This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with Doctor Nguyen Thi Man - Obstetrician and Gynecologist - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.In the absence of complications, pregnant women should give birth at 38-41 weeks.
1. Factors determining the time of birth with gestational diabetes
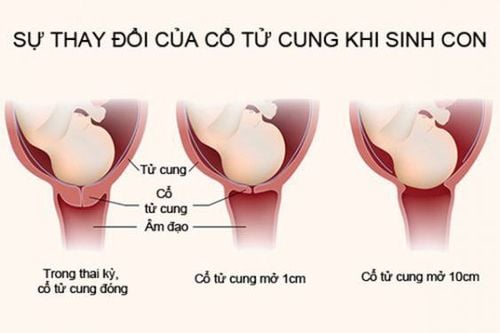
Based on the results of the medical examination for the mother, the obstetrician will decide at what week is the best time to give birth with gestational diabetes. In case no complications are detected, pregnant women should give birth at 38-41 weeks to prevent some risks when people with gestational diabetes are born prematurely (under 38 weeks).However, if the ultrasound shows that the baby is already large, it can be delivered before the 38th week. Some women with gestational diabetes give birth before 37 weeks, so delay the delivery until about 38 weeks. -41 and try to avoid caesarean section.
In case through clinical examination and ultrasound, it is found that the fetus is large, specifically larger than 4.2 kg, then a cesarean section should be indicated. If not, it can cause a few risks, including:
Big baby will be prone to injury, shoulder dislocation Fetal suffocation: Maternal blood sugar during labor is higher than 8.3 mmol/l This means that the baby will be deprived of oxygen. Fetal heart failure due to difficult birth, prolonged delivery time, or ketoacidosis. Therefore, during labor, medical staff still need to continuously monitor the baby. Monitor fetal heart rate and blood sugar status for timely adjustment and treatment. In addition, induced delivery is another option that both supports the mother giving birth naturally thanks to the labor stimulant that is passed into the lower birth canal, while reducing the rate of serious complications to a lower level.

2. Common risks when pregnant women have gestational diabetes
2.1 Acute respiratory failure
If the pregnant woman does not actively control her blood sugar well, there is a high risk that the fetus's lungs are not fully developed. This is the cause of the baby's acute respiratory failure within the first week after birth. Common symptoms of this disease are: rapid breathing over 60 times/minute, wheezing, chest and abdominal cramps, cyanosis...However, nowadays with advanced development According to modern medicine, the amniotic fluid test results also help to know whether the baby's lungs are fully mature or not to limit the cases of gestational diabetes born prematurely.
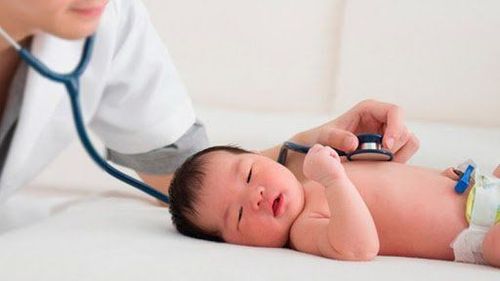
2.2 Lower blood sugar
Hyperinsulinemia puts the newborn at risk of hypoglycemia in the first 48 hours after birth, specifically below 1.7 mmol/l (while in adults, the reading is lower than 2.8 mmol/l). l is considered hypoglycemia). Common signs of low blood sugar in the fetus are:Coma instead of crying loudly at birth May stop breathing or rapid breathing The body is blue, there are signs of convulsions There are also cases where the baby has low blood sugar blood but looks healthy. Oral administration of a glucose solution or a nasogastric tube approximately 1 hour after delivery is the usual prevention of hypoglycaemia. If the above method does not work, the child can be given intravenous glucose infusion.
Other disorders that can be mentioned in babies of mothers with gestational diabetes include: hypocalcemia, jaundice, polycythemia vera and poor appetite. The cause of these complications can be due to the increased blood sugar and insulin of the fetus, sometimes related to the period of hypoxia during birth.
In summary, how many weeks pregnant women with gestational diabetes should give birth depends on the health status and development of the fetus. To avoid preterm gestational diabetes or other unforeseen risks, the best way is to always keep a woman's blood sugar at an appropriate level. Besides, women also do not forget to have regular antenatal checkups on schedule and follow the advice of obstetricians to maintain a safe pregnancy and help the baby stay healthy.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.