This is an automatically translated article.
Omnipaque is a drug indicated in X-rays of cases such as cardiovascular, arterial, urinary tract, vein. In addition, the drug is also indicated for intramedullary use in adults, including myelogram.
1. What are the uses of Omnipaque?
1.1. What is Omnipaque? Omnipaque belongs to the group of diagnostic drugs, with registration number VN-10687-10, manufactured by GE Healthcare - Ireland, registered in Vietnam by Zuellig Pharma Pte., Ltd.
Omnipaque drug has the main active ingredient is Iohexol 300mg/ml or 350mg/ml, bottled 50ml or 100ml, box of 10 bottles.
The drug is recommended for use from infants to adults.
1.2. What does Omnipaque do? Omnipaque is an X-ray contrast agent, used in adults and children to:
Uterine - fallopian tubes, retrograde cystogram - urethra; Lumbar - thoracic - neck and full-column myelogram (with conventional imaging or computed tomography). X-ray of the cervical spine, after subarachnoid injection. Aortic angiography (ascending aorta, aortic arch, abdominal aorta, and branches). X-ray of cerebral or peripheral arteries. Intravenous X-ray, hernia in adults, highlighting computed tomography (body, brain). X-ray of the salivary glands and study of the gastrointestinal tract. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography and endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. Omnipaque is contraindicated in the following cases:
Patients who are allergic to the main ingredient Iohexol or any other ingredient of the drug. The patient presents with thyroid toxicity. People with a history of allergies, asthma or severe kidney failure. Meningeal radiographs are contraindicated in chronic alcoholics, history of seizures, subarachnoid hemorrhage, severe systemic/local infections, or disseminated sclerosis. Angiography is contraindicated in patients with hyperthyroidism and sickle cell disease. Cardiovascular radiographs are contraindicated in patients with severe pulmonary hypertension or in onset heart failure. Cerebral angiography is contraindicated in people with decompensated heart disease, people with long-term (severe) hardening of the arteries, people with severe hypertension, people with recent cerebral embolism, senility or thrombosis.
2. Usage of Omnipaque
2.1. How to use Omnipaque Drug Omnipaque is used for injection into veins, arteries, intramedullary, body cavity. In some cases it can be taken orally.
The medicine will be taken orally or injected before the X-ray is performed.
2.2. Dosage of Omnipaque The dose, route of administration and drug strength will vary depending on the imaging technique and the route of contrast administration.
Reference dosage:
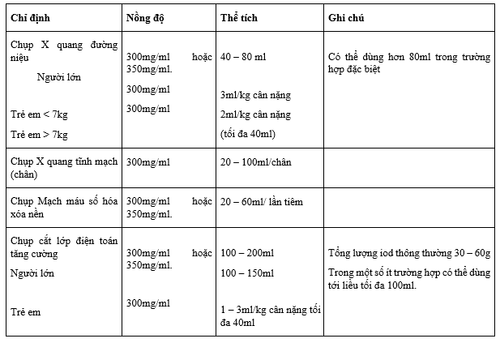
Intravenous dose:
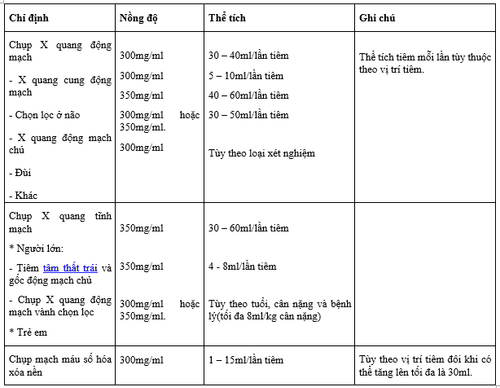
Intra-arterial dose:
Intrathecal dose:
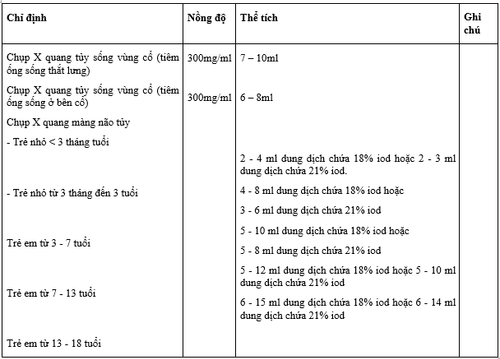
It must be injected slowly into the meninges over a period of 1 to 2 minutes to avoid mixing too much of the drug with the cerebrospinal fluid, leading to dilution of iohexol concentrations and adverse premature dispersal of the drug. Do not repeat injection immediately, because there is a risk of overdose. Preferably 5 to 7 days or a minimum of 48 hours. Dose injected into body cavity:
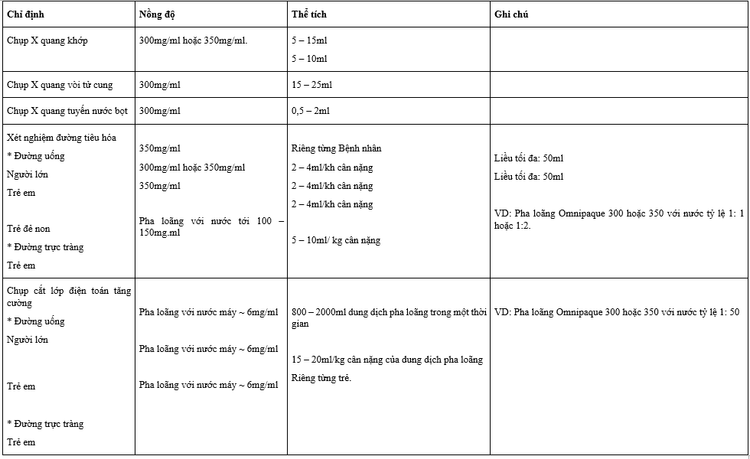
Treatment for missed dose:
Because the medicine is administered right before the X-ray and is done by medical staff, it is not possible to miss a dose.
Treatment of Overdose:
Omnipaque overdose is unlikely in patients with normal renal function, unless the patient has received more than 2000 mg/kg body weight for a limited time. The prolonged duration of the test has an impact on the renal tolerability of high doses of contrast medium (the half-life is about 2 hours). Accidental Omnipaque overdose is most likely to occur after complex angiographic testing in pediatric subjects. Especially when using multiple contrast injections at the same time with high concentration. In the event of an Omnipaque overdose, correction should be made for any water or electrolyte imbalances that occur. Renal function should be monitored for the next 3 days. If necessary, hemodialysis may be used to remove excess contrast.
3. Notes when using Omnipaque
People who are sensitive to iodine and other iodinated contrast agents may also be at increased risk of anaphylaxis. Using Omnipaque for a hysterosalpingogram may increase the risk of complications in people with genital tract infections, making acute pelvic inflammatory disease worse. Care should be taken when having surgery on the cervix or uterus to avoid the risk of ectopic pregnancy. When injected intravenously, Omnipaque can increase blood pressure in people with pheochromocytoma. The dose of Omnipaque must be kept to a minimum and blood pressure monitored during imaging. Using peripheral angiography, Omnipaque can cause vasoconstriction of veins or arteries in buerger's disease. In addition, there is an increased risk of complications in people with severe ischemia due to infection. Using Omnipaque for cerebral angiography may increase the risk of thrombosis and embolism in people with homocystinuria. Using intravenous radiography, Omnipaque may increase the risk of acute renal failure in people with diabetes. Using an X-ray of the joints, Omnipaque may increase the risk of complications in people with bacterial infections at or near the examined joint. Do not use Omnipaque for pregnant and lactating women. Do not drive or use hazardous machinery for the first 24 hours after an endothelial test.
4. Omnipaque side effects
Undesirable effects of Omnipaque can vary directly according to the technique of use, concentration and underlying pathology. Increased osmotic pressure, concentration, volume, viscosity, and injection rate may increase the incidence and severity of undesirable effects. Common side effects of Omnipaque are: mild to moderate headache, dizziness, pain (possibly due to pressure and volume when injected into the pancreatic duct, hepatic duct), mild/moderate nausea and vomiting, and diarrhea. mild and temporary bleeding, back pain, abdominal pain, stomach upset, meningeal irritation, slow heart rate, joint pain or worsening of joint pain, joint swelling. Common side effects of Omnipaque are: Unusual fatigue or muscle weakness, severe headache, sweating, fever, loss of appetite, tinnitus, drowsiness, increased sensitivity to light, blurred vision, other visual changes, erratic heat sensation, difficulty urinating, urticaria, pain and burning at the injection site. If you experience these symptoms, you need to stop using Omnipaque and notify your doctor for appropriate treatment.
5. Omnipaque drug interactions
Concomitant intravenous administration of Omnipaque with beta-adrenergic blocking agents may increase the risk of moderate to severe anaphylaxis, and the hypotensive effect may also be aggravated. Oral drugs for cholecystography may increase the risk of nephrotoxicity when Omnipaque is required immediately afterwards, especially in patients with impaired liver function. There may be an increased risk of severe hypotension if Omnipaque is used concomitantly with medicinal products with antihypertensive effects. Intrathecal or intravascular administration of Omnipaque with other nephrotoxic drugs may increase the likelihood of nephrotoxicity. To avoid interactions, before being prescribed, the patient should inform the doctor about the drugs they are using, including functional foods. The doctor will base on that to prescribe the appropriate Omnipaque.
6. How to store Omnipaque thuốc
The shelf life of the drug Omnipaque is 36 months from the date of manufacture. Store Omnipaque in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight. The ideal Omnipaque storage temperature is 15-30 degrees Celsius. Do not freeze the medicine. Keep Omnipaque out of the reach of children and pets. Above is all information about Omnipaque drug, patients need to carefully read the instructions for use, consult a doctor / pharmacist before using. Omnipaque is a prescription drug, absolutely do not self-treat at home because patients may experience unwanted side effects.