Another electrode is placed on the forehead. The computer will record two recordings of the electroretinogram taken. After the eyes adjusted to the dark, the electrical response of the eyes was measured when moving the eyes from side to side. When the lights came on, electrical activity was measured again when moving the eyes from side to side (at the same angle). Total time is about 40 to 45 minutes. Evoked potential (VER)
The computer records changes in brain waves when looking at picture patterns. Electrical signals are measured in the visual tract, the area of the brain involved with vision (primary visual cortex).
During the examination:
The patient needs to sit in front of the screen. A patch is placed over one eye. Electrodes are placed on the scalp, near areas of the brain involved with vision. For several minutes, the patient looks at repeating patterns (checkerboard or dotted patterns) that appear as rapidly flashing lights on the screen. The size or intensity of the samples can be changed to test certain parts of the visual field. The recording computer measures the electrical retina of the brain waves as well as the response time (latency) and electrical activity of the brain. A patch is placed on the other eye and the test is repeated similarly.
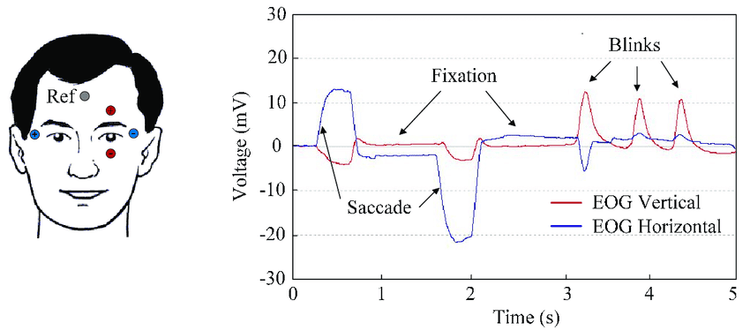
Hình ảnh mô phỏng cách đo điện quang (EOG) trong xét nghiệm điện sinh lý mắt
4. Results of eye electrophysiology
Electromyography (ERG)
ERG helps measure the amplitude (height) of certain brain waves (A and B waves) to detect vision problems. The time from the beginning to the end of the eye's response to a light stimulus is called the latency. Possible results are:
Normal: Normal wave A and wave B and normal delay response time.
Abnormal: Wave A and wave B are abnormal or response time has abnormal delay.
Electromyography (EOG)
EOG test results use a numerical measurement known as the Arden ratio. This is the ratio between the maximum electrical activity of the eye in light and the minimum electrical activity in the dark.
Normal: Arden ratio is in the normal range.
Abnormal: Arden ratio is below normal range.
Evoked potential (VER)
Normal: There is no delay in neurotransmission in the brain's visual pathways.
Abnormal: There is a delay between eye stimulation and nerve response. Abnormal results can be a sign of problems in the visual pathway between the eye and brain.
In summary, ophthalmic electrophysiology is used to diagnose and monitor the progression of disorders affecting vision similar to how electrocardiogram (ECG) recording is used to monitor heart disease. The retina of the eye, optical pathways in the brain and visual cortex produce electrical signals that can be recorded directly from the eye or measured by a computer. From there, the results of the electroretinogram show where the abnormality is on the optic nerve pathway to guide appropriate treatment.
If you have a need for consultation and examination at Vinmec Hospitals under the national health system, please book an appointment on the website (vinmec.com) for the best service.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.