This is an automatically translated article.
Caffeine is a drink that many people use as a stimulant to become more awake, but now there is a lot of controversy about whether daily caffeine consumption is good or bad for health?
1. What is caffeine?
Caffeine is a natural stimulant found in tea, coffee and cocoa plants. They work by stimulating the brain and central nervous system, keeping people awake and preventing fatigue. The Ethiopian shepherd was the first to discover this stimulant, noticing the extra energy it gave his goats. Today, more than three-quarters of the world's population consumes a caffeine-containing product every day, and this figure goes up to 90% for adults in North America.
Caffeine is a bitter white substance that occurs naturally in more than 60 plants, including coffee beans, tea leaves, and cocoa pods (used to make chocolate). The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) considers caffeine to be both a food additive and a drug.
The most common sources of caffeine for most people are coffee, tea, soda, and chocolate. The amount of caffeine in foods and beverages varies. For coffee and tea, the amount of caffeine per cup depends on the brand, the type of bean or leaf used, how it was prepared, and its length. Most sodas, not just colas, contain caffeine. Energy drinks are growing in popularity, especially among teenagers and young adults. The caffeine content in these drinks ranges from 60 mg to over 250 mg per serving.

Caffeine có trong cà phê
Trắc nghiệm dành riêng cho người mắc đái tháo đường: Chế độ ăn của bạn đã hợp lý chưa?
Người bị bệnh đái tháo đường cần phải quan tâm nhiều hơn đến cách tính toán khẩu phần ăn sao cho phù hợp với nhu cầu và tình trạng sức khỏe. Nếu chưa rõ, bạn có thể tìm hiểu kỹ hơn thông qua bài trắc nghiệm ngắn sau đây.2. The mechanism of action of caffeine
Once tolerated, caffeine is quickly absorbed from the intestines into the bloodstream. From there, they go to the liver and are broken down into compounds that can affect the function of various organs especially the brain. Caffeine works by blocking the effects of adenosine, a neurotransmitter that relaxes the brain and makes you feel tired. Normally, adenosine levels build up day by day, making you increasingly tired and making you want to go to sleep. Accordingly, they keep you awake by connecting to adenosine receptors in the brain without activating, blocking the effects of adenosine, leading to reduced fatigue. They can also increase blood adrenaline levels and increase brain activity of the neurotransmitters dopamine and norepinephrine. This further stimulates the brain and promotes a state of excitement, alertness and focus. Because it affects the brain, caffeine is often referred to as a psychoactive drug. Also, caffeine tends to work quickly. For example, the amount found in one cup of coffee can take as little as 20 minutes to reach the bloodstream and about an hour to reach the full effect.
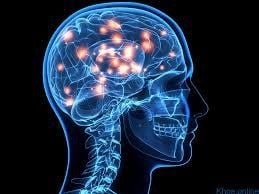
Caffeine tác động lên hệ thần kinh trung ương
3. Effects of Caffeine on the Body
Many of us rely on a morning cup of coffee or a little caffeine in the afternoon to keep us awake all day. Caffeine is widely available, and about 80 percent of Americans use some form of caffeine every day. But caffeine doesn't just keep you awake. It is a central nervous system stimulant that affects the body in many ways. Example:
3.1 Improves mood and brain function Caffeine has the ability to block the brain signaling molecule adenosine, causing an increase in other signaling molecules, such as dopamine and norepinephrine. This change is beneficial for mood and brain function. Studies have shown that caffeine helps to stay awake, reduce the risk of suicide, and avoid depression. However, research has also shown that a second cup of coffee offers no further benefits unless it is consumed at least 8 hours after the first cup. Accordingly, drinking about 3 to 5 cups of coffee a day can also reduce the risk of brain diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's.

Caffeine giúp người dùng tỉnh táo
3.2 Caffeine can aid in boosting metabolism and speeding up weight loss Due to its central nervous system stimulant, caffeine can increase metabolism by up to 11% and fat burning by up to 13%. In fact, consuming 300 mg of caffeine per day can allow you to burn an extra 79 calories per day.
3.3 Caffeine can enhance exercise performance When exercising, caffeine increases the use of fat for fuel. This is very beneficial as it can help the glucose stored in the muscle last longer, potentially delaying the time it takes for the muscle to reach exhaustion. Caffeine can also improve muscle contraction and increase fatigue tolerance. Researchers observed that a dose of 2.3 mg/lb (5 mg/kg) of body weight improved endurance performance by up to 5%, when consumed an hour before exercise .

Caffeine tăng sức bền trong luyện tập thể dục
3.4 Caffeine protects against heart disease and type 2 diabetes Caffeine does not increase heart disease risk. In fact, recent evidence suggests a lower risk of heart disease in men and women if they drink one to four cups of coffee a day. Other studies show that drinking 2-4 cups of coffee or green tea per day is associated with a lower risk of stroke. Caffeine can increase blood pressure. However, this effect is usually small and tends to fade away for most individuals as they consume coffee regularly. Caffeine may also protect against diabetes. A recent review notes that people who drink a lot of coffee have a lower risk of type 2 diabetes. Consumption of decaffeinated coffee has also been linked to a reduced risk of diabetes.
3.5 Other health benefits Protects the liver: Coffee can reduce the risk of liver damage (cirrhosis) by up to 84%, slow disease progression and improve response to treatment. Increases life expectancy: Drinking coffee can reduce the risk of premature death by up to 30%, especially for women and diabetics. Reduces cancer risk: 2 cups of coffee a day can reduce the risk of liver cancer and colorectal cancer by up to 64%. Protects skin: Consuming 4 or more cups of caffeinated coffee per day can reduce the risk of skin cancer by 20%. Reduced risk of multiple sclerosis (MS): Coffee drinkers may have a lower risk of multiple sclerosis. Prevents Gout: Regular intake of four cups of coffee a day can reduce the risk of gout by 40% in men and 57% in women. Supports gut health: Consuming 3 cups of coffee a day for 3 weeks can increase the number and activity of beneficial bacteria in the gut.

Tăng tuổi thọ nhờ caffeine
4. Safety and side effects
Caffeine can be addictive and some people's genes are sensitive to it. Some of the side effects associated with too much caffeine include anxiety, restlessness, tremors, irregular heartbeat, and trouble sleeping. Too much caffeine can also cause headaches, migraines, high blood pressure in some people, cause confusion, hallucinations, vomiting, or can lead to death from seizures. In addition, caffeine can easily crosses the placenta, which can increase the risk of miscarriage or low birth weight. Pregnant women should limit caffeine consumption. It's worth noting that caffeine can interact with some medications. Accordingly, patients who are taking the muscle relaxer Zanaflex or the antidepressant Luvox should avoid caffeine because these drugs can increase its effects.
It is safe to consume 400 mg of caffeine per day. The equivalent of 2 or 4 cups of coffee a day, but an overdose can be fatal. Therefore, it is advisable to limit the amount of caffeine consumed at once to 200 mg at a time. Pregnant women should limit their daily intake to 200 mg.

Người dùng cần sử dụng caffein một cách hài hòa
Caffeine is not as harmful to health as we once thought. In fact, evidence suggests it may be the opposite. Therefore, it's safe to consider your daily cup of coffee or tea as a fun way to boost your health. However, you should still use it in moderation, not abuse it as a stimulant to help you stay awake every day.
References: healthline.com, my.clevelandclinic.org
MORE:
Caffeine – truths and myths Can Keto coffee help you lose weight? Caffeine: How much is too much?













