This is an automatically translated article.
Eggplant is a type of eggplant that belongs to the white family and is used in many different dishes around the world. Although they vary in size and color, eggplants with deep purple skin are the most common. In addition to bringing a unique texture and mild flavor to recipes, eggplant is also a fruit with many health benefits, including reducing obesity.
1. Eggplant Overview
Although often thought of as a vegetable, eggplant is, in essence, a fruit, as eggplants grow from flowering plants and contain seeds. Usually, people only know about the glossy, purple, teardrop-shaped eggplant because they are in fact the most common type of eggplant, however, this versatile vegetable comes in a variety of colors and shapes. difference. Dig a little deeper at local farmers markets around the world and you can find oval, long, slender eggplants or melon-shaped eggplants with white, green skins. , pink, orange and even striped.
When you cut a piece, you will see the inside of the eggplant is white like flesh, maybe a little green or yellow, dotted with clusters of small beige seeds. If the inside is brown, the eggplant may have gone bad. Eggplant is a vegetable (albeit still a fruit) used relatively commonly in European meals, like potatoes, tomatoes, and peppers. Originally, eggplants came from India and Asia, where they grew in abundance in the wild. Eggplant came to Europe with the Muslim empire in the 7th and 8th centuries. Historians believe that the British coined the term eggplant for this vegetable during their occupation of India. Aubergine and Brinjal are other names for it. Eggplant has a lot of flesh inside, has a creamy consistency when cooked.
Eggplants come in several fairly common varieties:
The classic type that we often see with purple, shiny blood. Oval type with teardrop shape and dark purple shell. Black bell type with pear shape and glossy black shell. The type is long, white, and oval in shape. Thin, bright purple eggplant. Eggplants are small, oval-shaped, white, orange, yellow or green. According to the calculations of nutritionists, in 100 grams of eggplant contains the following nutrients:
Energy: 25 Kcal. Protein: 1 gram. Fat: 0.2 grams. Carbohydrates: 6 grams. Fiber: 3 grams. In addition, in 100 grams of eggplant also contains vitamins and minerals such as:
Folate: 22 micrograms Vitamin A: 23 IU Vitamin C: 2.2 milligrams. Vitamin K: 3.5 micrograms. Calcium: 9 milligrams. Iron: 0.23 milligrams. Magnesium: 14 milligrams. Phosphorus: 24 milligrams. Potassium: 229 milligrams.
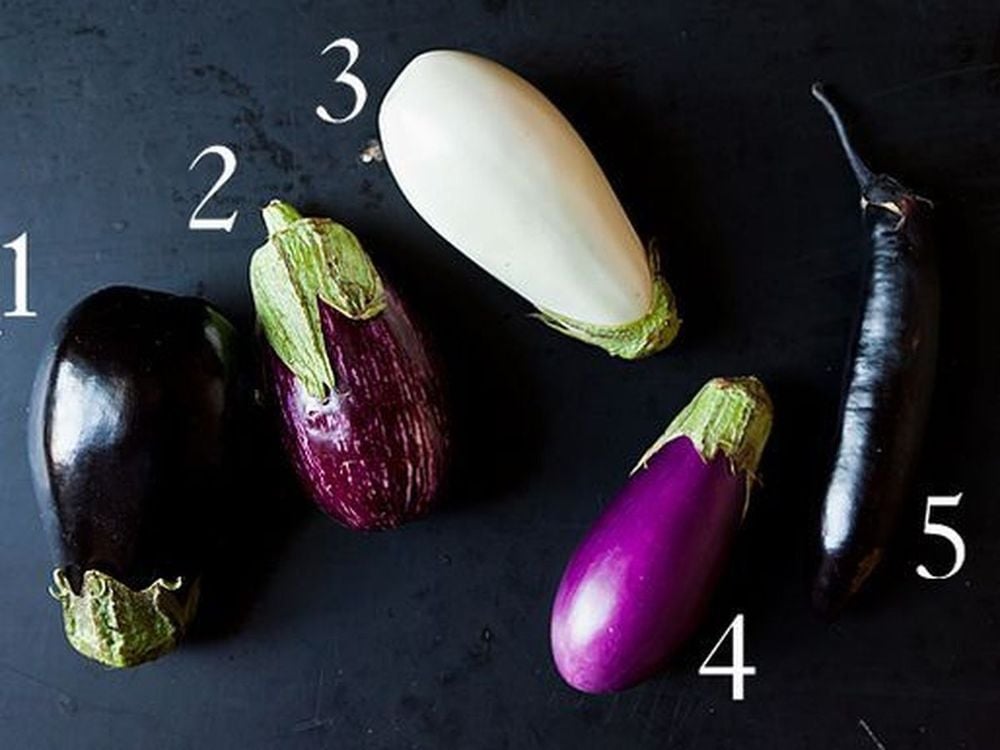

Cà tím thực chất có rất nhiều loại với màu sắc khác nhau.
2. The effect of eggplant in reducing overweight and obesity
In Austria, a research team from the University of Graz has demonstrated the anti-perspirant effect of eggplant, which is clearly shown by the people here using eggplant as animal feed. . In addition, eggplant also works to increase blood circulation, reduce cholesterol stagnation as well as blood urea, so it is very beneficial in the treatment of diseases related to heart disease, high blood pressure, obesity, diabetes. sugar, gout. Besides, because it contains very little energy (only 25 Kcal in every 100 grams of eggplant), eggplant is also one of the reasonable foods in diets aimed at weight loss.
Fiber in eggplant and other plants can help people control weight, prevent overweight and obesity. A person following a high-fiber diet will eat less of other foods because fiber makes people feel fuller for longer. Eggplants are high in fiber and low in calories - they can contribute to a healthy, low-calorie diet. However, eggplant can absorb a lot of oil during frying and cooking. Anyone who wants to lose weight should prepare the dish in another way, such as boiling or even eating it raw.

Chất xơ trong cà tím có thể giúp mọi người kiểm soát cân nặng, phòng tránh tình trạng thừa cân béo phì.
2.1. Health benefits of eggplant
Eggplant has been an important ingredient in traditional medicine for thousands of years. In the ancient Indian system of ayurvedic medicine, scientists used white eggplant to treat diabetes and their roots to relieve coughs caused by asthma. Although eggplant is not the most nutritious vegetable, it provides the body with a good amount of potassium and fiber.
And with only 25 Calories and less than 1 gram of fat per 100 grams, eggplants are a must-have in any low-fat diet, as long as they're not sauteed with a lot of oil. Eggplant is also rich in antioxidants like vitamins A and C, which help protect the body's cells from damage as well as slow down the aging process.
Eggplant also contains a naturally occurring plant-based chemical called a polyphenol. Polyphenols can assist cells in better processing sugar molecules if the patient has diabetes. Early cell-lab studies suggest that eggplant may protect against DNA-related damage that leads to cancer. However, scientists still need more time to study in humans before making a final conclusion for this statement.
Fiber, potassium, vitamin C, vitamin B6 and antioxidants in eggplant all support heart health and prevent metabolic cardiovascular diseases. A review released in 2019 by scientists found that eating foods containing certain flavonoids, including anthocyanins, helps reduce markers of inflammation, one of the factors that increase the risk of heart disease. . A 2013 study found that middle-aged women who ate a lot of blueberries and strawberries each week - good sources of anthocyanins - had a 32 percent lower risk of heart disease than those who consumed the least amount of the fruit. this. In another investigation, researchers concluded that women who ate a lot of anthocyanins seemed to have significantly lower blood pressure and less hardening of the arteries than those who ate less of these compounds.

Cà tím đã là một thành phần quan trọng trong y học cổ truyền hàng ngàn năm.
2.2. Health problems can be encountered when eating eggplant
Eggplant and some other vegetables have been shown to contain a chemical called solanine, which some claim increases inflammation and makes it difficult for patients with certain conditions such as arthritis. more bearable. To date, there is no solid evidence that the small amount of solanin in eggplant aggravates arthritis symptoms. But if you notice a flare of joint pain after eating eggplants, consider stopping them. Rarely, someone is allergic to eggplant. Symptoms of an eggplant allergic reaction include rash, facial swelling, itching, hives, and a hoarse voice.
3. How to process eggplant for maximum slimming effect
Before cooking eggplant, wash and cut off the ends. The skins are edible, but are usually discarded because they can be too tough. Eggplant is naturally slightly bitter. Therefore, sprinkle a layer of salt on it and leave it for 30 minutes. Salt will lessen the bitterness. It will also prevent the eggplant from absorbing too much oil and becoming greasy during cooking. Wash the salt before processing.
You can roast, bake, steam or saute eggplant. When chopped, it is a good addition to curries and soups. Europeans have a favorite recipe for eggplant parmesan, but keep in mind that rolling eggplants in breadcrumbs and frying them in oil will add calories and fat. Therefore, to cater for a slimming diet, bake eggplants instead of frying them. To bake a whole eggplant, first pierce the skin with a fork like a potato. After about 30 minutes in the oven, you can take the insides and stuff the eggplant, or mash the pulp into a soup, stew, or dip. Don't cut the eggplant until you're ready to cook it. These vegetables go bad very quickly. Instead, place it in the refrigerator so it can be safely stored for up to a week.
Eggplant can be a great addition to a healthy diet with lots of fruits and vegetables, low in calories and fat for weight loss. Polyphenol compounds in eggplant can give it a bitter taste that many people don't like. Eggplant has many health benefits, especially for the cardiovascular system. There are different ways of preparing eggplant to maximize the weight loss effects of eggplant.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference sources: webmd.com, medicalnewstoday.com, viendinhduong.vn