This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Tong Diu Huong - Radiologist - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.X-ray is an imaging technique that helps to provide clear images of the inside of the patient's body. Today, along with the development of modern technology, X-ray techniques play an increasingly important role in disease diagnosis and treatment.
1. Learn about the Schuler position radiography technique
Schuller position X-ray is an imaging technique used to expose the two sides of the septum of the striatum, the temporomandibular joint, and the atrial fascia, making it easier for doctors to evaluate. damage to the temporomandibular joint and the mastoid sinus in patients.
1.1 Indications and contraindications to Schuller position X-ray
The doctor will appoint the patient to take Schuller position X-ray in the following cases:
There are signs of underdevelopment of the ear Injury, suspected fracture of the stone bone Cholesteatoma in the ear Neuroma VIII Have temporomandibular joint disease Have semicircular canal fistula Acute and chronic otitis media Contraindications: No absolute contraindications, contraindications to Schuller position X-ray in women pregnant
1.2 Schuller X-ray procedure
Step 1: The technician prepares supplies, the patient removes jewelry (necklace, earrings) if any.
Step 2: Carry out the scan: The patient lies on his back, the body is tilted towards the side to be taken and the opposite shoulder is elevated. The frontal plane is parallel to the film, the head is slightly bent so that the Virchow plane is parallel to the upper border of the film, the ear hole is in the middle of the film. The central ray lies in the plane through the ear, the ray hits the point 7cm from the opposite ear, 25-30 degrees down to the foot and goes to the side of the ear on the right side to be photographed. Take 2 times at the time of opening and closing the mouth to examine the temporomandibular joint.
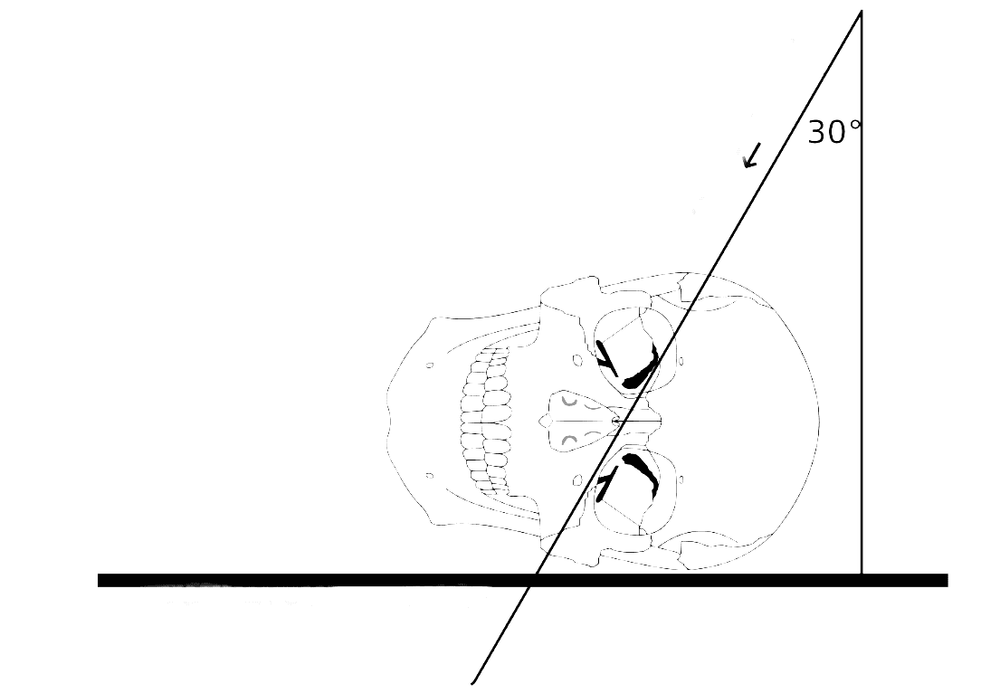
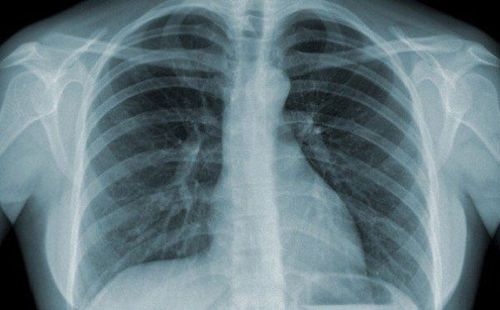
X quang tư thế Schuller
1.3 Evaluation of the results of the Schuller position X-ray
Normal results: The septum and ossicles are clearly visible. Abnormal results: The septum is opaque, the septum is not clear in acute mastoiditis. or translucent cells, the septum is lost, there are bright areas, around the edges are blurred, sharp edges, clear like clouds.
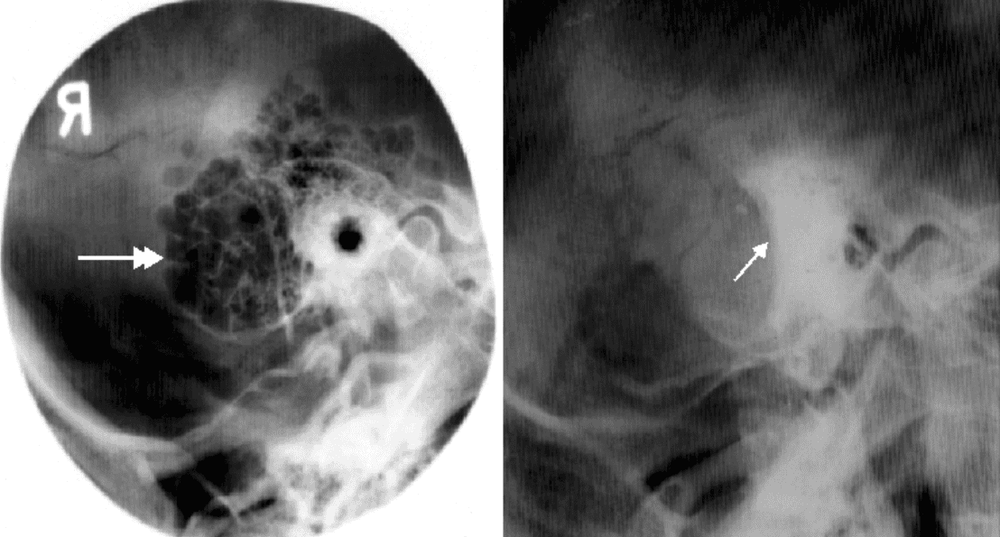
Kết quả chụp X quang tư thế Schuller
2. Learn the technique of X-ray taking the Chaussé III position
Like the Schuler position radiograph, the Chaussé III radiograph is intended to expose the two sides of the striatum and the atrial septum, but the results are often complementary to the Schuller imaging technique in assessment of mastoid sinus lesions.
2.1 Indications and contraindications to X-ray Chaussé III position
Indication for X-ray Chaussé III position in the case of:
Acute and chronic otitis media The ear does not grow Ectopic epidermoid tumor of the middle ear or mastoid fistula Semicircular canal tumor VIII cranial nerve trauma Suspicious fracture of the rock bone. Contraindications to X-ray Chaussé III position: There are no absolute contraindications, temporary contraindications for pregnant women
U dây thần kinh VII
2.2 Chaussé III X-ray procedure
Step 1: The technician prepares supplies, the patient removes jewelry (necklace, earrings) if any.
Step 2: Prepare 18x24cm film, place it vertically on the shooting table.
Step 3: The patient lies supine on the imaging table, legs extended, arms down to the body. Place the occipital in the center of the film. Align the front plane perpendicular to the film. Adjust the seam connecting the two outer ear holes parallel to the film. The patient's face is slightly bowed.
Step 4: Select the central ray:
Then 1: Shine at an angle so that the vertical line passes through the outer edge of the patient's eye socket 2cm and the horizontal line passes through the temporal fossa and the rim of the ear. Central ray to the outer end of the brow arch. Stage 2: Fixing the occipital head rotate the head slowly to the side without the need to capture so that the central ray enters the temporal fossa on the side to be photographed (about 1/3 between the line connecting the tail of the eye and the auricle). The scan results were successful when the mastoid cells were clearly seen in the middle of the film and were fully visible with the paracavernous cells, superior semicircular canal, and extra-vestibular semicircular canal.
X-ray of Chaussé III position is a simple technique, without complications, however, if the patient cannot keep still during the imaging process, the joint image will not be clearly revealed, so he will have to perform the technique again.
X-ray techniques as well as many other medical examination and treatment techniques at Vinmec International General Hospital are conducted by a team of highly qualified and experienced medical doctors; the system of advanced and modern machinery should significantly reduce radiation dose with the best image and always be updated according to medical progress in the world; Especially, professional service quality will help customers have the most comfortable and secure experience when visiting Vinmec. To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE
SEE MORE
Relationship between X-rays and Pregnancy What is an X-ray of the uterus and fallopian tubes (HSG)? Mammomat Inspiration X-ray machine - An effective "assistant" in the diagnosis and treatment of breast tumors