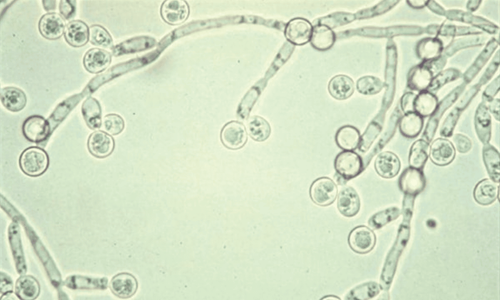
Fungal infections of the genitals are common in women because of their distinct anatomical features, but there are still some cases of penile yeast infection in men. This may be a symptom of sexually transmitted diseases or dangerous andrological diseases, so the patient should be examined early for appropriate treatment.
1. What is penile yeast infection?
Penile yeast infection is a fungal infection in the male genitals with the most notable cause being candida, accounting for 35%. Many types of candida live in the intestinal tract and other moist areas of the body without causing disease. However, in some cases, they can overgrow and begin to cause dangerous diseases. One person with penile yeast infection often has a history of unsafe sex with an infected person. However, candida infection is not classified as a sexually transmitted disease because men can still contract it without having sex with other people.
Factors that increase the risk of penile yeast infection include:
- Overuse of antibiotics leads to the beneficial bacteria that control candida to be reduced.
- Immunocompromised patients
- Diabetes
- Patients taking corticosteroids
- Obesity
- Cancer
- Long, narrow foreskin without circumcision
- Unprotected sex
- Improper personal hygiene irritates the genital skin, making the fungus grow.
- Masturbation intensity, wearing tight underwear
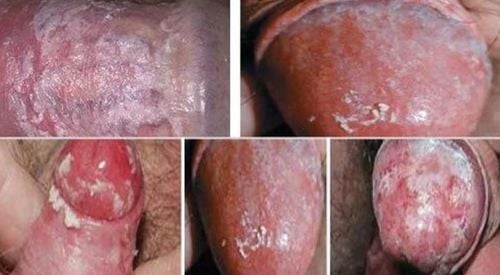
2. Symptoms of penile yeast infection
Men with penile yeast infection may experience the following symptoms:
- Itching and burning around the head of the penis, foreskin fungus.
- Redness and pain, white fungal skin of the penis.
- There are red bumps like rash that can be accompanied by pus.
- Pain during sex or urination.
- In the case of penile yeast infection combined with inflammation, symptoms may include foreskin discharge of mucus and lumps, milky white, an unpleasant odor, or difficulty pulling down the foreskin.
- If timely untreated, even all skin of the penis can have ulcer lesions, pus, foul odor, hematuria (blood in urine), or hematospermia (blood in semen).
3. How to treat penile yeast infection?
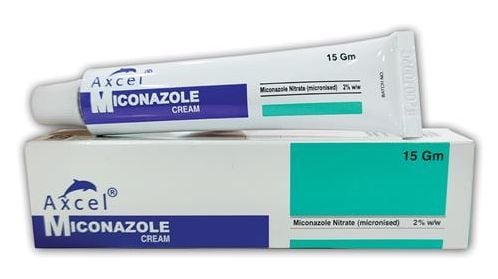
Treatment of penile fungus needs to start from lifestyle to medication. Men need to limit alcohol, build a good diet that is nutritious and probiotics for the body, and limit foods high in sugar. Patients also need to note to clean their bodies, bathe with warm water, not use shower gels or scented soaps, and completely dry the groin and penis area to avoid creating a proper environment for fungus growth. Also, in most cases, topical antifungal ointments and creams are sufficient to clear the infected area. Antifungal drugs are commonly used, including:
- Miconazole
- Imidazole
- Clotrimazole
4. Methods to prevent penile fungus
Usually, if treated early and responds well to antifungal drugs, the disease will be completely cured within a week. If fungal infections recur frequently, you need to see a specialist for advice on other underlying conditions such as diabetes. In cases of the long foreskin make difficult to clean the penis, causing the accumulation of residues to create genital warts. To prevent penile fungus, you can follow the following measures:
- Use condoms when having sex
- Monogamous relationship (one wife and one husband)
- Keep genitals clean, penis dry
To arrange an appointment, please call the HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.