This is an automatically translated article.
When a person has acute respiratory failure, the normal exchange of oxygen and CO2 in the lungs does not occur. The body does not have enough oxygen to supply the heart, brain, or the rest of the body. This can cause symptoms such as shortness of breath, cyanosis of the face and lips, and disturbances in consciousness.
1. What is acute respiratory failure?
Respiratory failure is an acute decrease in the ventilation function of the respiratory apparatus and/or the gas exchange function of the lungs. What is acute respiratory failure? Acute respiratory failure is defined as severe disturbance of oxygen exchange in the blood; Arterial oxygen partial pressure decreases (PaO2) < 60 mmHg, arterial CO2 partial pressure (PaCO2) may be normal, decreased or increased.
There are 2 types of acute respiratory failure:
Acute respiratory failure with hypoxia without CO2 retention Acute respiratory failure with hypoxia with hypoxia
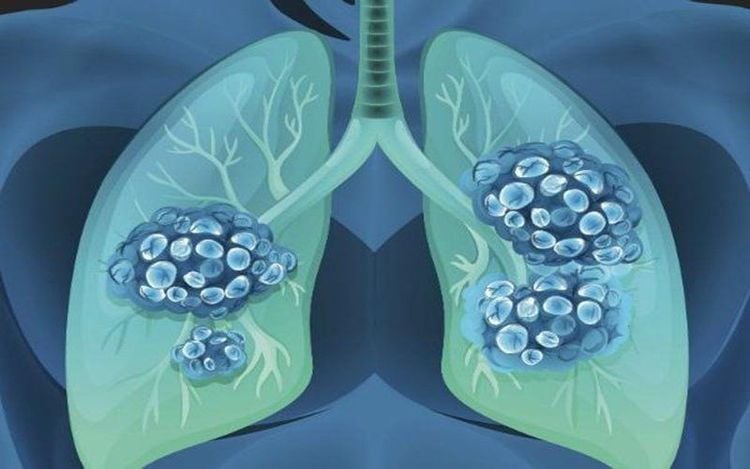
Suy hô hấp khiến người bệnh khó thở, thiếu máu
2. Causes of acute respiratory failure
2.1 Pulmonary causes
Acute decompensation of chronic respiratory failure: Some favorable factors cause acute respiratory failure such as bronchopulmonary infection, pulmonary artery obstruction, pneumothorax. Infectious lung disease: Occurs on the lungs of healthy people, it only causes acute respiratory failure when the lung infection spreads to many lobes or bronchiolitis caused by bacteria, tuberculosis, and malignant viral infection. Acute pulmonary edema: Acute cardiac pulmonary edema: persistent hypertension or hypertensive crisis, coronary insufficiency, myocardial infarction, aortic regurgitation, mitral regurgitation, cardiomyopathy, mitral stenosis , pulmonary embolism Acute pulmonary edema on benign cardiac: excessive fluid infusion causes increased capillary pressure. Neurological causes: traumatic brain injury, tumor or surgery with brain stem damage, encephalitis Injured pulmonary edema: first of all, malignant influenza is caused by many factors: viruses, local factors, because severe forms seen mainly in people with left heart disease, mitral stenosis, especially in the elderly, pregnant women; in children with severe viral infections in the form of bronchiolitis-alveolitis. Less commonly due to toxicity (heroin, carbon monoxide, venom), septic shock, fat embolism, drowning, Mendelson's syndrome (aspiration of gastric juice from belching). Severe bronchial asthma: This is a common disease, usually due to improper or untimely treatment. May be due to the patient's location is prone to severe asthma Acute bronchial obstruction: This disease is uncommon, in children it may be caused by a foreign body, in adults it may be caused by a tumor, acute atelectasis may be caused by intubation manage .
2.2 Extrapulmonary causes
Central nervous system Due to side effects of some drugs: sedation, sleep, anesthesia; The respiratory regulation center in the medulla oblongata is damaged: trauma, cerebrovascular disease, hypothyroidism; Sleep-related respiratory disorders: central sleep apnea, obesity-induced hypoventilation syndrome; Increased intracranial pressure; Central nervous system infections; Idiopathic hypoventilation syndrome. Obstruction of the larynx - trachea: Due to laryngeal tumor, sunken thyroid goiter, esophageal tumor, due to infection such as laryngitis, tetanus; due to large foreign body; Pleural effusion: causes acute respiratory failure when the effusion is acute, the volume of fluid increases rapidly. . Thoracic trauma: Causes broken ribs, thereby causing damage to the pleura and lungs Respiratory muscle damage: Common causes are anterior keratitis of the spinal cord, Guillain Barré syndrome with acute Landry paralysis, tetanus, snakebite , organophosphorus pesticide poisoning, severe myasthenia gravis, polymyositis.
3. Symptoms of acute respiratory failure
Breathing rate: Lack of oxygen and/or hypercapnia causes the patient to breathe rapidly, the respiratory rate is about 40 times/minute in combination with the contraction of the respiratory muscles, clearly visible in the upper sternal cavity and the intercostal spaces; In children, it may be accompanied by a bulging nose. In cases of paralytic lesions (polyneuritis, quadriplegia due to spinal cord injury, severe myasthenia gravis...), respiratory rate is often reduced, respiratory amplitude is weak, patient does not cough. , thereby causing sputum sputum in the bronchi. Cyanosis: this is the main symptom, appearing on the lips, fingertips, feet, face or whole body. Cyanosis is more pronounced when blood hemoglobin is high (in chronic respiratory failure); cyanosis is not evident in severe anemia. Purple is often associated with hypercapnia, cyanosis is accompanied by vasodilation in the extremities, sometimes with sweating. Circulatory symptoms: tachycardia, hypertensive crisis and increased cardiac output, may have supraventricular arrhythmias, later blood pressure may drop. Symptoms of acute right heart failure: Especially common in acute exacerbations of chronic respiratory failure. The main symptoms are: hepatomegaly, jugular venous reflexes (+), more severe than spontaneous cervical veins (in position 45), these symptoms subside when acute respiratory failure subsides. Neuropsychiatric symptoms: This symptom is only seen in severe acute respiratory failure; it is a state of excitement, irritability, disturbances of consciousness such as lethargy or coma.
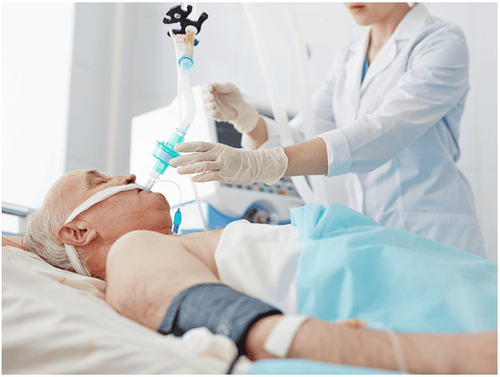
Đối với bệnh nhân suy hô hấp, cần được cấp cứu và thực hiện các biện pháp hồi sức hô hấp ngay lập tức
4. Subclinical tests in the diagnosis of acute respiratory failure
Chest X-ray: very meaningful in diagnostic orientation. Electrocardiogram: helps diagnose some heart diseases and find electrocardiographic signs of lung disease, arrhythmias due to respiratory failure... Other possible tests: Blood count Echocardiogram, electrocardiogram Cardiac, Nt-ProBNP Lower extremity venous ultrasound, D-dimer Pulmonary perfusion ventilation, CT lung scan CT or cranial magnetic resonance and/or spinal cord Electromyography, lumbar puncture Organic phosphorus test muscle, MetHb,...
5. How to treat acute respiratory failure?
For patients with respiratory failure, need to be given emergency care and perform respiratory resuscitation measures immediately, the more urgent the patient's chances of survival are higher.
5.1 Pleural drainage
Indicated in the syndromes of pneumothorax, pneumomediastinum and in hemothorax, pleural effusion. In case of bronchial rupture, tear, large pneumothorax, ineffective drainage, urgent surgical intervention and Carlens tube or endobronchial intubation are required.
5.2 Clearing the air passage
Procedures in opening the airways include:
Hook mouth, nose, throat, wipe clean, suck out soil, sand, mud, food, blood, etc. Lift jaw, put Mayo canu to raise tongue, place head Very backward tilting - or pulling the tongue out when the tongue is retracted - is typical in maxillofacial trauma. Thread the polyester wire through the ring armor. In patients with extensive obstruction of sputum that cannot be aspirated in time and cannot be completely drained, a polyethylene wire can be threaded through the cricothyroid membrane into the trachea and deep down into the carena to stimulate the cough to expel the sputum and thereby inject an expectorant. sputum, antibiotics into the respiratory tract. Extensive suction of sputum, blood and pus in the trachea - bronchial Intubation, tracheostomy: these are the most basic procedures to open the airways.
5.3 Tracheostomy
Indicated in the case of patients:
There are obstacles in the upper respiratory tract that cannot be resolved by the above methods such as: laryngospasm, laryngeal edema, laryngeal ulcers (diphtheria), laryngeal wound; Long-term mechanical ventilation; When it is necessary to reduce dead space to increase alveolar ventilation.
5.4 Intubation
Intubation with indications similar to tracheostomy. There are two methods of intubation: through the mouth and through the nose.
The oral method is easy and fast to place, but requires a laryngoscope, the patient can bite the tube and it is difficult to clean the teeth. Nasal placement can be done without an illuminator, and may take longer. The disadvantage of this method is that it causes ulcers, nosebleeds, more difficult care, and more easily blocked tubes.
5.5 Respiratory support, artificial respiration
This method is performed on patients with hypoventilation. There are many methods of artificial respiration such as:
CPR: Performed in first aid outside the hospital, at the accident site. This method is simple, but effective, and has saved many patients with cardiac arrest, stopped breathing, thanks to breathing in combination with chest compressions, it has timely shortened the time of brain hypoxia. complete recovery of the cerebral cortex. Mechanical ventilation: indicated when conventional methods of respiratory support are unsuccessful. There are 2 types of machines: Pressure breathing, volume breathing
5.6 Oxygen therapy
Applied to patients breathing when hypoxic, in case of both hypoxia and melancholia, the patient must breathe well, expelling excess CO2 out before breathing oxygen.
Commonly used methods of breathing oxygen:
Breathing oxygen through the nose; Breathe through the mask; Oxygen in a tent or incubator; Hyperbaric oxygen inhalation.
5.7 Bronchoalveolar lavage
This trick is easy to do and works. However, the patient needs to breathe 100% oxygen at least 20 minutes before the procedure. Inject through the endotracheal tube 20-0ml of distilled water, insert the flexible suction cannula, at least two sizes (large and small) suction in multiple positions. Occasionally give the patient oxygen or a balloon stove. Time: Do not last more than 4 minutes.
Bronchoalveolar lavage combined with thoracotomy, supportive cough are positive measures to loosen phlegm.
5.8 Anti-acidosis
Drip infusion of alkaline solutions such as sodium bicarbonate or THAM.
5.9 Respiratory stimulants
Only indicated after the patient's airway is clear and the patient must be oxygenated. These drugs have a good effect on patients with chronic respiratory failure, acute respiratory failure.
5.10 Use of antibiotics
Use antibiotics when there are signs of infection (pneumonia, exacerbation of COPD with evidence of infection).

Ngừng hút thuốc là biện pháp cần thiết để bảo vệ lá phổi của bạn.
6. How to prevent acute respiratory failure?
Not all causes of acute respiratory failure are preventable, eg traumatic respiratory failure. However, in the case of respiratory failure due to pneumonia and some other airway related diseases, everyone can take some precautions below to protect their lungs:
Limit smoking , because secondhand smoke can damage the lungs; See your doctor for signs of a bacterial infection, such as fever, cough, and increased mucus production; Adhere well to taking medication for respiratory failure to keep the heart and lungs healthy; Maintain appropriate physical activity to enhance lung function. Acute respiratory failure is a serious medical condition that has many potential causes. Symptoms include confusion, rapid breathing, shortness of breath, cyanosis. Patients should be hospitalized at the first signs of respiratory failure to prevent further deterioration.
Vinmec International General Hospital is currently the address for examination, diagnosis and treatment of acute respiratory failure trusted by many customers.
At Vinmec gathers a team of experts, pediatricians, pharmacists and nurses with high qualifications, good expertise, a lot of experience, especially dedicated and professional attitude.
With the full support of many modern technical means, Vinmec always ensures to provide the most comprehensive and effective health care services. Professional medical examination, consultation and treatment service, space Medical examination and treatment focuses on civility, courtesy, safety and maximum sterilization. For details and to book an appointment for examination and consultation, customers can call hotlines of hospitals or register for online consultations. with Vinmec HERE.