This is an automatically translated article.
AFB sputum test is a microscopy test for TB bacilli in the patient's sputum. This test is used to diagnose pulmonary tuberculosis, a common infectious disease caused by the Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria, also known as the BK test - the bacteria that causes tuberculosis, used in the diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis.
1. What is the AFB sputum test?
AFB sputum test, also known as test for BK - TB bacteria, is used in the diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis. This test has the English name Acid Fast Bacillus, abbreviated AFB) in the patient's sputum using a microscope.
Tuberculosis is a common infectious disease caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis. There are 2 types of pulmonary tuberculosis identified when AFB sputum test is positive and negative. Even so, AFB-positive and negative TB have similar symptoms and treatments.
Pulmonary TB AFB positive: AFB sputum test is positive. Tuberculosis bacteria cause bronchial infections and lesions in the lung caverns, often found in sputum. Typical symptoms are persistent cough, continuous cough, and hemoptysis. Pulmonary TB AFB negative: AFB sputum test is negative.
2. How is the AFB sputum test done?
AFB sputum test is done as follows:
Samples are taken at 3 different times (sample 1 at medical examination, sample 2 when waking up early in the morning, sample 3 when examining sample 2). For young children who have not been able to spit up sputum, sputum fluid or aspirate can be taken from the child's stomach.
Sputum smear with the following methods:
Ziehl-Neelsen - Staining on light microscopy shows red bacilli; Molecular methods performed when the number of TB bacilli is very low Immunoassays, performed to supplement the diagnosis.
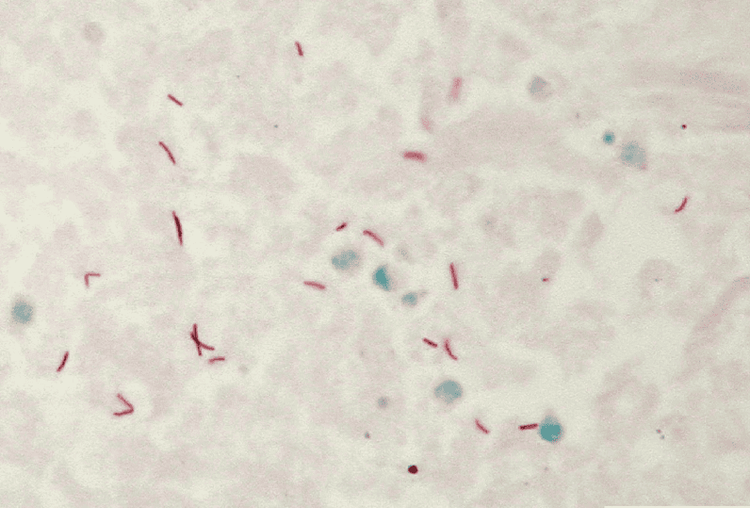
Nhuộm soi trên kính hiển vi quang cho thấy trực khuẩn lao bắt màu đỏ
3. Diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis with AFB . sputum test
To diagnose pulmonary tuberculosis, doctors rely on the following factors:
Source of infection: Identifying the source of infection is especially important for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis in children. Clinical symptoms: Patients with pulmonary tuberculosis often have persistent clinical symptoms due to chronic TB bacteria. Laboratory methods: The initial method of identification is the AFB sputum test. However, depending on the stage of the disease, the results will vary or the patient (HIV) has been treated with drugs that affect TB bacteria. Tuberculosis culture is also difficult and takes a long time (4-12 weeks), so a chest X-ray is suggested further or a skin test for tuberculin is recommended. In case the test for BK does not give results, the gene amplification reaction is replaced by sensitivity and specificity, giving quick results. 3.1 Diagnosis of AFB-positive pulmonary TB Diagnosis of AFB-positive pulmonary TB is established when the patient has 1 of the following 2 criteria:
1 AFB specimen (+) and culture of TB bacilli (+). 1 specimen of AFB (+) and on x-ray showed progressive tuberculosis. More than 2 AFB (+) specimens were obtained from 2 different sputum samples. In HIV-infected patients, AFB pulmonary tuberculosis is positive when there is 1 specimen of AFB sputum (+). The diagnosis of AFB-positive pulmonary TB is different when the patient has previously been treated for TB with no results and the treatment regimen is unknown.
Diagnosis of AFB-positive pulmonary tuberculosis helps to divide the degree of pulmonary tuberculosis:
AFB 1+: AFB sputum test has results from 10 - 99 AFB/100 microfield, corresponding to a lump size from 10 - 14mm. AFB 2+: AFB sputum test has results from 1 - 10 AFB/microfield and scanning >= 50 microfields. AFB 3+: AFB sputum test with results of 10 AFB/microfield or more
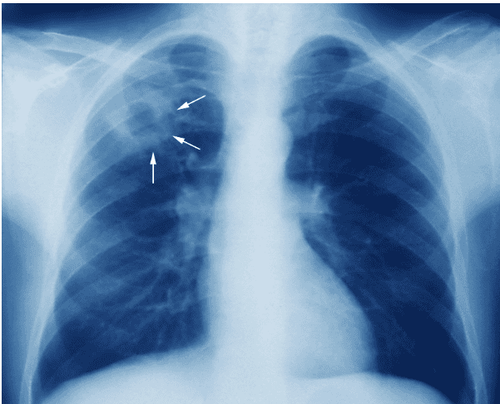
Trên X-quang cho thấy hình ảnh lao tiến triển kết hợp xét nghiệm AFB giúp bác sĩ chẩn đoán xác định bệnh lao phổi
3.2 Diagnosis of AFB-negative pulmonary TB Diagnosis of AFB-negative pulmonary TB is established when the patient has 1 of the following 2 criteria:
2 AFB sputum tests (-) and on X-ray shows an image progressive tuberculosis. The test was performed 3 weeks apart, with 3 sputum samples taken each time. Test for BK (+) or Xpert MTB/Rif (+) or Haintest (+). In HIV-infected patients, AFB-negative pulmonary TB is defined as having 2 AFB sputum tests (-), X-ray showing tuberculosis, and treatment unresponsive to broad-spectrum antibiotics. The diagnosis of AFB-negative pulmonary TB is different when the patient has been treated for TB.
Tuberculosis is an infectious disease. The AFB sputum test is considered the leading standard for the diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.