This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Huy Nhat - Respiratory Doctor - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Danang International General HospitalRespiratory failure is one of the most dangerous and unpredictable conditions today. They can happen suddenly, with no warning signs, but sometimes it happens so gradually that many patients are subjective until the symptoms become more obvious.
1. When is it called respiratory failure?
Respiratory failure is a condition in which your lungs have difficulty exchanging oxygen and carbon dioxide with the blood. It can leave you with low oxygen and/or high carbon dioxide.2. Common types of respiratory failure
Acute respiratory failure : This is a condition of respiratory failure that occurs rapidly, this is an emergency, the patient needs immediate emergency care. Chronic respiratory failure: A long-term respiratory failure that requires regular care and monitoring.
3. Causes of respiratory failure
Breathing may seem like a simple act, but there are many moving parts to achieve the action. When one of those parts fails, it can lead to respiratory failure, including:Trauma to the chest or ribs. Using a drug or drinking too much alcohol can damage the brain, which in turn affects breathing. Lung damage from inhaling smoke or dust. Lung diseases such as: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), cystic fibrosis, pneumonia,... Muscle and nerve damage from other medical conditions such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) , spinal cord injury and stroke . Scoliosis or other spinal problems can affect the bones and muscles involved in breathing. Reduced blood flow to the lungs, possibly due to a blood clot.
4. Risk factors for respiratory failure
You may be at higher risk of respiratory failure if you have one of the following conditions:Have a chronic respiratory disease such as COPD, asthma . Constantly exposed to toxic dust. Drink a lot of alcohol. There is a family history of respiratory problems.
5. Symptoms of respiratory failure
Symptoms also depend on the cause of the disease and the degree of hypoxia, high carbon dioxide levels, or both. Some symptoms that the patient may notice are:Bluish skin, lips and nails. Feeling that I can't get enough air. Feeling bewildered. Heart rate decreases. Fast breathing or extremely slow breathing. Shortness of breath, effort to breathe. Drowsiness or possible unconsciousness.
6. Diagnosis of respiratory failure
The doctor will start with a physical exam, asking questions about the patient's health. The patient may then have one or two of the following tests:Check blood oxygen levels with a small device on the patient's finger or ear. Arterial blood gas test: This basic blood test shows the level of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the patient's blood. In addition, the doctor may need to do other tests to find the cause of the patient's respiratory failure. Those tests are:
Chest X-ray Electrocardiogram....
7. Treatment of respiratory failure
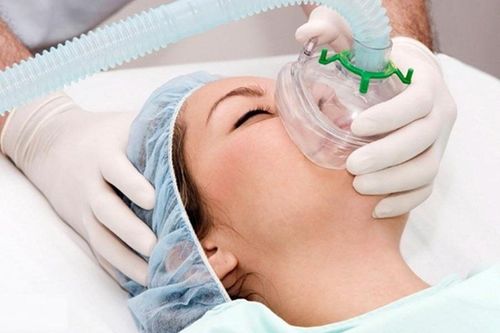
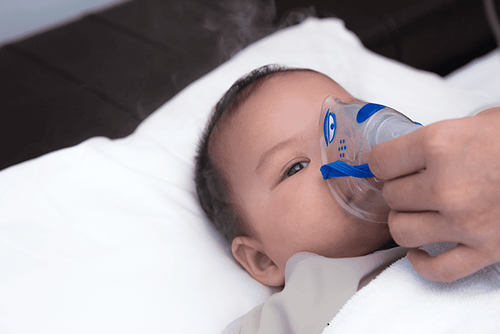
Depending on the condition of each specific patient, the treatment method can be one or more measures at the same time. Measures to treat respiratory failure include:Oxygen therapy: The patient is given oxygen through a mask or a tube with two branches placed on either side of the nose. Patients may have a portable oxygen tank so they can go out with it. Ventilator: Patients may need to use a ventilator if oxygen therapy does not provide enough oxygen or the patient is unable to breathe on their own. The ventilator will help push air into the patient's lungs, so that they get the oxygen they need without having to work to breathe as usual. The machine also helps reduce carbon dioxide. Some patients may have a mask over their nose or mouth along with a CPAP (Continuous Positive Airway Pressure) machine used for sleep apnea. Tracheostomy: this is a surgery in which the doctor makes an opening in the neck and windpipe to place a small catheter to make breathing easier. This catheter can be connected directly to the ventilator if the patient needs the ventilator for more than a week or two. Treating the cause: Once the cause of the respiratory failure has been identified, a combination of treatment for both the respiratory failure and its cause must be combined. Depending on the cause, there will be appropriate treatment measures, such as: using antibiotics to treat pneumonia, using drugs to dissolve blood clots, using airway relaxants. Thoracic tube to drain blood or air in case of trauma causing pneumothorax/pleural effusion. Treatment depends on the cause and whether the respiratory failure is acute or chronic. Different cases cannot be treated in the same way.
Treatment of acute respiratory failure is as follows:
This is a case where the patient needs to be taken to the emergency room immediately. If the problem is resolved, the patient can be discharged early. With severe symptoms, the patient may be taken to the intensive care unit. The patient can be treated with oxygen, possibly requiring a ventilator until he can breathe on his own. With that, patients can be treated with medications and fluids to ease the symptoms and causes of respiratory failure. Treatment of chronic respiratory failure is as follows:
The patient can receive ongoing care at home. Treatment is usually the use of medications every day. In severe cases, patients may also need oxygen therapy. Respiratory failure can make it difficult for patients to sleep, so they may need extra help at night. This means you may need one of the smaller ventilators such as a CPAP machine, which, in more severe cases, will require a ventilator at night.
8. Prognosis of respiratory failure
Acute respiratory failure, if treated immediately, can help the patient return to normal activities. Patients with chronic respiratory failure should follow their physician's advice for continuity of care. People need to know their symptoms and know when to see a doctor.Respiratory failure can be divided into many different types, the most common today is the division of acute respiratory failure and chronic respiratory failure. Depending on the type of respiratory failure, the cause and the extent of the damage, the doctor will choose the appropriate treatment method and have a different prognosis.
Respiratory failure is a dangerous disease and can leave many complications, to prevent dangerous complications caused by the disease, patients need to be treated in hospitals with high reputation and quality. expertise and comprehensive health care services like the Vinmec International General Hospital system. Here, there is a full team of leading doctors and nurses in the country, dignified and polite facilities, a system of modern machinery, medical instruments are sterile according to international standards, bringing maximum safety. for patients to visit and treat.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: webmd.com