This is an automatically translated article.
Autoimmune encephalitis is characterized by brain damage caused by mistakes in the autoimmune system. The lesions are generally complex, causing severe neuropsychiatric deficits. Accordingly, this diagnosis needs to be quickly recognized as soon as possible, and proper treatment will improve the prognosis for patients in the hospital as well as limit sequelae.
1. What is autoimmune encephalitis?
Autoimmune encephalitis is a serious medical condition in which the immune system attacks the brain parenchyma, impairing function. Most cases of autoimmune encephalitis can be triggered by an infection; However, in many cases the cause is unknown.
Depending on which part of the brain is affected, the symptoms vary widely. However, in general, autoimmune encephalitis is still classified as a severe brain injury with a mortality rate of about 6 to 10%.
With today's advances in medicine, autoimmune encephalitis has made it possible to be diagnosed quickly and treated appropriately, allowing many patients to recover most of the central nervous system function. However, a large proportion of patients still have persistent symptoms, which negatively affect their ability to function later in life.
Bệnh viêm não tự miễn là một trong những bệnh gây tổn thương não
2. Symptoms of autoimmune encephalitis
Patients with autoimmune encephalitis may present with a wide range of neuropsychiatric symptoms.
Therefore, it is a big challenge in diagnosis when different symptoms can appear at different times and with different intensity and intensity. Many cases are easily confused with other diseases. Specifically, the commonly reported symptoms of autoimmune encephalitis include:
Cognitive impairment Memory difficulties Convulsions Uncontrollable muscle tremors Slow or inability to speak Behavioral changes such as agitation Loss of inhibitions Visual or auditory hallucinations Paranoid thoughts Anxiety, depression Sleep disturbances or even severe insomnia Weakness or numbness in part of the body Loss of balance Changes in vision If the patient only If you have one of these symptoms, autoimmune encephalitis is not the first thought to be identified. However, an unexplained mixture of the above neuropsychiatric symptoms may suggest an underlying cause of autoimmune encephalitis.

Bệnh viêm não tự miễn có thể gây ra trầm cảm
3. What is the cause of autoimmune encephalitis?
The direct cause of most cases of autoimmune encephalitis is still not fully understood. However, the following have been shown to trigger autoimmune encephalitis:
Presence of a teratoma, commonly found in the ovaries Precancerous syndromes, possibly potential for actual cancer, indirectly triggering an autoimmune response Exposure to some common bacteria and viruses such as streptococcus, mycoplasma that causes pneumonia, and the Herpes simplex virus. In addition, autoimmune encephalitis is sometimes one of the manifestations of multiple organ damage in a number of autoimmune diseases including:
Rasmussen Lupus Systemic Encephalitis Behcet's Disease Hashimoto Encephalopathy Sydenham Dance
Viêm não tự miễn có liên quan đến một số bệnh tự miễn như Lupus ban đỏ
4. How to diagnose autoimmune encephalitis
A rapid diagnosis of autoimmune encephalitis will allow patients to receive early and aggressive treatment from the outset, improving their chances of a speedy and complete recovery.
In clinical practice, autoimmune encephalitis is a complex disease that often requires collaboration between multiple medical specialties for effective diagnosis and treatment. Accordingly, in some cases, the diagnosis of a patient with autoimmune encephalitis may require consultation between a team of doctors from many different specialties, including neurologists, rheumatologists, and neurologists. rheumatologists, psychiatrists, immunologists, and other specialties if other injuries are present.
At this point, in patients with presentation consistent with autoimmune encephalitis, the test commonly used to support the initial diagnosis is contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging, EEG, and stool analysis. Accumulation of blood and cerebrospinal fluid for markers of inflammatory response. Your doctor may order specialized tests to look for antibodies that target the immune system to attack the brain causing encephalitis. These antibodies are electrically present and are found in both blood and cerebrospinal fluid. Therefore, it is always necessary to test both of these samples.
However, a negative test result for autoimmune antibodies does not rule out autoimmune encephalitis. This is because a significant proportion of cases of autoimmune encephalitis may be caused by other unknown antibodies or by known antibodies for which a diagnostic test may not be present in the specimen. . Even so, the diagnosis still cannot delay the treatment regimen, when it is possible to reduce the brain damage to a minimum.
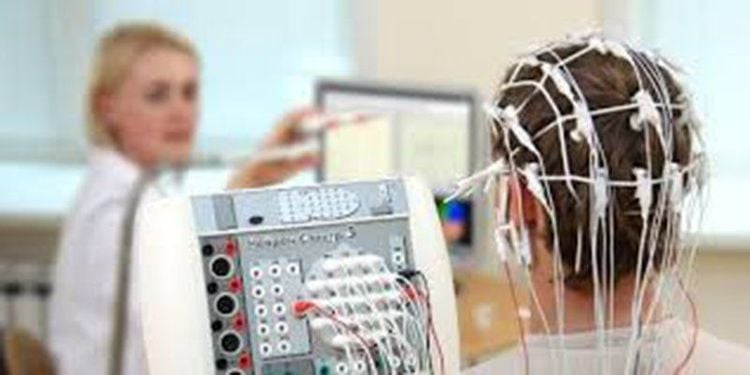
Điện não đồ được đưa vào chẩn đoán bệnh
5. Current popular autoimmune encephalitis treatments
As soon as a patient is diagnosed with autoimmune encephalitis, they will be treated with one or two of the following first-line treatments:
Find and remove teratomas if present as this can cause an autoimmune reaction High dose steroid therapy to reduce immune response and inflammatory response Plasma exchange to remove antibodies from the blood Intravenous immunoglobulin to speed up neutralize and eliminate antibodies, inhibit the binding of harmful antibodies, and reduce the inflammatory response to antibodies. In addition to the first-line methods as above, if the patient's condition continues to be unfavorable or the disease level is already severe from the beginning, the combination of immunosuppressive drugs along with the above-mentioned therapies is necessary. These drugs work by reducing the number and function of immune cells that cause inflammation and autoimmunity. The three most commonly used drugs are Rituximab, CellCept, and Cytoxan (cyclophosphamide).
In addition to treatments that target the autoimmune system and inflammatory responses, patients also need to be supplemented with drugs to treat symptoms, especially agitation and insomnia. The drugs commonly prescribed at this time are benzodiazepines, with Lorazepam representing high doses that can bring significant effects to patients. Even so, medications to treat symptoms will vary depending on what is involved in autoimmune encephalitis. Because, before starting immunotherapy, these drugs show less usefulness and cause more side effects. Meanwhile, once the inflammatory process is being brought under gradual control, these classes of drugs become essential to alleviating the symptoms of autoimmune encephalitis as well as maximizing the patient's function as the disease recovers. recovery, and limit the long-term sequelae.
In summary, because it is a complex and rare disease, autoimmune encephalitis will be difficult to detect at first if you don't think about it. Active examination as well as diagnostic measures, especially finding autoimmune antibodies in the blood and cerebrospinal fluid, will help the doctor soon give appropriate treatment. From there, patients will have the opportunity to recover neurological functions as well as preserve quality of life in the future.
For detailed medical advice, please come directly to Vinmec health system or register online HERE.
Reference source: gosh.nhs.uk; pennmedicine.org